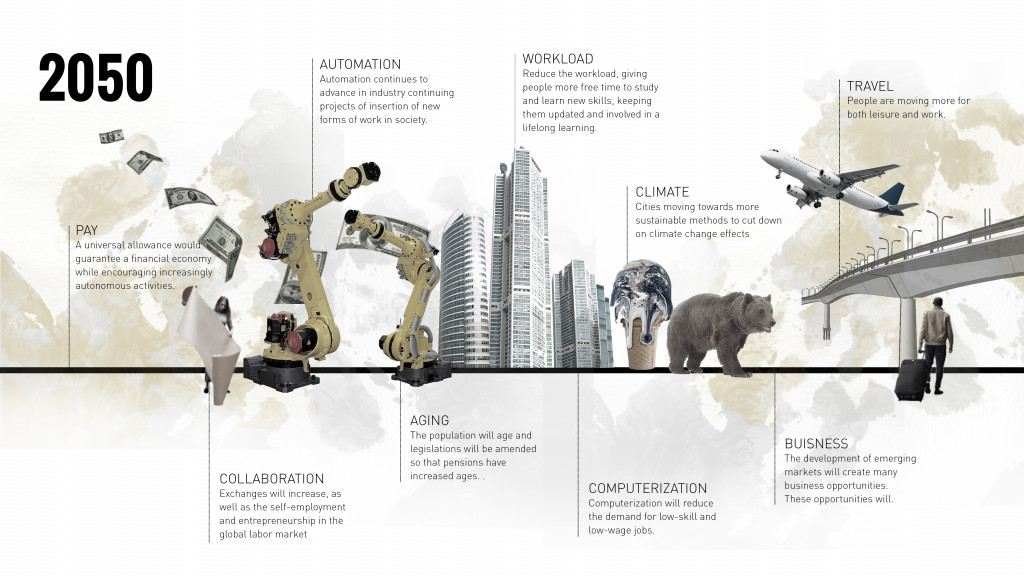
2050: How can we imagine the city in 30 years time?
Our role in this project, as city administration, was to tackle key future challenges in the city of Barcelona and engage the citizens in policy making. For a number of studies that we analyzed, we have arrived with certain assumptions about labor and living in 2050. For example, the introduction of UBI will guarantee financial stability and improved standard of living. Also, automation will advance in industry causing new forms of work will appear in society. These assumptions will result in a society where people have more time to live and travel.
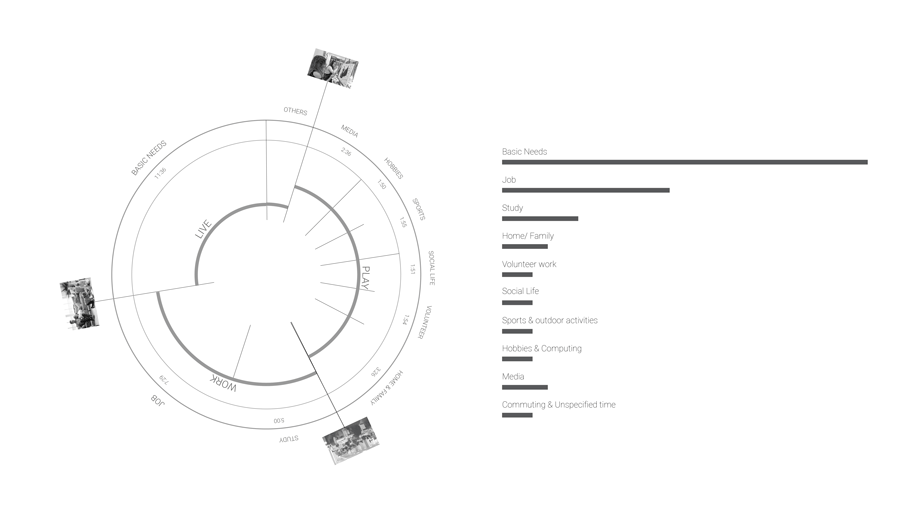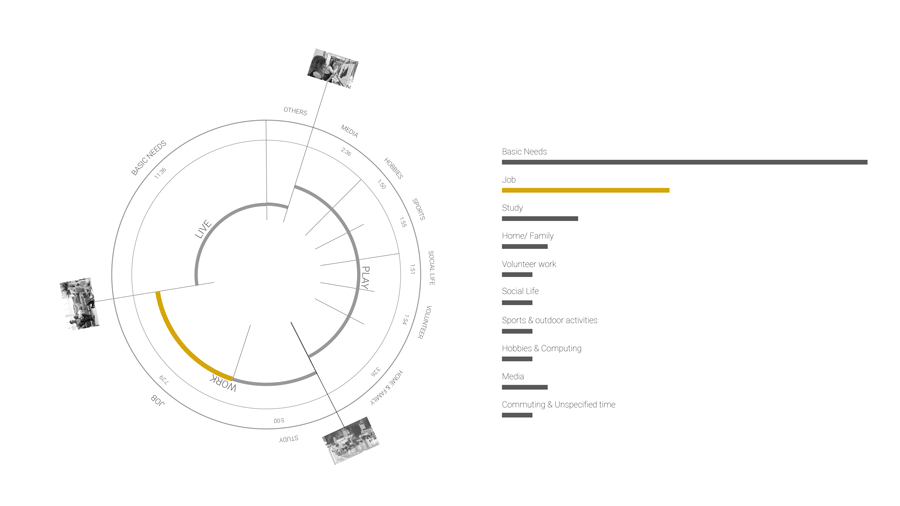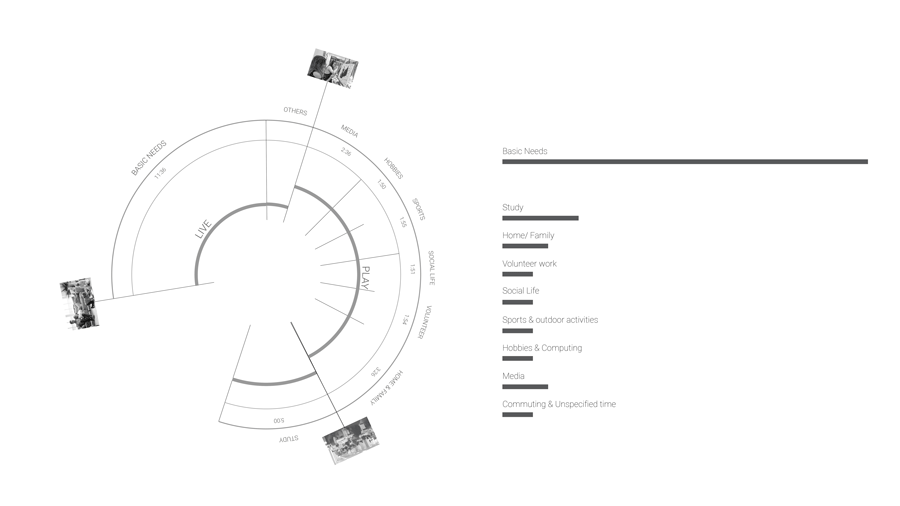
Currently according to the BCN statistics center, the average time distribution of a citizen. We divided this time in 3 different categories : Work, Live and Play. Currently, people spend 7.5 hours of their day working. So what happens when this proportion will change and people will have more free time?
Owning time
So what are the factors influencing this daily time distribution? Do we have the right to own time? To understand how availability of time is distributed in the city, we focused our study area to people who are not privileged to have free time. Based on our studies and analysis we selected few parameters and certain categories of people to derive the free time poverty map.
- People with Low Academic Level
- Working Age people that is between 16-65 as they are devoid of free time,
- then we also focused to identify that gender plays an important role in availability of free time like females are more involved in domestic work and child care
- and then to compare how they are economically distributed based on the disposable family income.
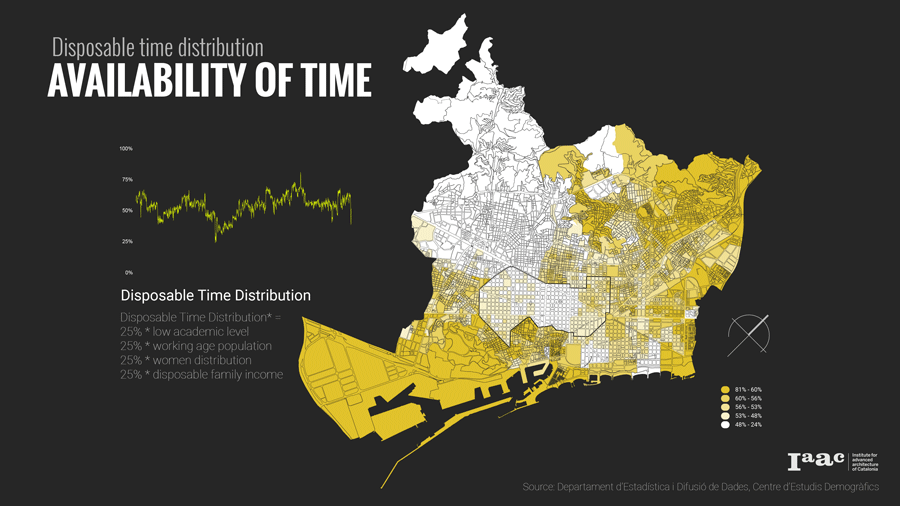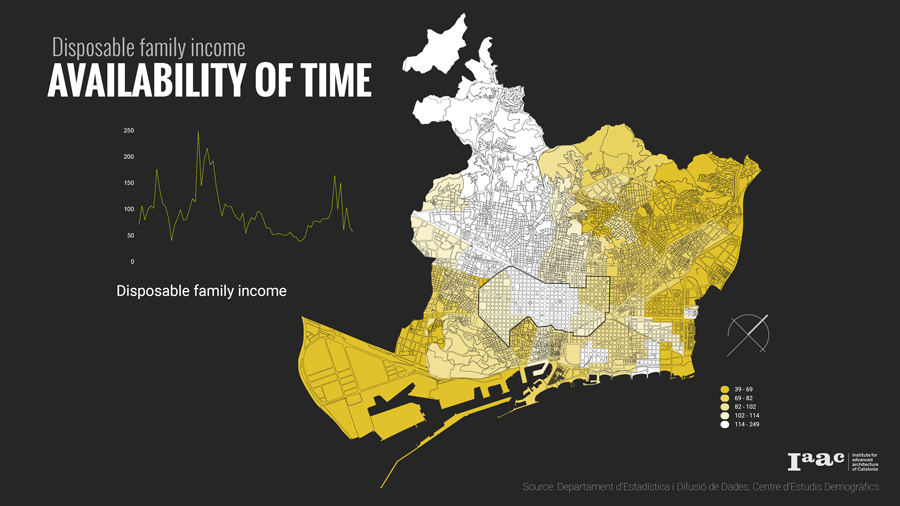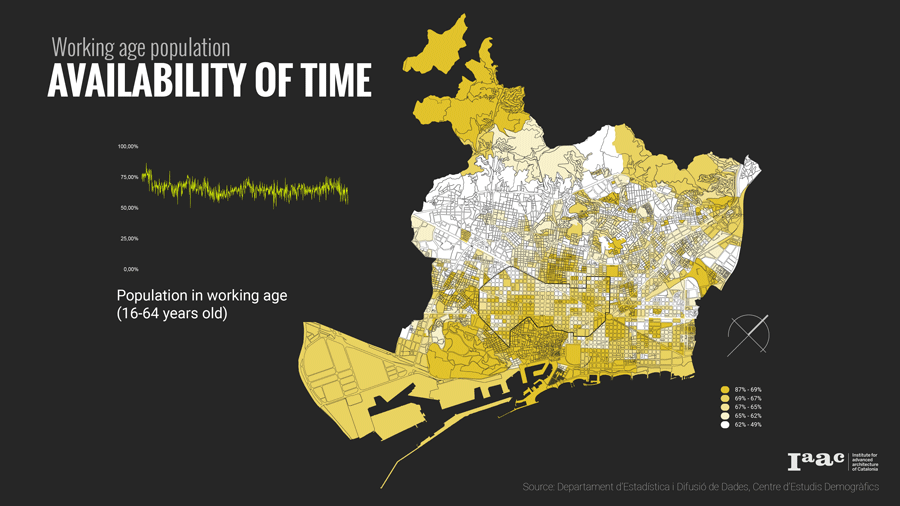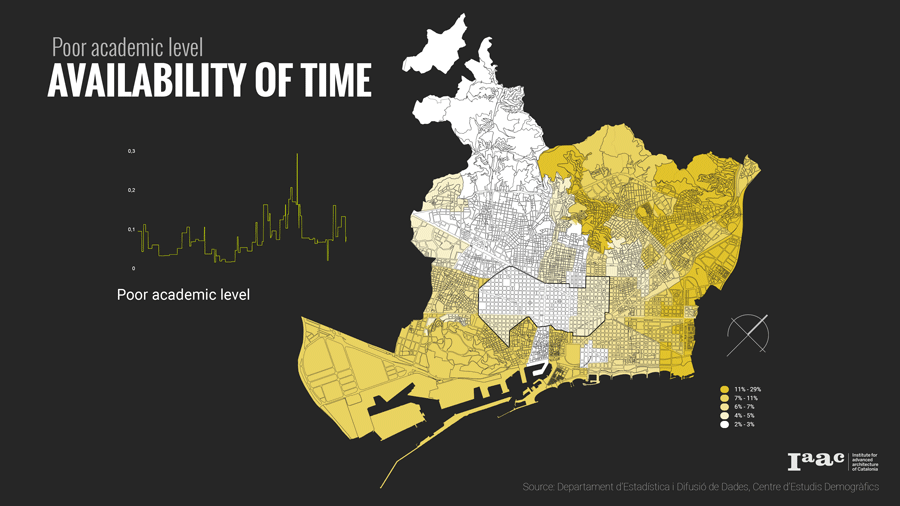
The distribution of land uses in a city determines where we spend our time and in what activities. Understanding the city for its work areas, residential areas, public engagement areas, leisure areas and mapping peoples engagement in time and space.
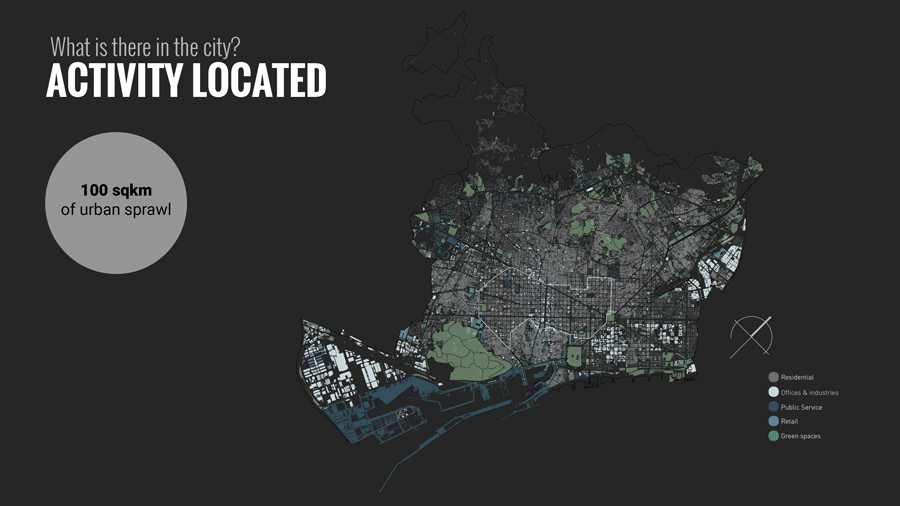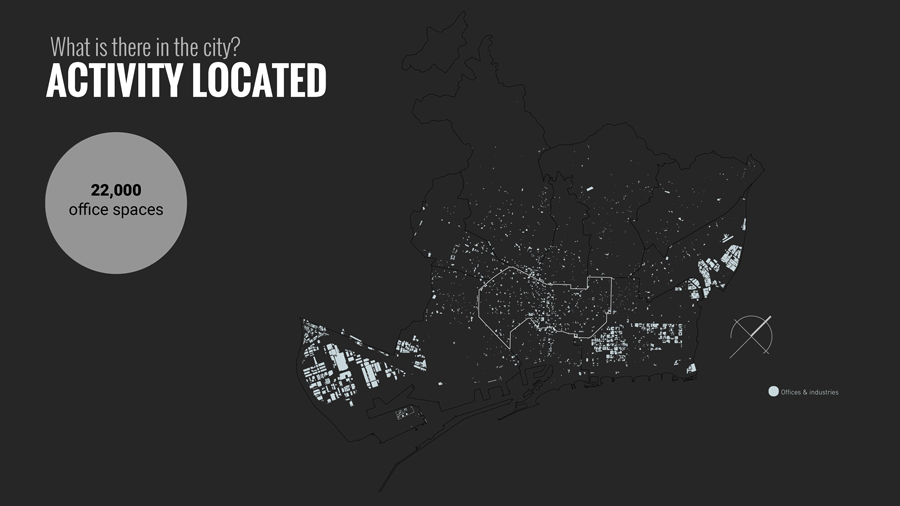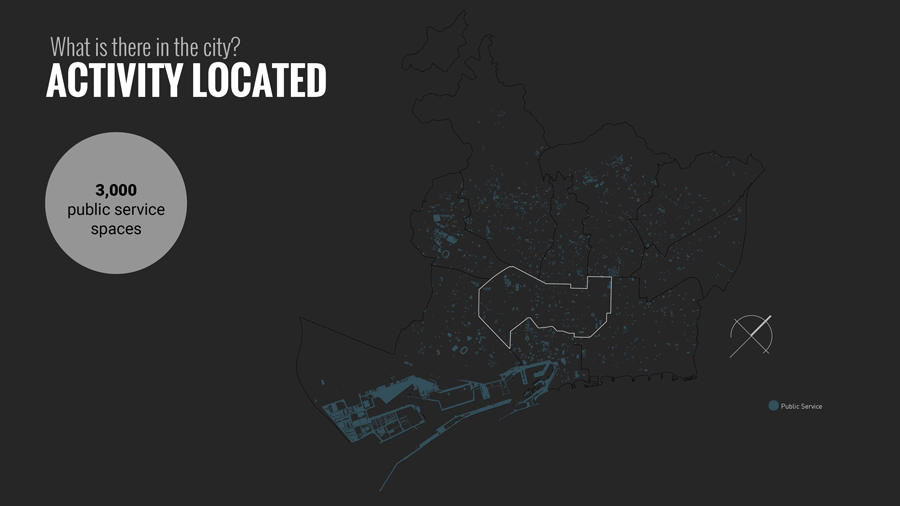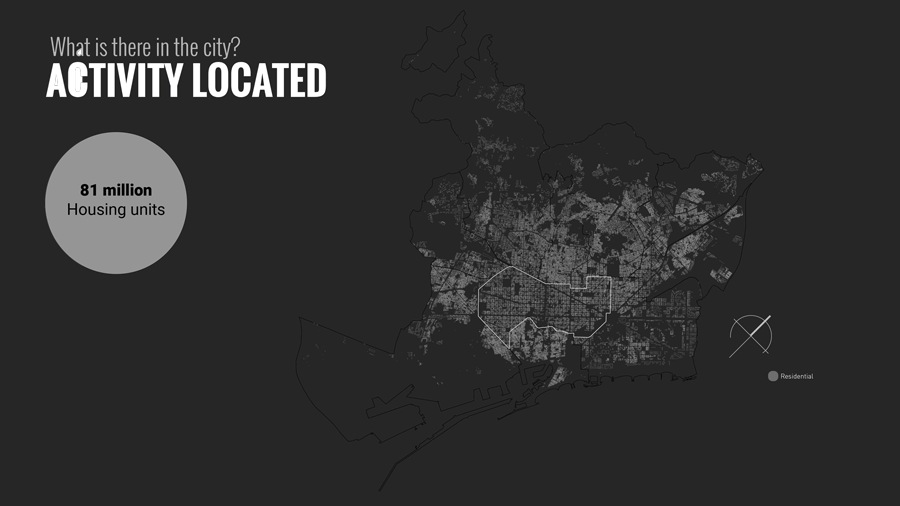
Further analysis was based on data to analyze Daily Timestamp, Weekly Timestamp, Monthly Timestamp and yearly Timestamp of people in Barcelona to know where and how they spend their current time.
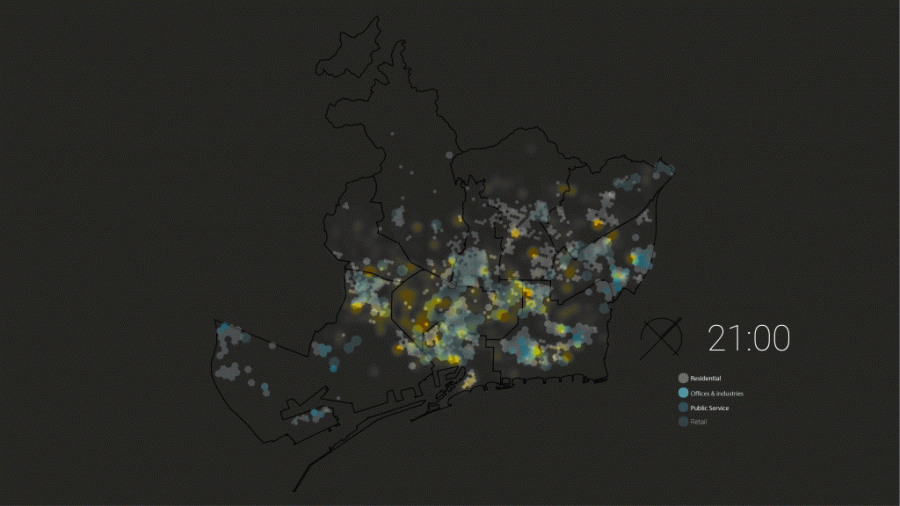
Daily Timestamp
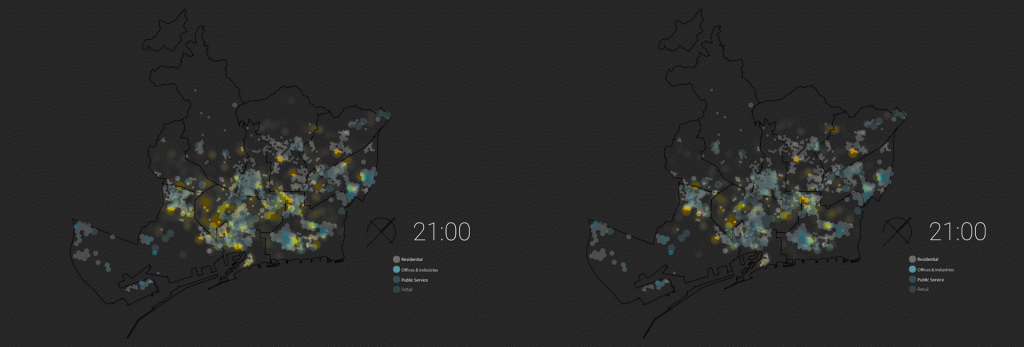
Weekly Timestamp:
Movement of people during the weekdays and weekends helped to understand how people engage with different spaces on different days and different times. Analysis of the first day of week -Monday and last day of week -Sunday to understand the pattern.
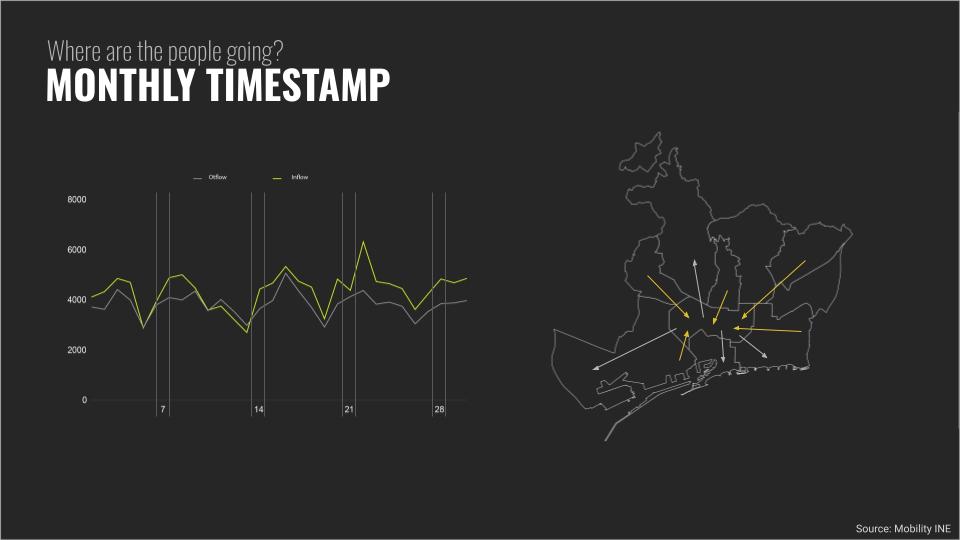
Monthly Timestamp:
Also , a monthly analysis is guided to understand where they spend their extra time. For example, movement of people to Eixample and and from Eixample during the weeks could be analyzed to understand working patterns. The footfall data for April helped to understand how people stay back during 22nd to 28th of April in Eixample. This time is a Sant Jordi festival.
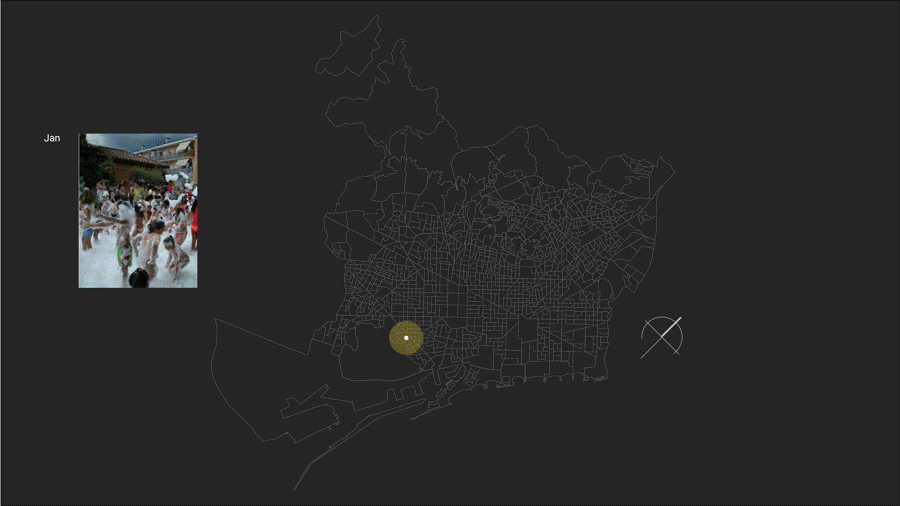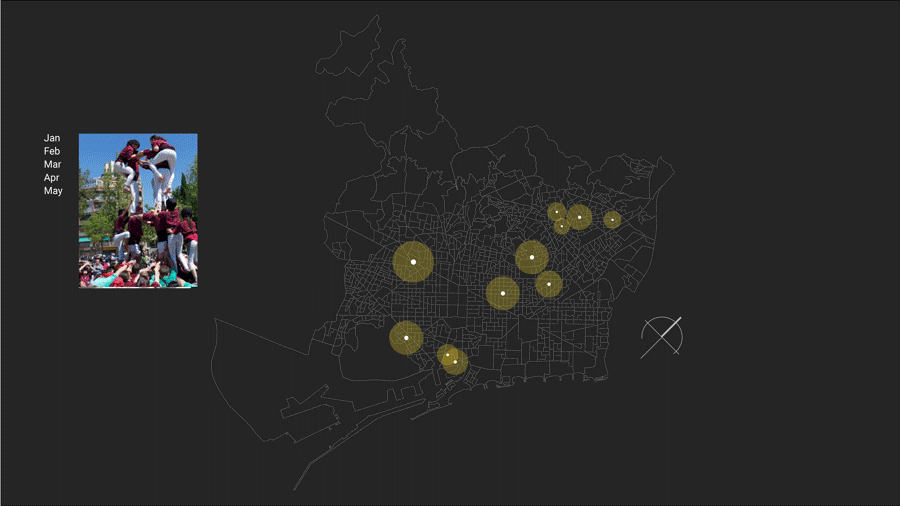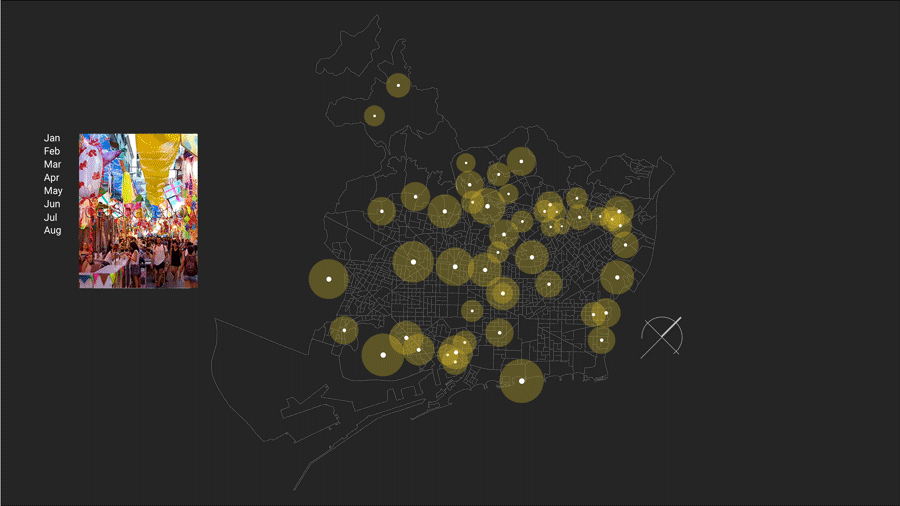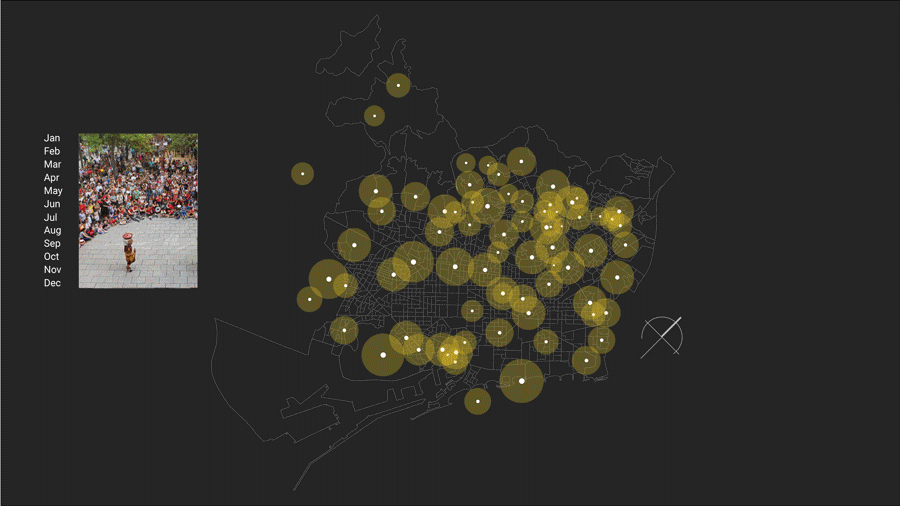
Yearly Timestamp:
There are variety of events, workshops and festivals for people planned during the year. Such as art, music, literature and multidisciplinary art festivals and work shops. This gives an overview of how people yearly spend their time apart from daily activities in different arts.
How will this impact the use of spaces?
Given the challenge of the Studio-Superilla project in order to understand how we can better relate the use of time with the use of spaces. The current Barcelona Superblock project focuses on pedestrian areas, mobility and air quality and so on, but does not cater to the land uses needed in future society with more free time.
Policy: “ Pla Estrategic d’us del Temps “
Policy aims putting together the opportunities in the city with the future needs of citizens through a collective platform.

Illustration by: Tiro Merello Vilar
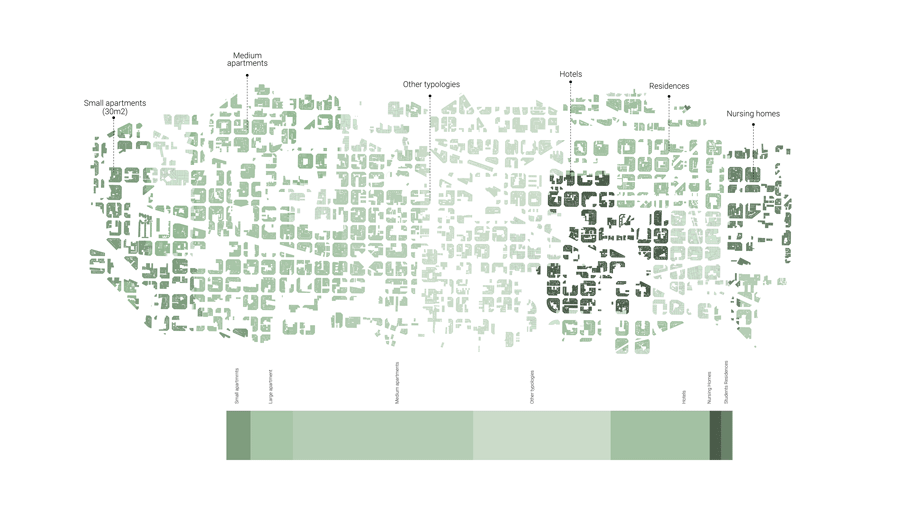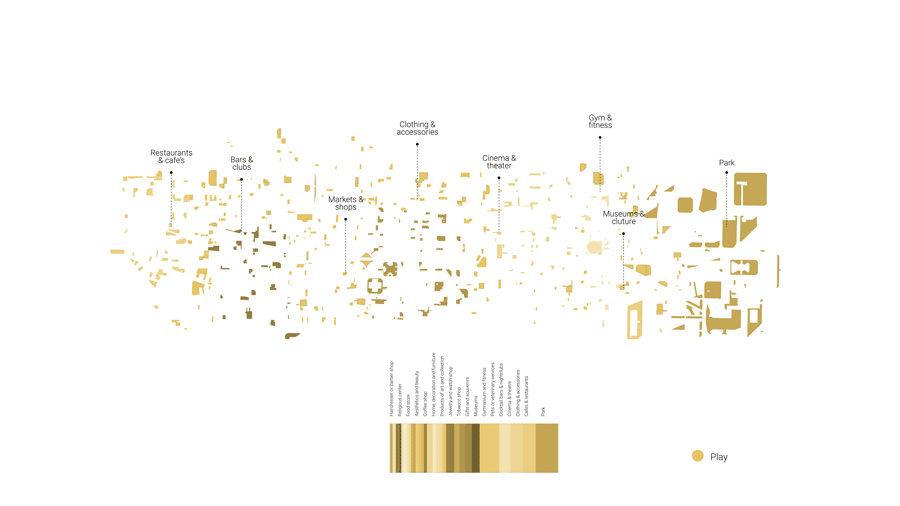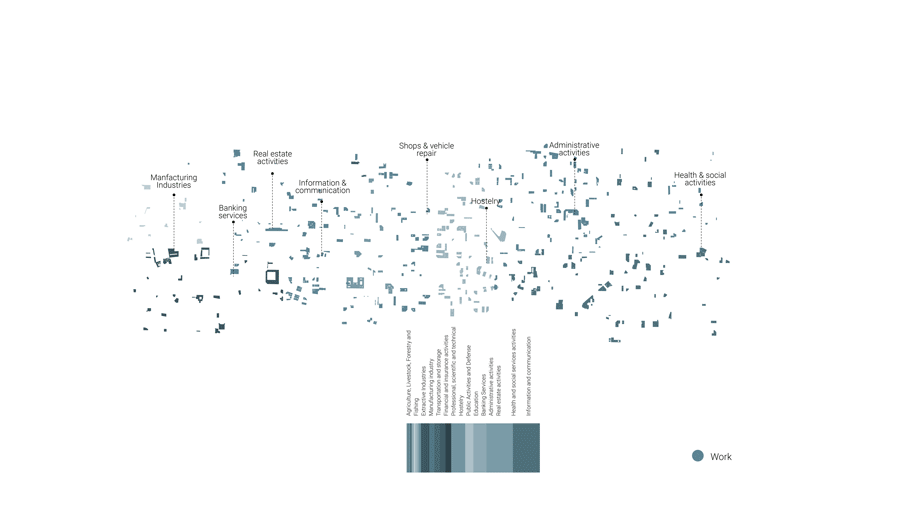
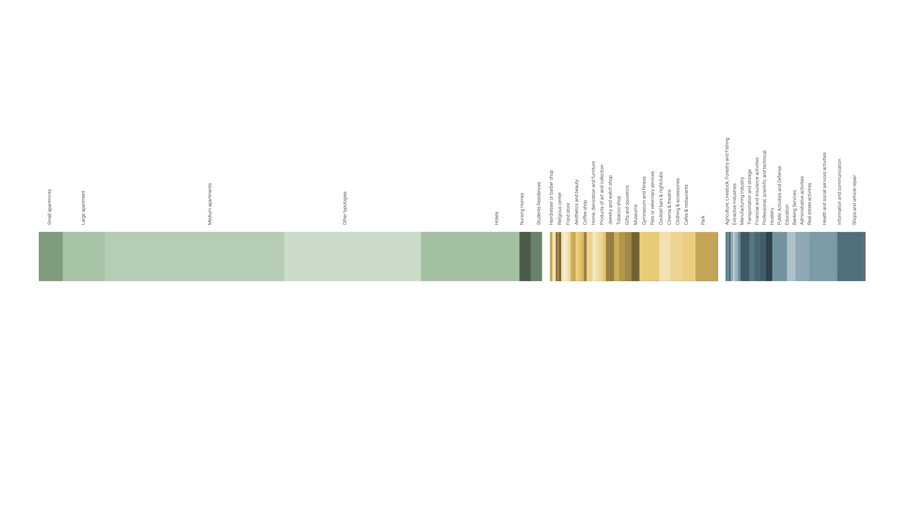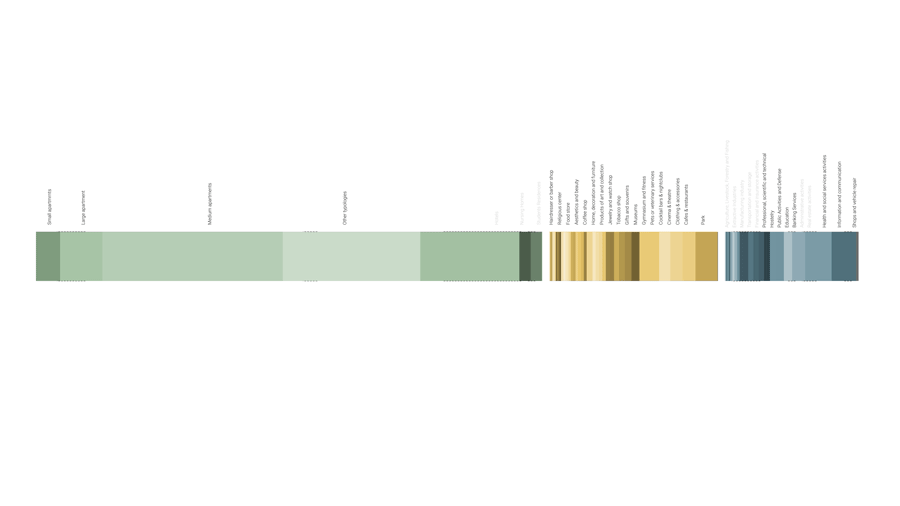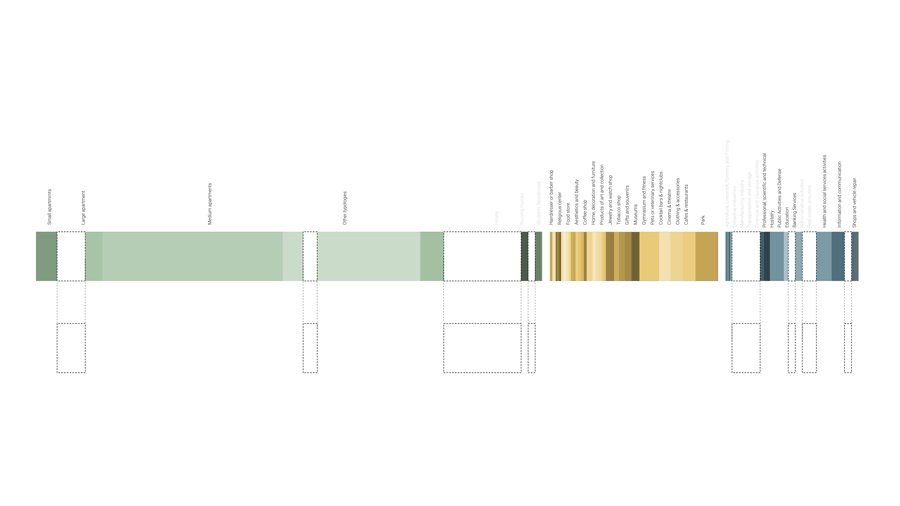
The first step of the policy will be to understand dynamics of land use in Eixample. We aggregated the current land use of residential/ offices into our three categories of time: Live, Work, Play.
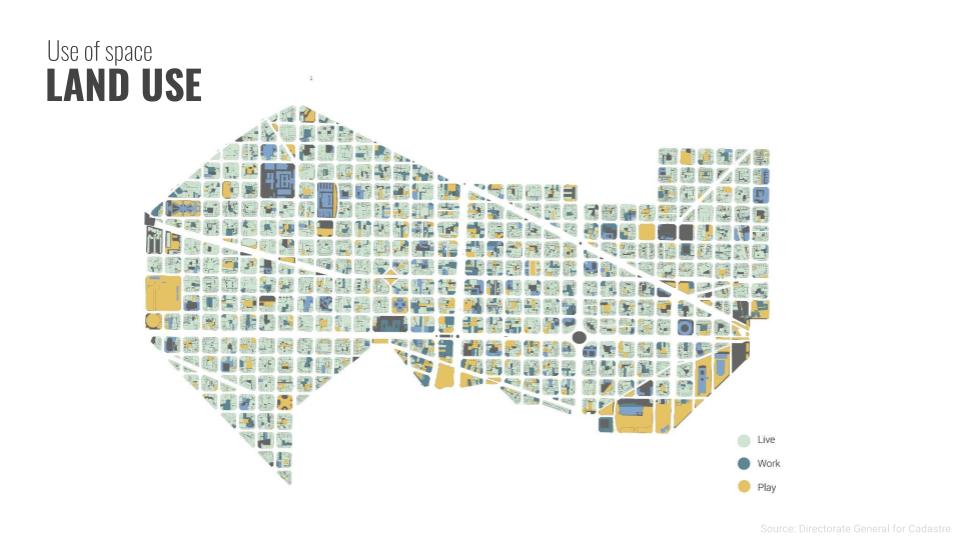

Live: Residences, the most dominant on site includes typologies from apartments to hotels.
Work: Work Spaces -from administrative offices to industries and shops and services
Play: Play areas such as parks and recreational areas. These are the main spaces here that we expect to see emerging in a society of free time.
In 2050
With growing automation and the emergence of AI, studies show replacement of jobs by robots in the near future. When jobs disappear many work spaces in the city will become obsolete. For example, research shows that 50% of people in the administration sector will lose their job, working hours will be reduced so how the city responds to these changes.
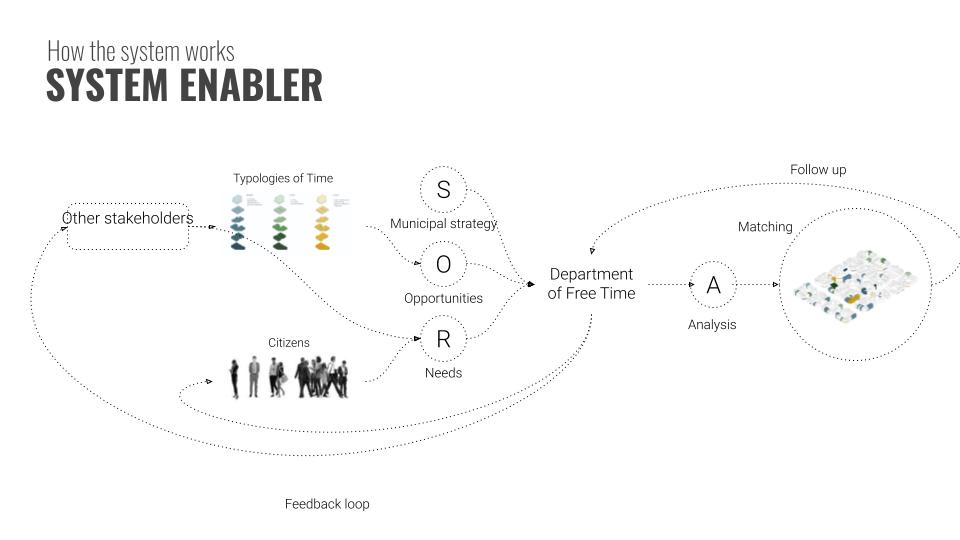
Department of free time
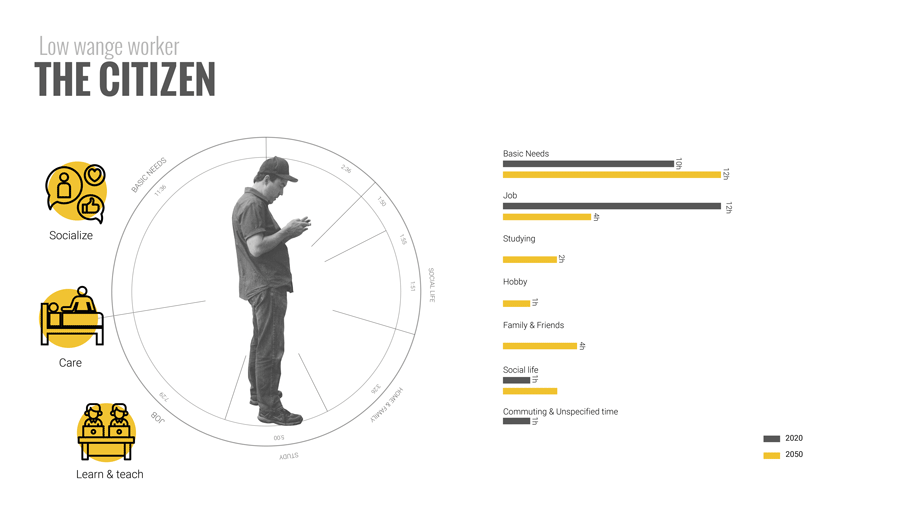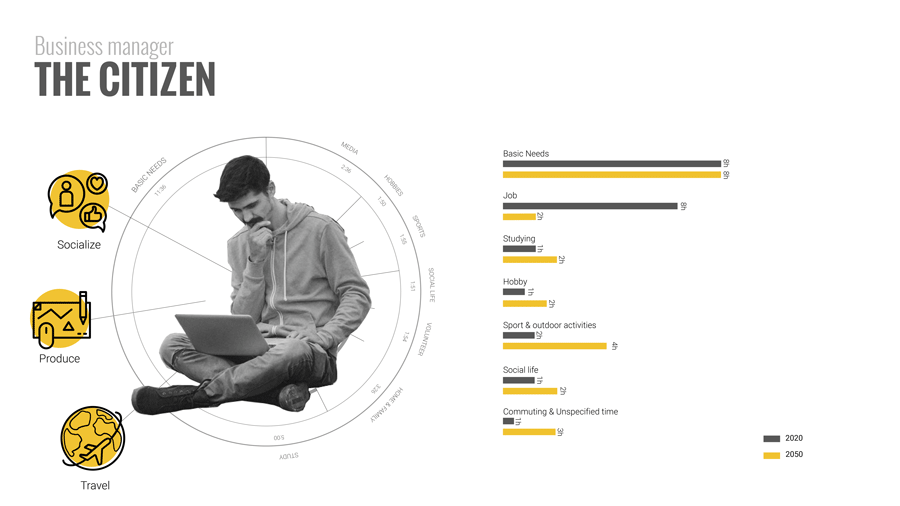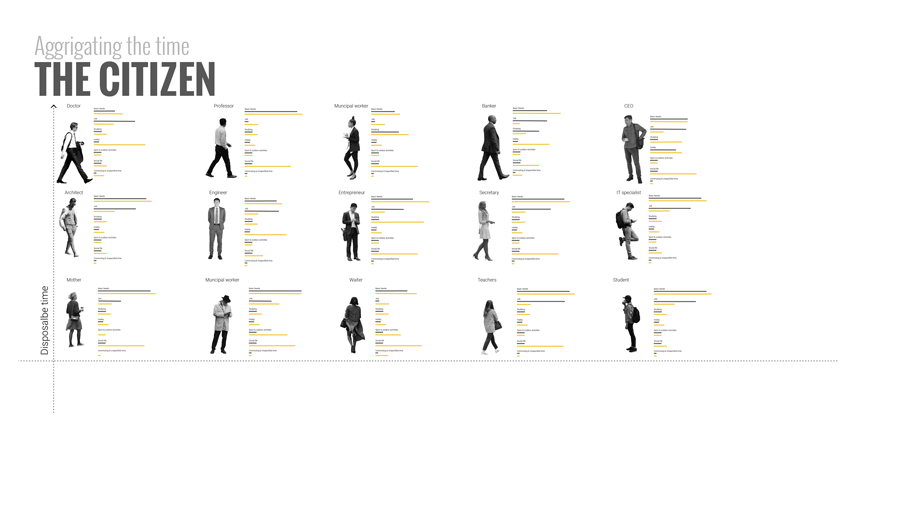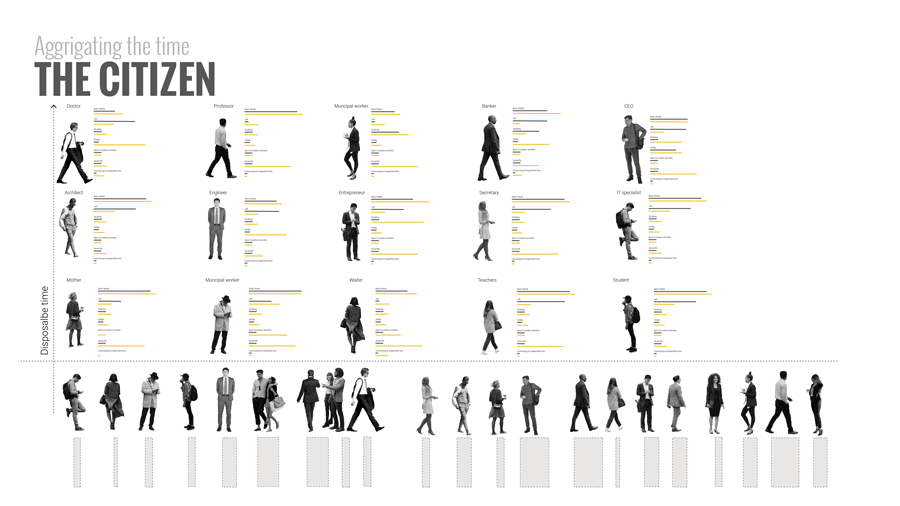
To answer that it is important to go back to understanding people’s time composition. Here we did a small exercise of listing a number of characters according to their job, and disposable time. For example, a low wage worker, who will still probably need to work for 4/5 hours a day, might want to spend his free time learning new skills to improve his conditions. On the other hand, a high earning manager might not need to work at all and instead use his free time to travel and socialize. When we aggregate the free time of all the people in the city we a barcode of free time.
The project then proposes a “ Free Time Department” in that works to bridge the gap between the future needs for utilization of free time and available spaces in the city. The department will work like an dynamic machine that will update itself with real time changes in future needs and available spaces in constant feedback loop of time and spaces.

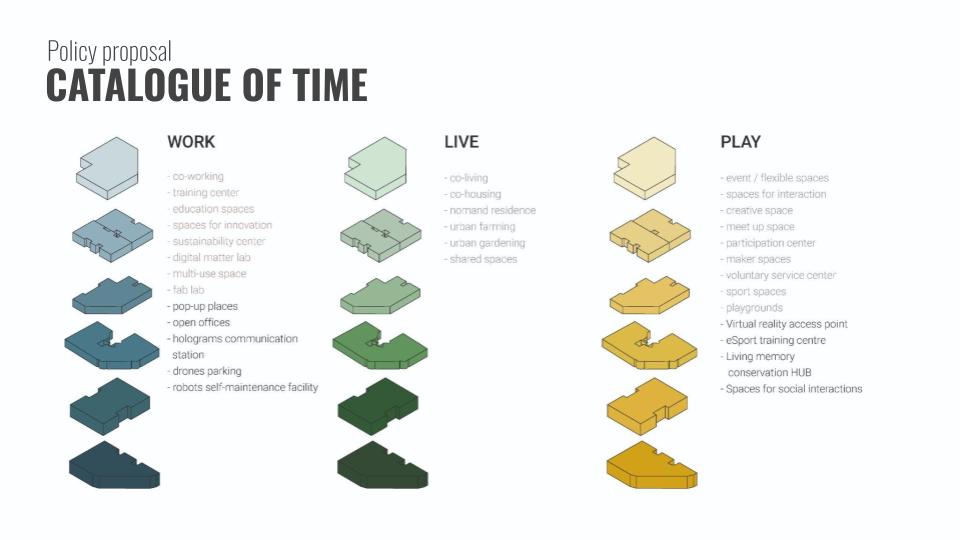
In order to implement the new uses in the available spaces, we categorize each use according to the aforementioned categories: work, live and play. These typologies are some of the options that, considering the current trends, could be developed towards the future: co-working spaces, co-living, etc.
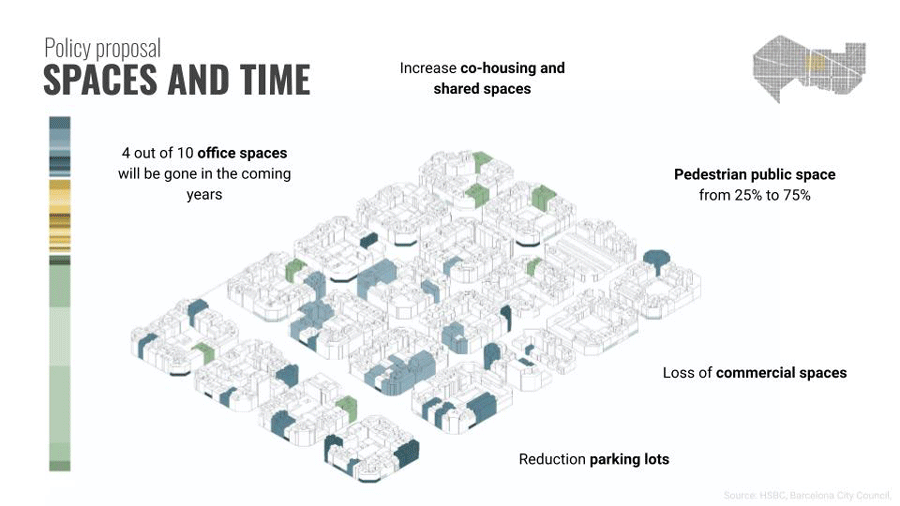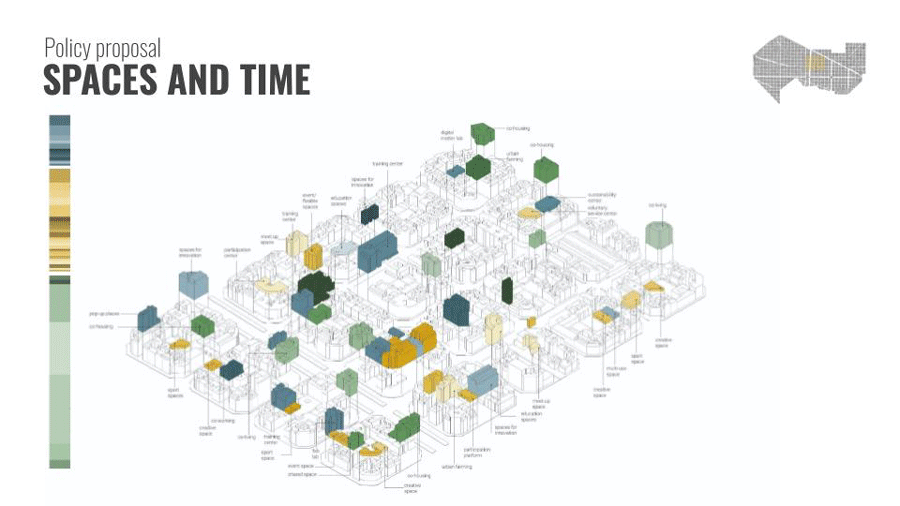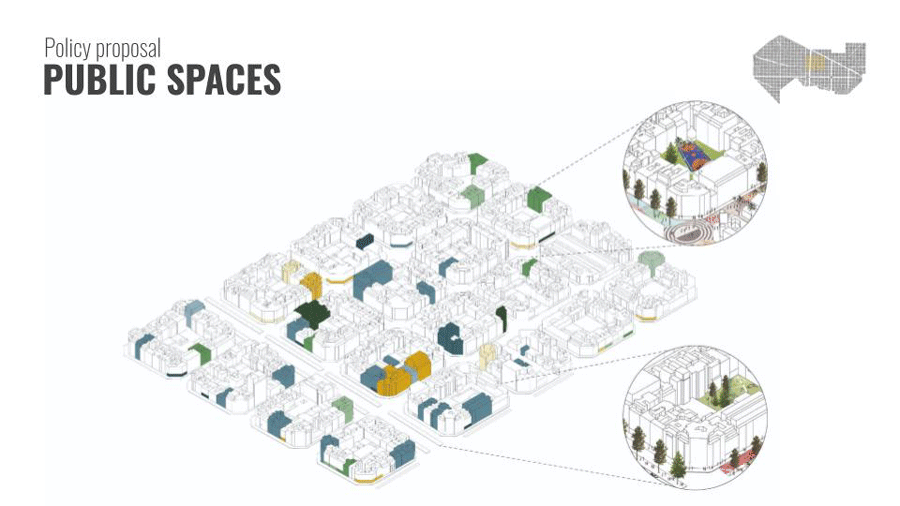
And then we identify the mentioned areas before for our interventions. Then we introduce to this typology new policies of land use to adapt the needs of 2050. For example we see how an office by regulation changed into a job training center.
How does the whole system work?
About [Free] time is a project of IAAC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at Master in City & Technology in 2020/21 by students: Hebah Qatanany ,Marta Galdys, Kshama Patil, Riccardo Palazzolo Henkes and faculty: Luis Falcón Martínez & Iacopo Neri
