Landscape design and reciprocal frame structure
Context
This independent research project was conducted as a duo. What had initially been two separate interests, where one was focused on the landscaping of an auxiliary space at Valldaura Labs led by Prasidh Choudhary and the other on reciprocal frame structures led by Romain Russe, have gradually merged into a common project.
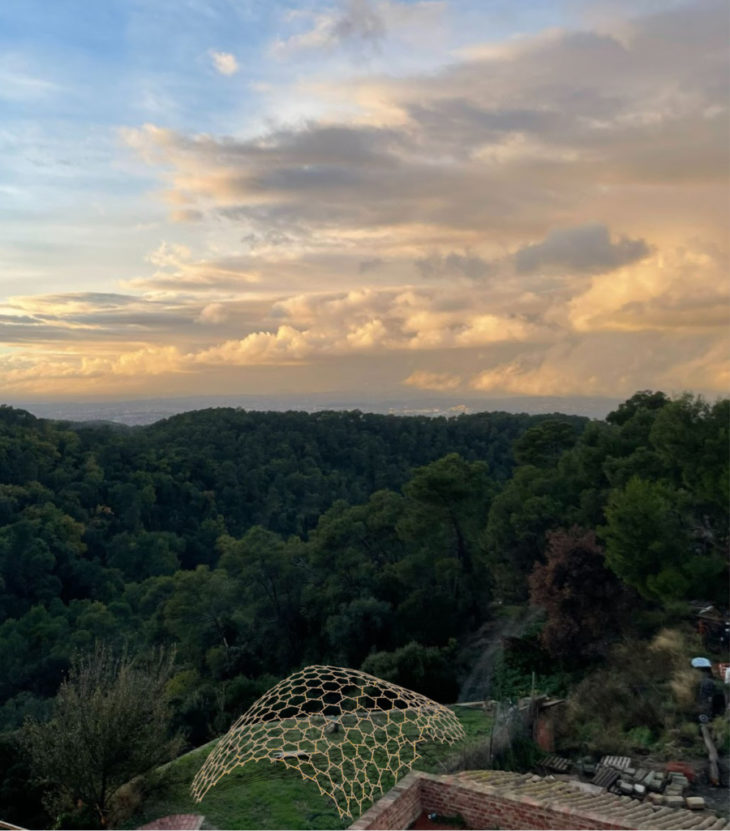

Projected view of what the reciprocal frame might look like structure in the site
Landscape design
First idea
From there, the intention was to landscape this space by mixing different elements such as planting beds, outdoor furniture and eventually a structure that would cover the whole.
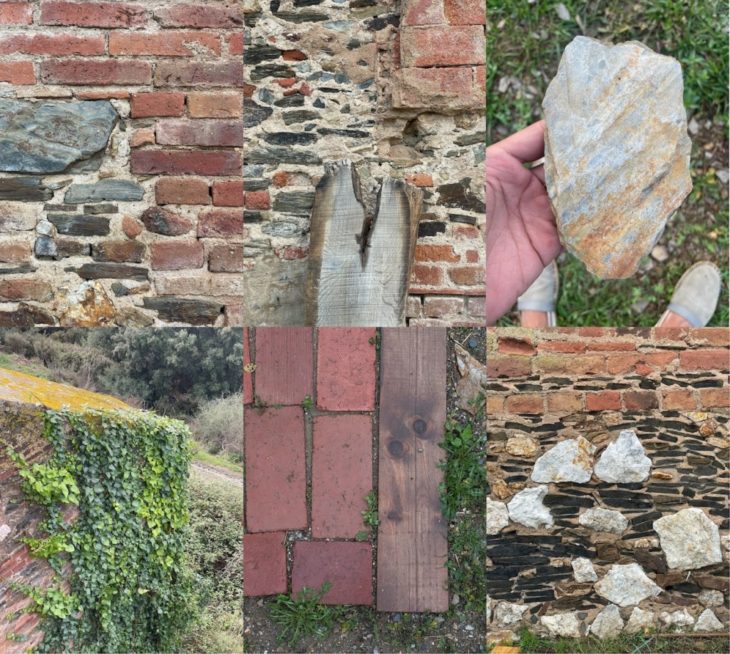

Patchwork of different textures and materials found on the site
Intentions and sketches
Based on the inspirations of Burle Marx’s work, the first sketches had the intention of mixing textures and colors by combining the materials available on the site and different flowers growing in the province of Barcelona.
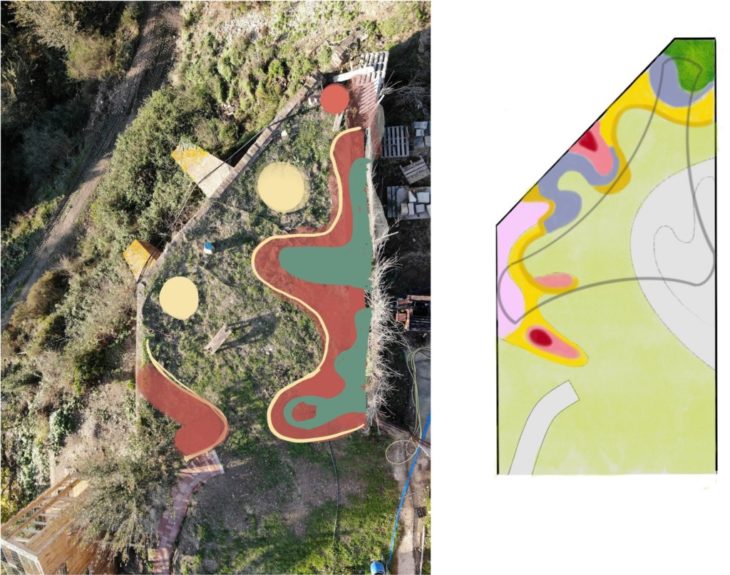

On the left: draft of the landscape design. On the right: draft of the canopy’s shape.
Reciprocal frame structure
Initial intention
This research project on reciprocal structures was born first out of a personal interest, well known for centuries but little used in contemporary architecture. This later merged with the landscaping project, itself needing a covering element while the structure project needed a land on which to be erected.
Reciprocal structure: basic principle
The particularity of this type of structure is that all the elements that compose it are structural. Each element supports the weight of a the neighbouring one therefore there are no superfluous elements. Moreover, this type of construction does not require additional structural elements such as columns at mid-span.
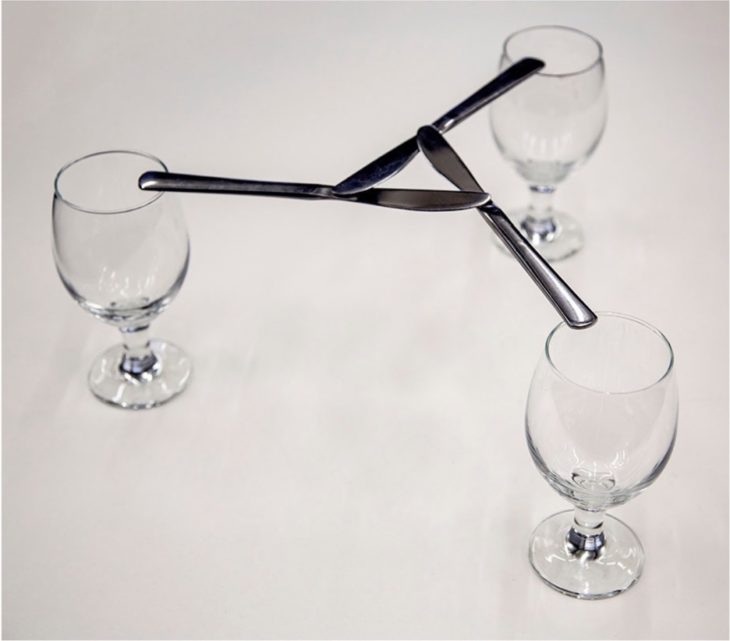

Illustration of the basic principle of reciprocal frame structure
Geometric construction and scripting
In order to build a reciprocal structure, one must first design a surface on which the geometric pattern will be applied. For this, a form-finding process using Kangaroo (a Grasshopper plugin for structural physical simulation) is required in order to create a vault-like geometry. In a first sketch, the choice was made to use a square mesh as an initial surface to decrease the level of geometric complexity. This type of structure can use different types of geometric patterns. In this case, it was decided to use a pattern working with a scaling factor.
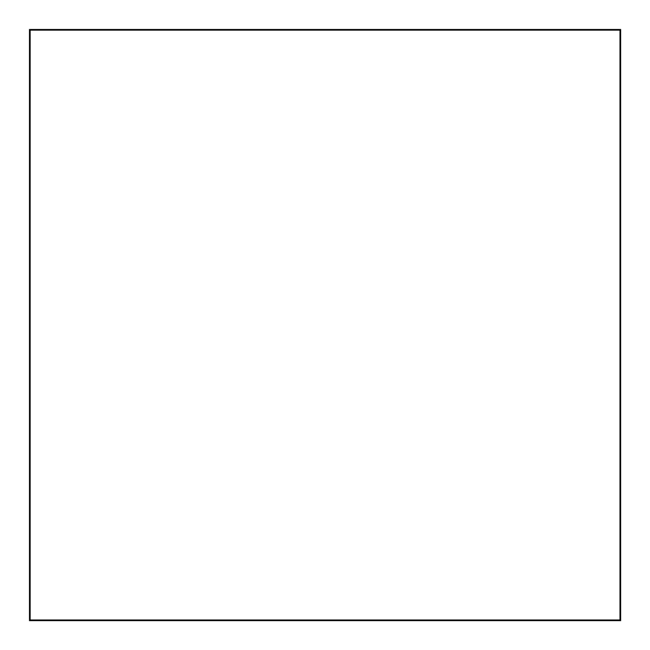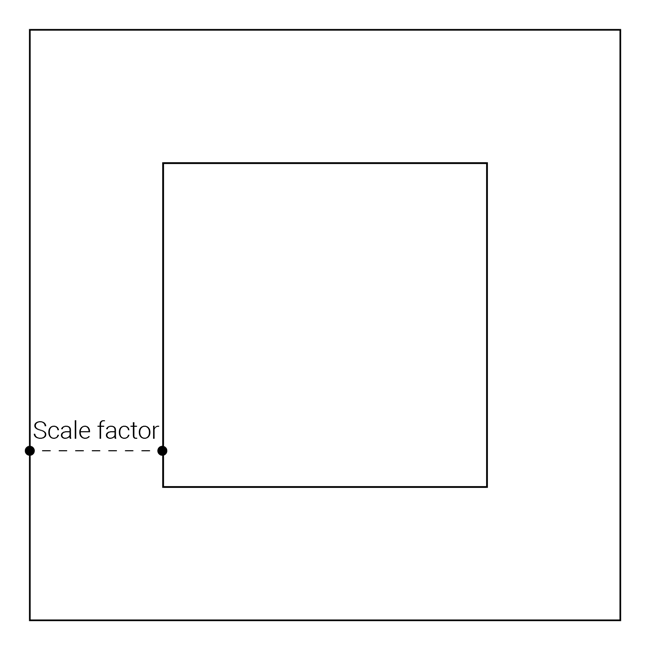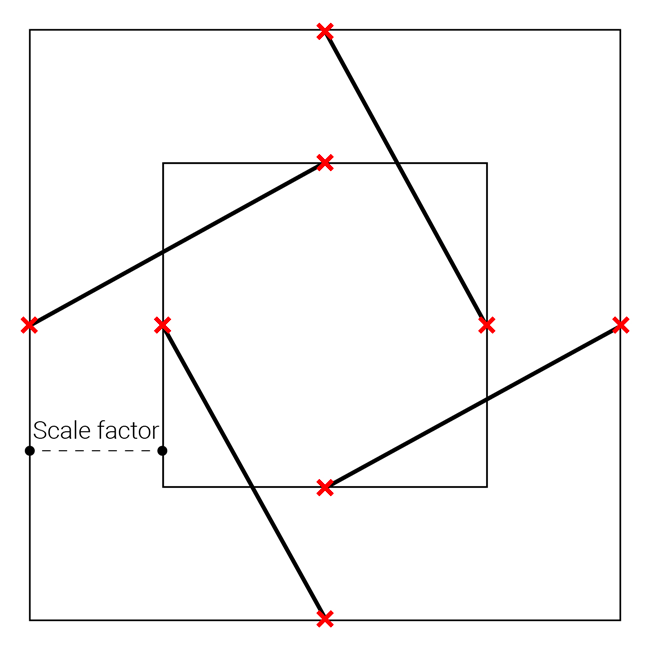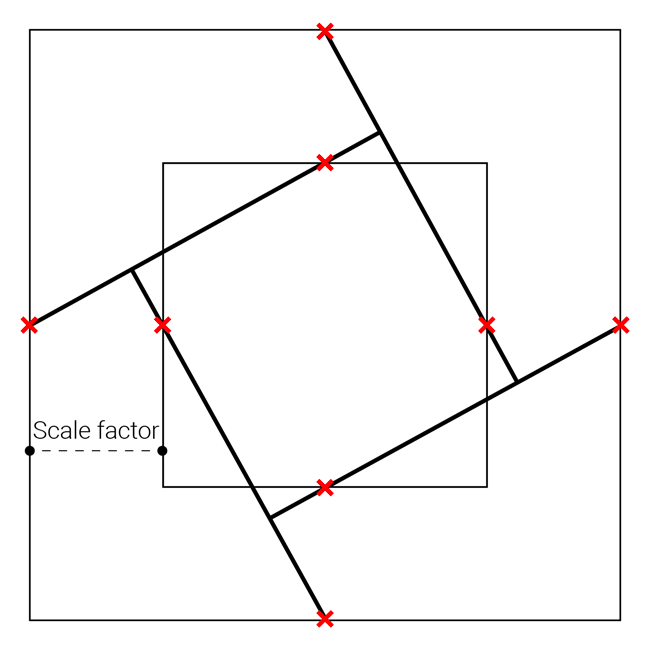
Geometric construction of a reciprocal frame pattern using a scaling factor
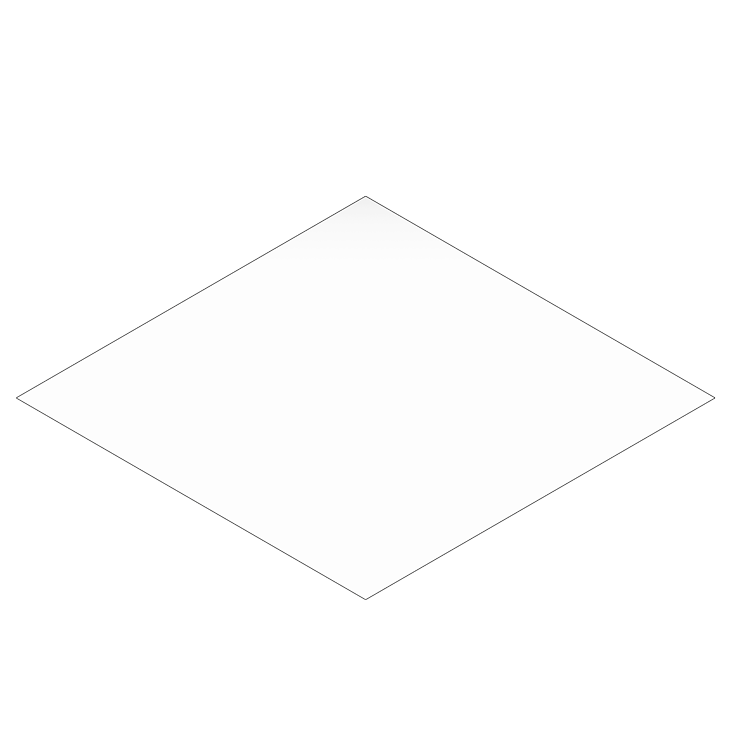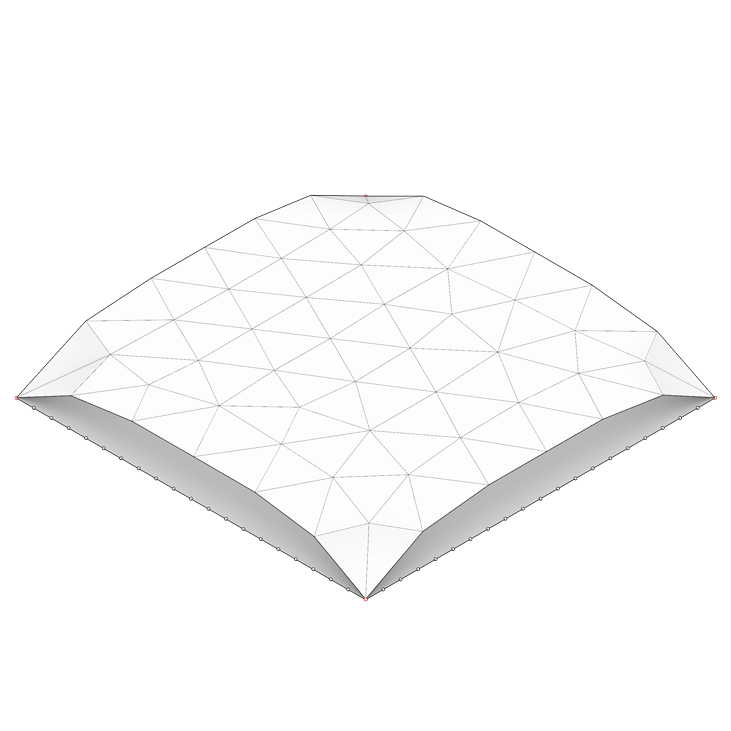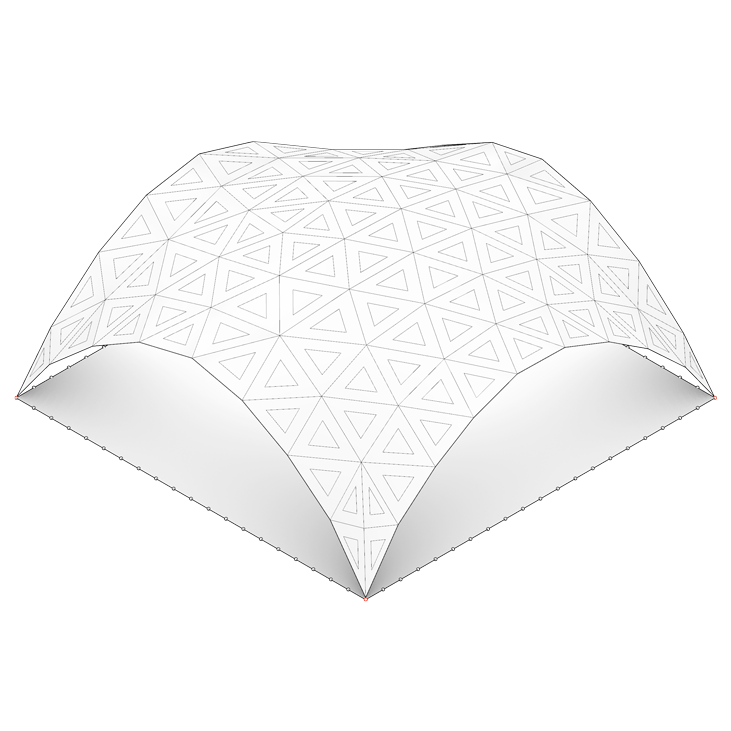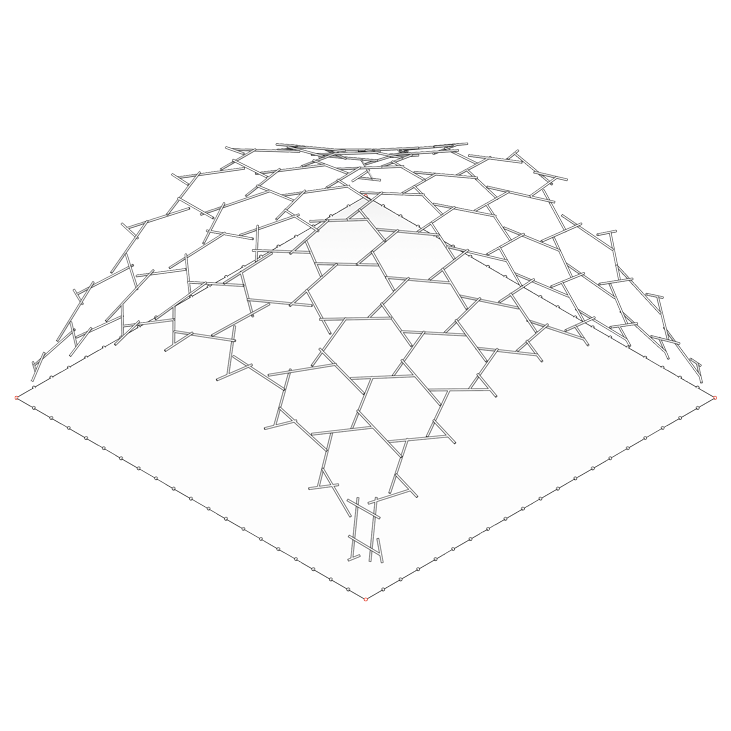
Geometric construction of a reciprocal frame structure applied to a simple vault
Site specific geometry
Finally after obtaining a simple functional geometry and an analysis of the site, it was possible to generate a site specific structure.
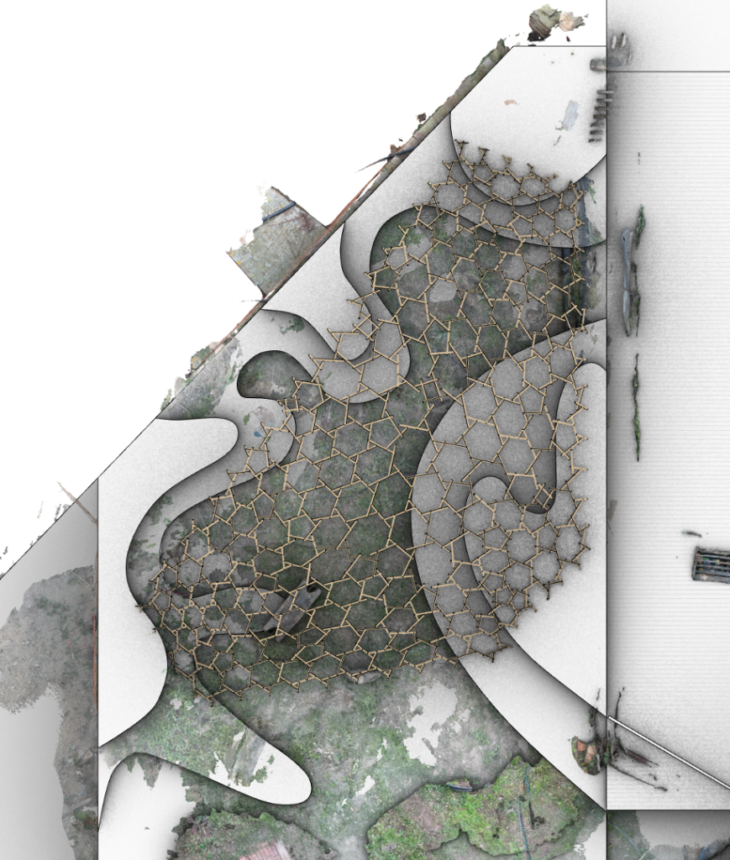
Plan view of the corner with both the structure and landscape design.
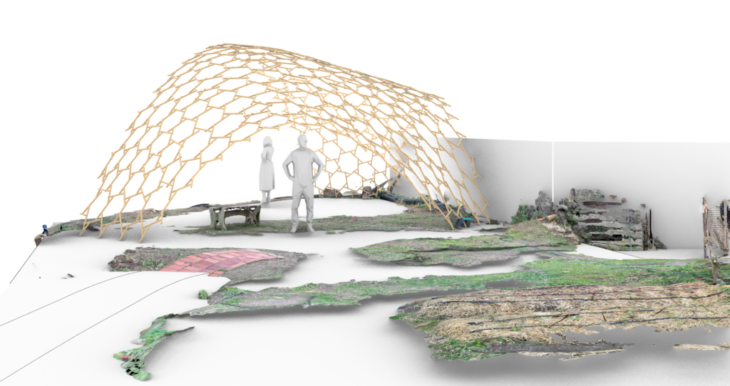
Render of the reciprocal frame structure
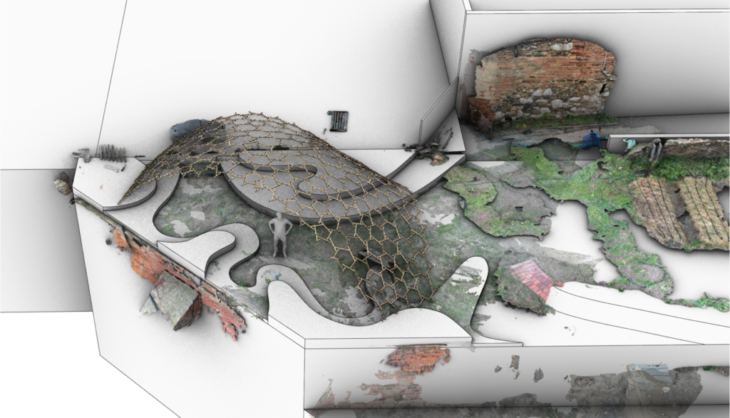
Aerial view of both the landscape design and the reciprocal frame structure
Improvements and further work
Concerning the landscaping, it is now necessary to specify the plants as well as to formalize the ideas related to the urban furniture.
Concerning the structure, it is necessary to reduce the scale in order to have a manageable number of components. But also to complete the script by adding the eccentricity of the elements, a part of structural analysis and optimization and finally to produce manufacturing details to allow the construction of this project.
“Terraza” is a project of IAAC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia, developed at Masters in Advanced Ecological Buildings and Biocities in 2021-22 by:
Students: Prasidh Choudhary and Romain Russe – Faculty: Kya Kerner