OVERVIEW
The following studio project presents the Sports and Recreation orbital space modules configuration which is part of an orbital space habitat proposal on the Lower Earth Orbit. The project is based on a platonic shape given by the infrastructure orbit group, to create a modular system to be aggregated as a complete sufficient habitat. The development of the project begins with the study of the forms of exercise, recreation, and sports that are currently practised inside the International Space Station (ISS). Then, alternative ways were studied to extend the use of the interior spaces. Consequently, human ergonomics about microgravity was investigated to develop interior spaces suitable for the physics of the environment. Finally, the modules’ structural functioning, composition, and design were developed for their possible transport from the earth and later construction in space.
CONTEXT
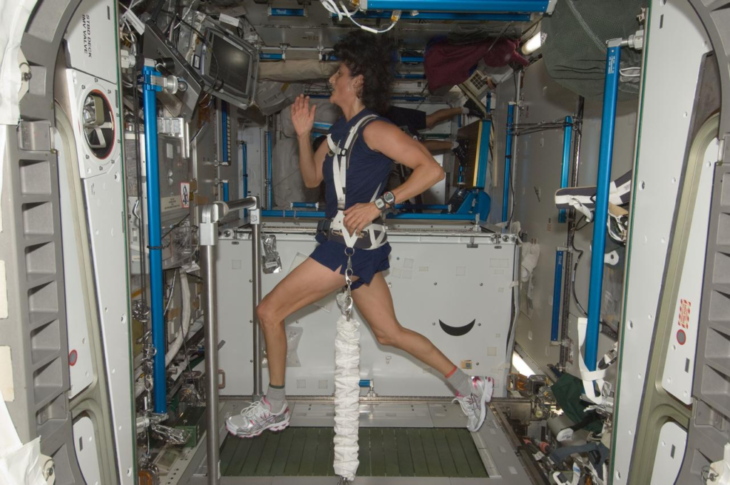
Exercise in space is part of a necessary daily routine, performed for at least 2 hours to prevent bone and muscle loss. In addition, recreation is part of the routine and usually involves sports, fun activities, and experiments regarding microgravity. Several additions to the ISS have been done throughout its existence. The different countries that work inside, have introduced major advancements for entertaining, and sports equipment. Just to state a few, in 1974 the Salyut 3 incorporated a wardroom for meals and relaxation and a window to view Earth and space. In 1977 the Salyut 6 offered improvements in living conditions with machinery being soundproofed and an extensive gymnasium. In 1986 MIR introduced articles about everyday life, such as photos, children’s drawings, books and a guitar. In 2001 Tiangong-a‘s experimental module was equipped with exercise gear. To maintain orientation, the interior walls of the spacecraft had a two-colour paint scheme – one colour to represent the ground, and the other the sky. More detailed information is found in the image below.
EXERCISE INSIDE THE ISS
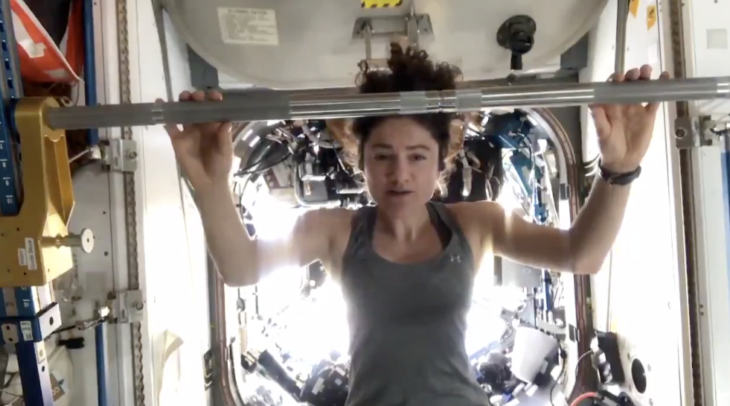
Each exercise machine targets different muscles. Likewise, each piece of equipment has different functionality in microgravity. Elastic resistance bands, pumps or “two canisters that create small vacuums“, are some of the internal functions of these machines.



RECREATION INSIDE THE ISS
How do Astronauts overcome boredom in long periods in space? – Most activities outside exercise are translations of common earth-recreational activities with the fun microgravity gives. Sports like American Football, Golf, Volleyball, and Chess are very common inside the ISS but a little different!!



PROJECT RESEARCH
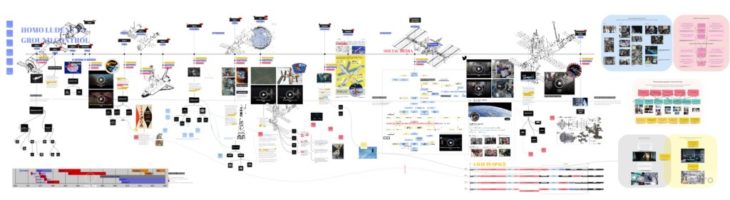
This research is presented in five sections, first introducing the problems within the ISS and the 500 Mars Programmes in regard to sport and recreation. Second, a proposal to humanise long space staying and travel. Third, is the module structure. Fourth, is human space ergonomics. Last, is space configurators.
PROBLEMS INSIDE THE ISS AND 500 PROGRAM
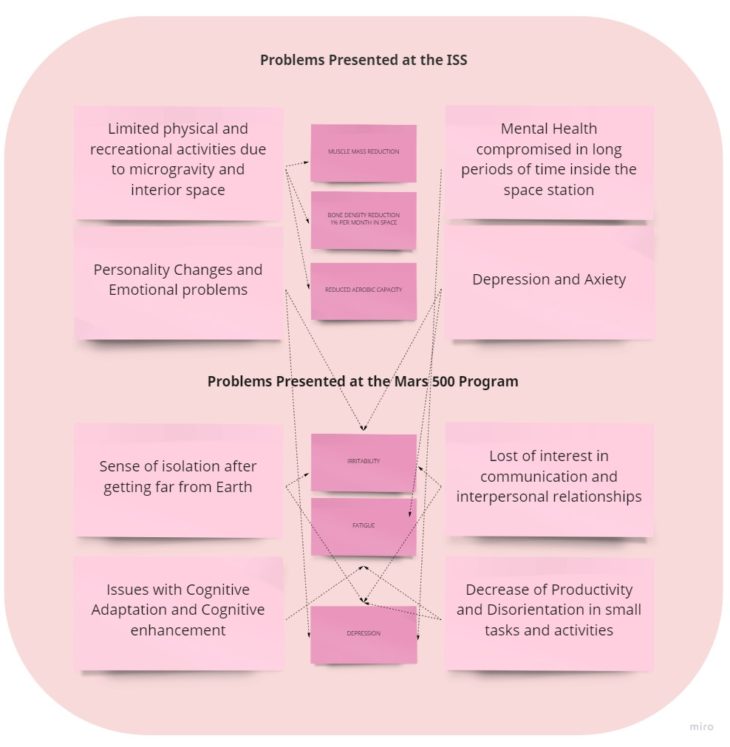
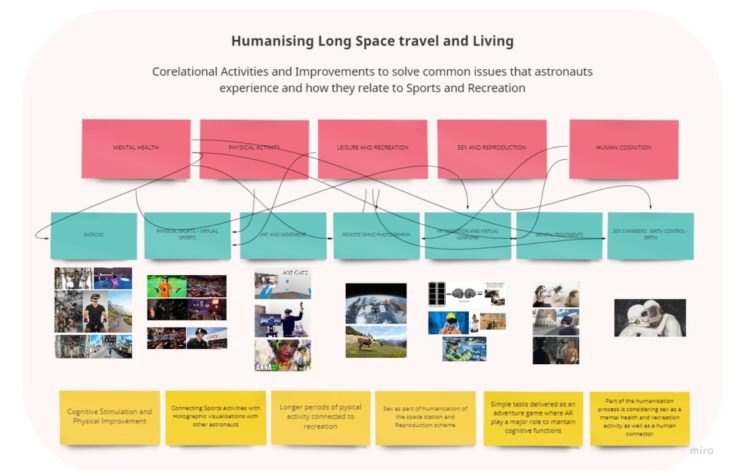
HUMANISING NEBULAE
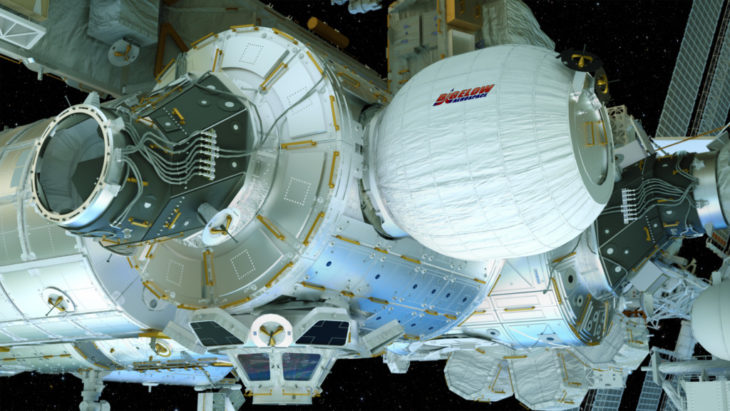
STRUCTURE AND MATERIALITY
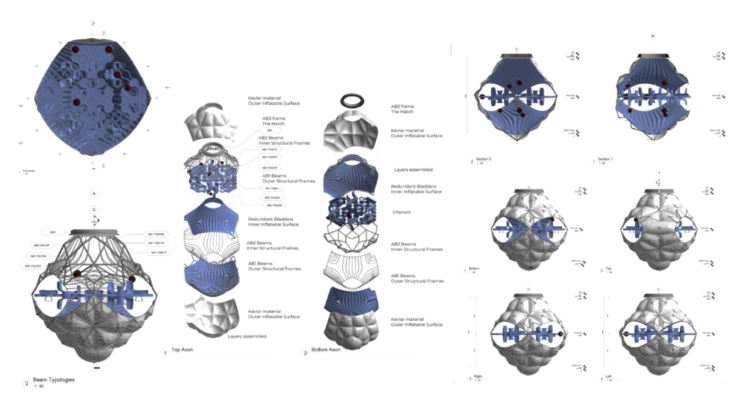
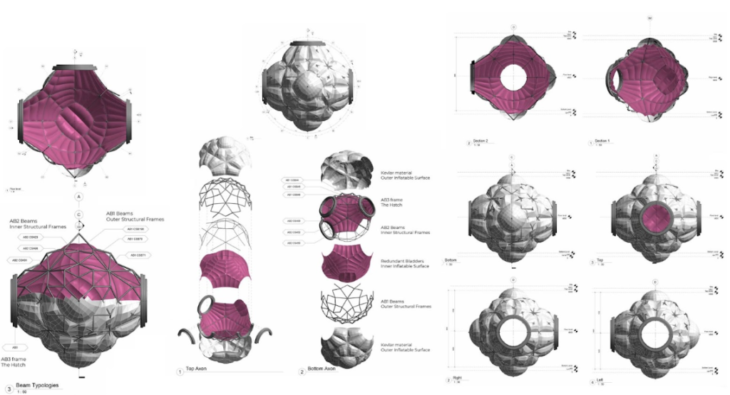
To reduce transportation and assembly costs, the modules are configured through inflatables. We rely on NASA’s Bigelow Expandable engineer to develop the interior and exterior structure of the proposed module.

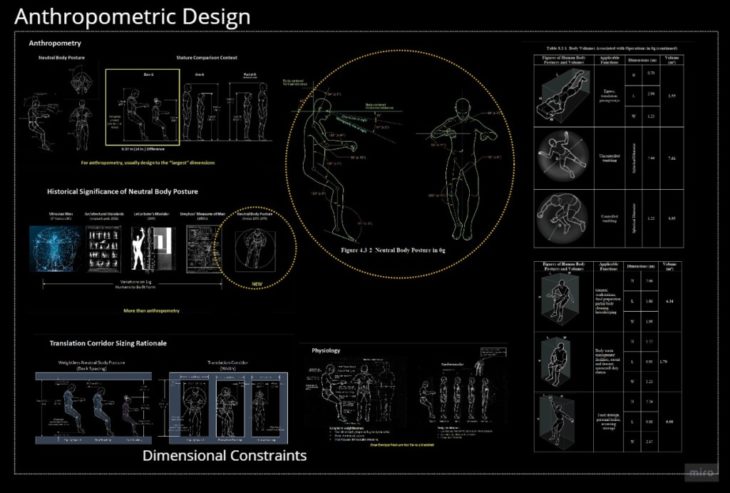
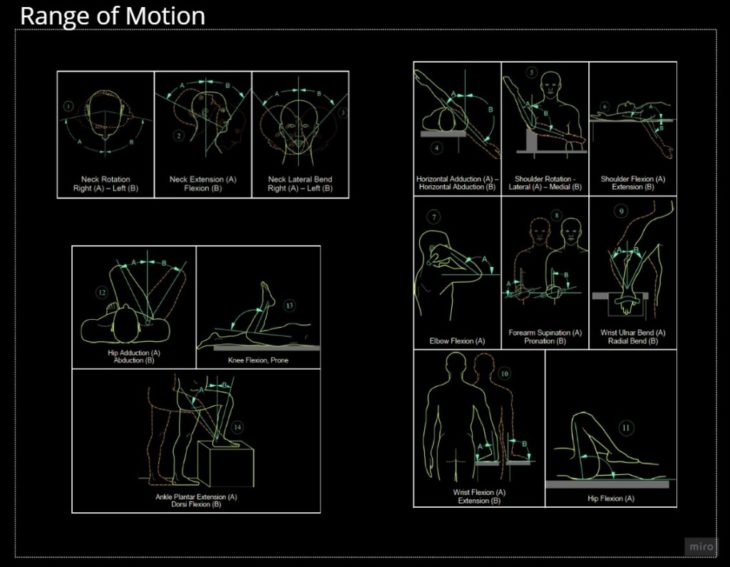
SPACE ERGONOMICS
It starts with the anthropometric design strategies, analysing the human posture in microgravity compared to the range of motion of the human body. Also, we determined the volume required per exercise activity to establish the appropriate module interior space. We determined that each person occupies around 0.65 to 1.00 m3 of space. This means the minimum space for 6 people is an average of 4.95 m3.
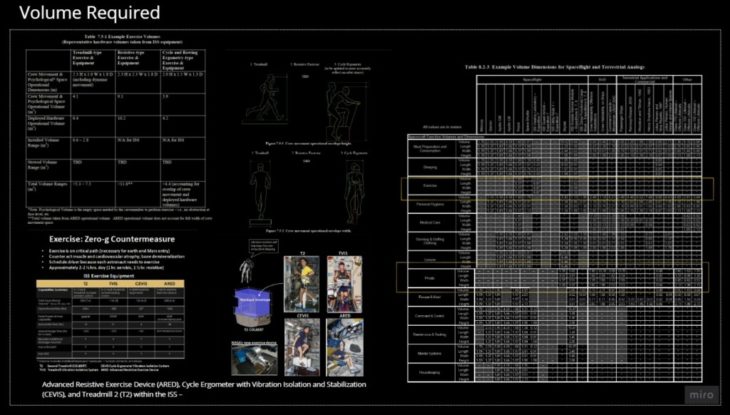
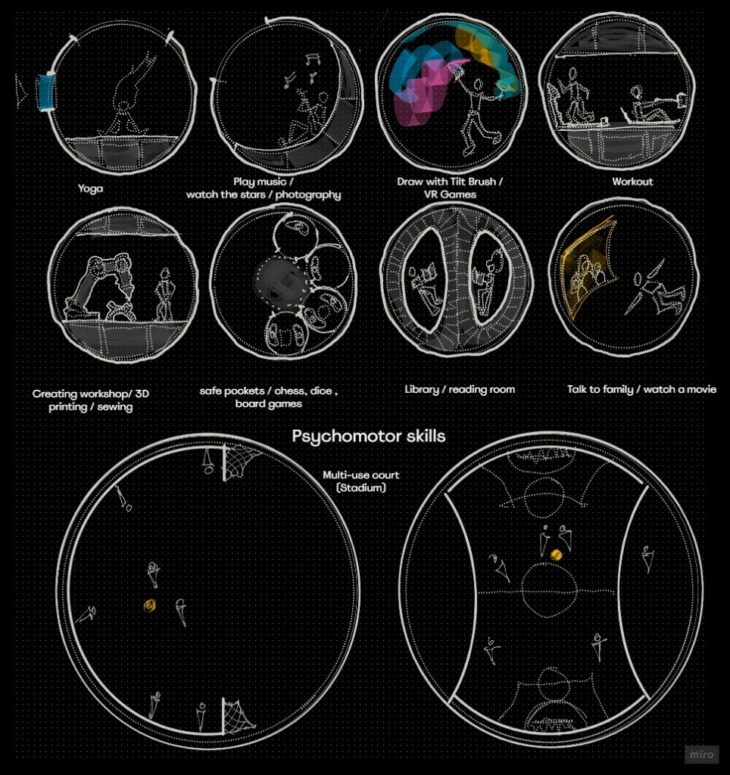
INTERIOR SPACE CONFIGURATOR
The internal circulation of the modules is directly related to the activity to be proposed. This is why a minimum circulation space was determined concerning the interior useful space. The activities are coupled with spatiality and freedom.
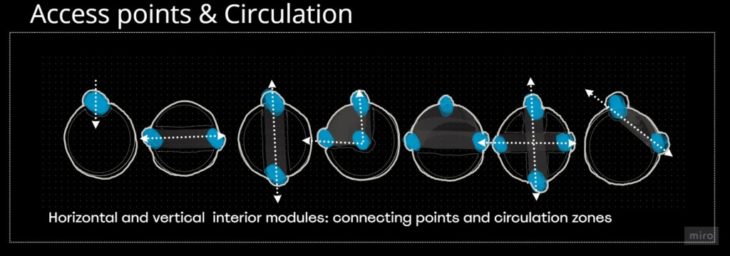
MODULE EXTERIOR CONFIGURATION
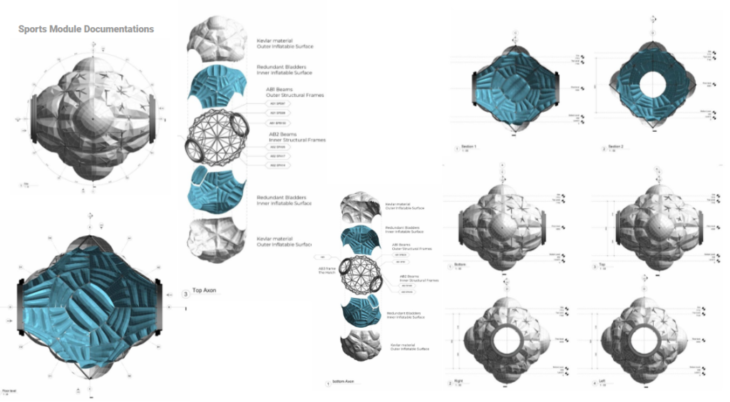
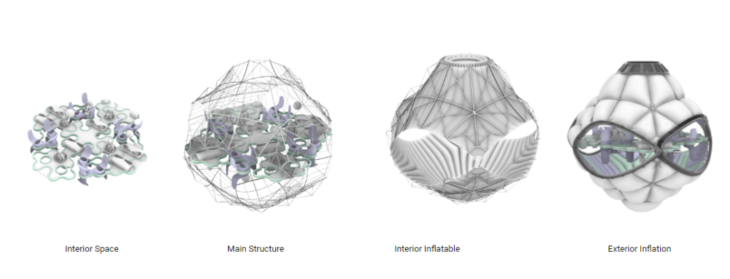
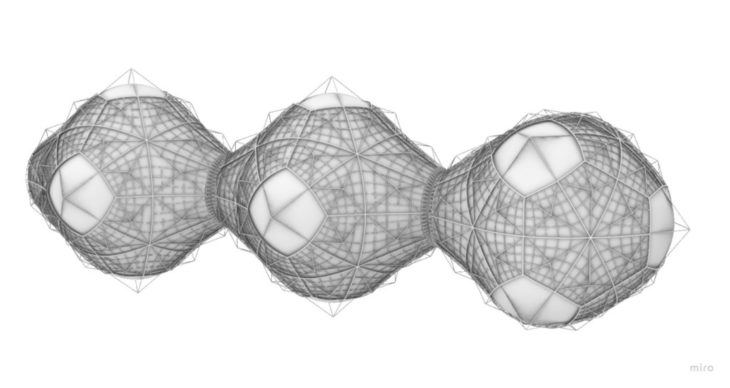
The initial module concept and external configuration of the modules are based on two types of engineering. First, the structural elements are tubes that can be assembled using the principle of tensegrity. The outer and inner layer of the module is based on inflatables. Once inflated, the structural elements self-position to shape the module.
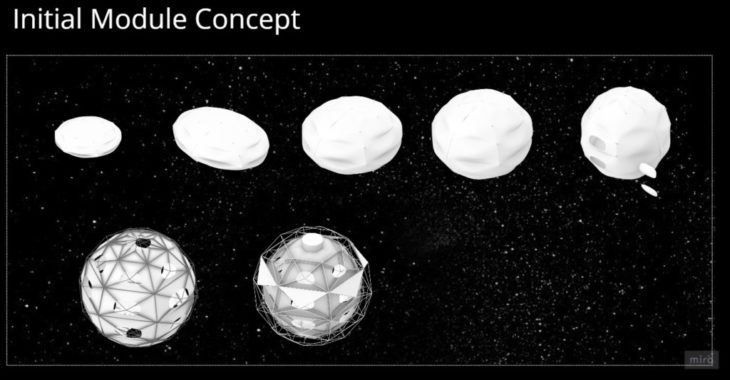
MODULE SHAPE
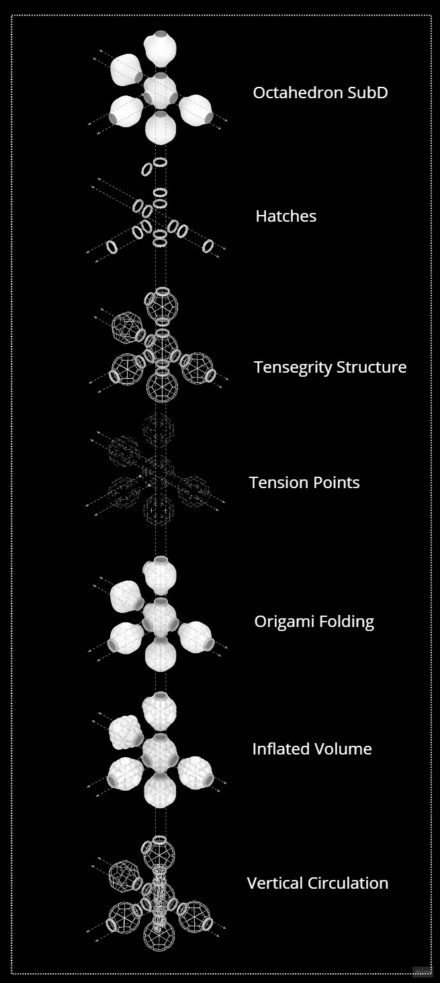
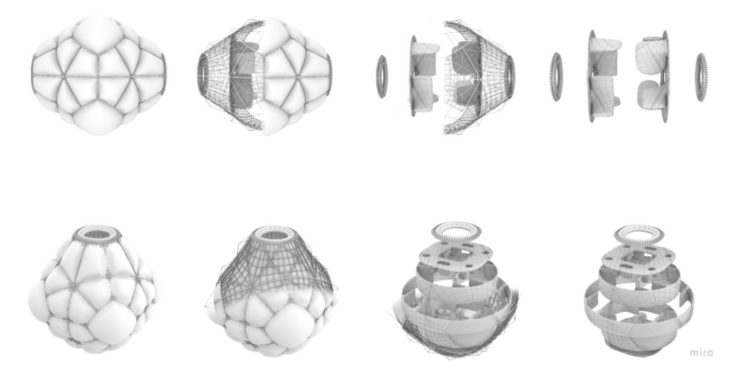
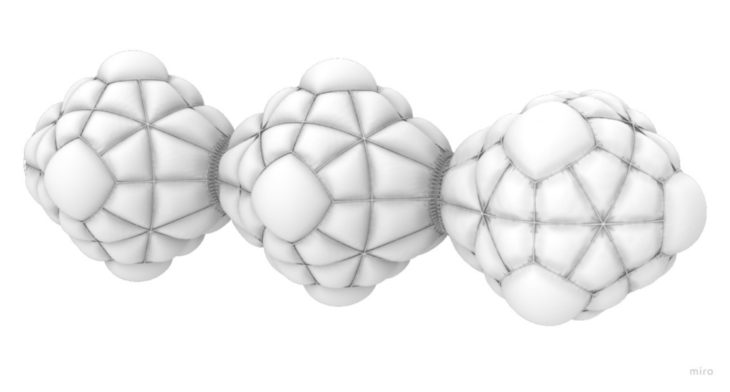
The platonic solids from the infrastructure group are the main shape of the modules. It is based on a 3D Octahedron, the one we decided to soft its geometry by introducing inflatables without losing the main shape for aggregation.
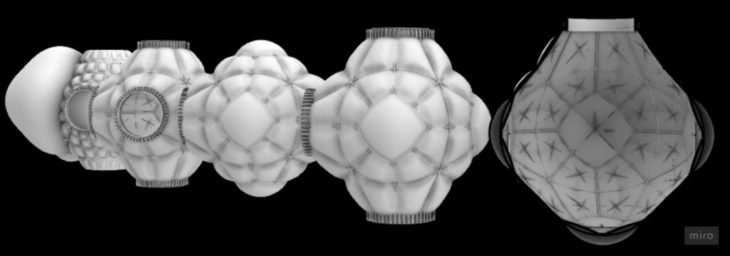
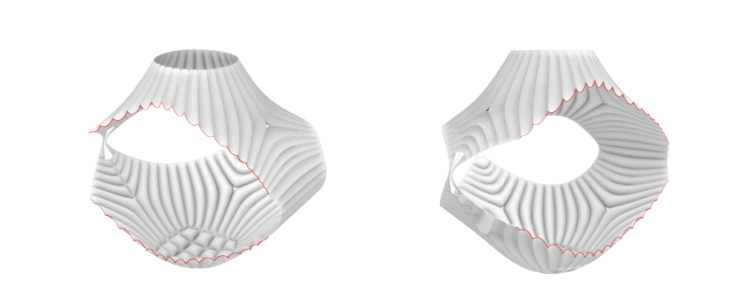
ORIGAMI AND INFLATION
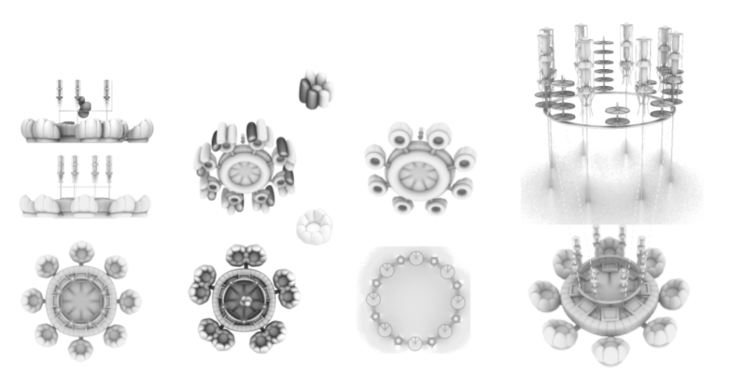
The first step was to develop an appropriate folding method for easy transportation. We decided to use an origami folding-like form. The volume and the inflation depend on the number of people using the module. All modules are capable of enlarging their shape once more people inhabit the orbital space station. The image below shows the growing module from 6 to 18 inhabitants.

UNIT CONFIGURATION AND ASSEMBLY
The central module connects its neighbours by hatching its connecting faces. The tensegrity structure presents tension points within the structure to perfectly shape the origami unfolding.
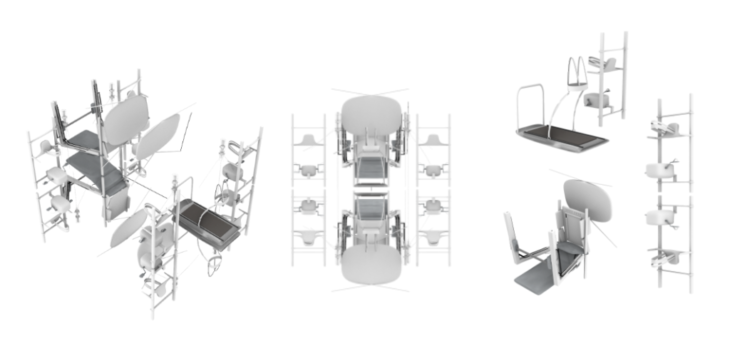
MODULE FUNCTION PROGRAMME
The system presents the connection between the research and the functionality of each of the modules, and a schedule of activities that can be performed inside them. Similarly to what NASA does for Astronauts, we determined certain activities about time and use. Introducing now, SLEEP – WORK – EAT – PARTY – REPEAT
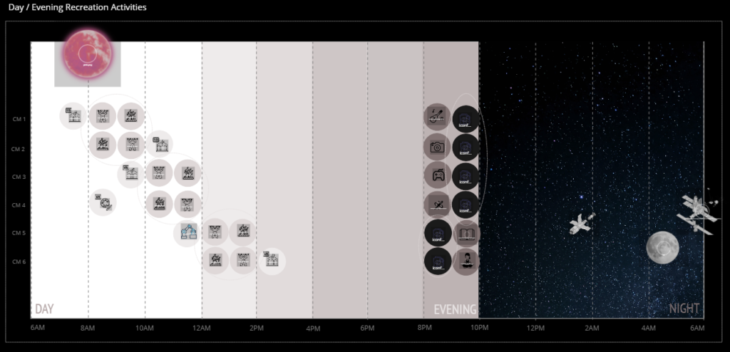
DAY AND NIGHT MODULES
To determine the activities of each module we are based on present and absent activities. That is, the present activities are related to the necessary ones established by NASA, while the absent ones are those related to recreation. Recreational activities are divided into 4 modules that present: sport + physical activity, fun activities, sociability, and mental health. To increase the quality of mental health for astronauts and visitors, each activity is divided into day and night activities. Where the user chooses how to feel. As is known, every 45 minutes approx. dawn and dusk inside the station. This is why each module presents a different opening to the activity, creating a catalogue of modules by activity. The socialization module or CASINO is a night module, mental health – MEDITATION, READING + AR and a hybrid -Isolation module, GAMING + SPORTS and EXERCISE are daytime modules. Finally, the middle module is assigned as a connector.


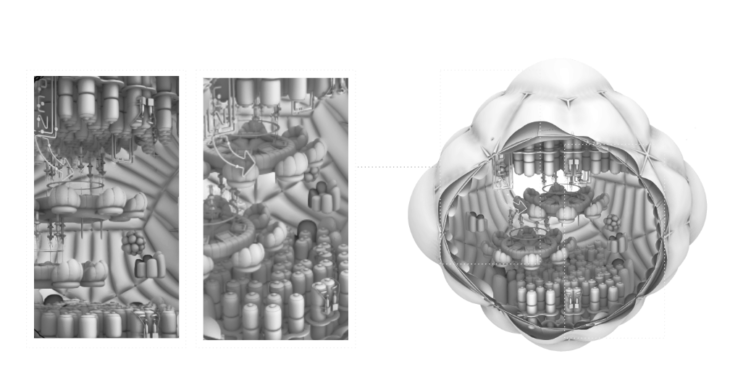
NEBULAE – RECREATION MODULES CONFIGURATION
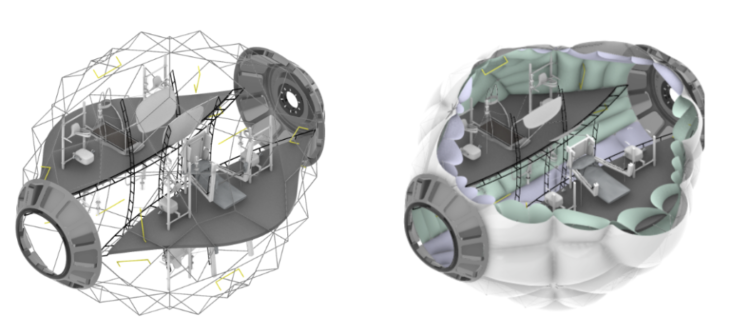
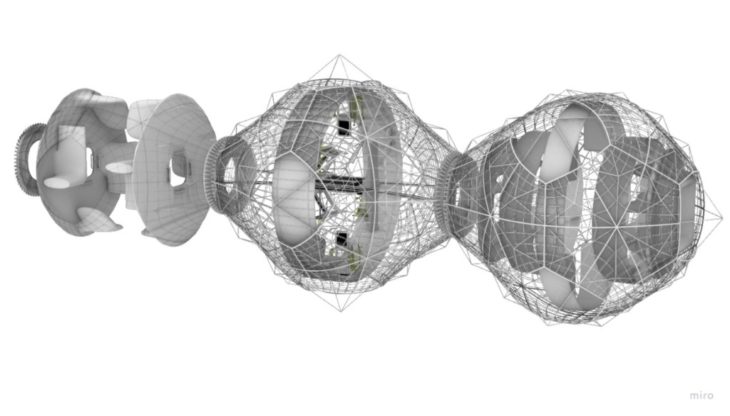
The modules are made up of two structures, one internal and the other external, that support and shape the two inflatable faces of the modules. The internal chamber that is generated is a radiation isolate as it is the receptive chamber for humidity and fluids for recycling.

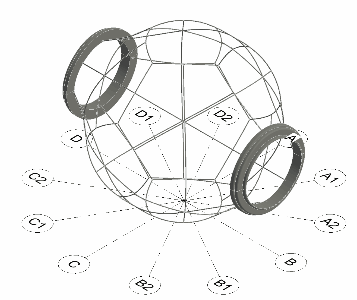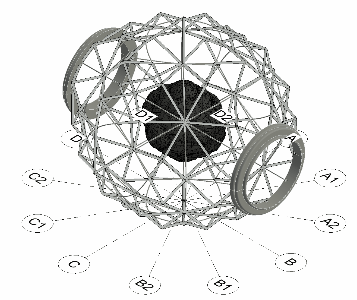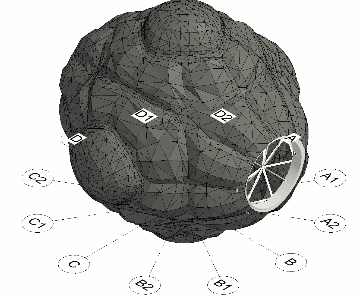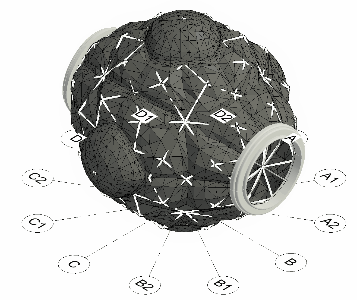
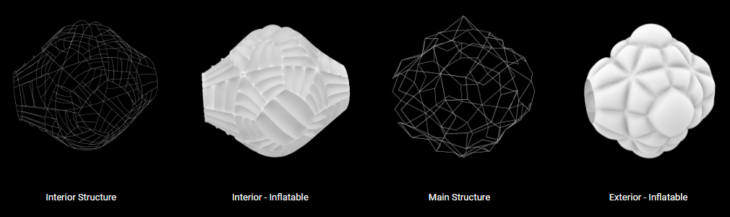
Module structural configuration
EXERCISE
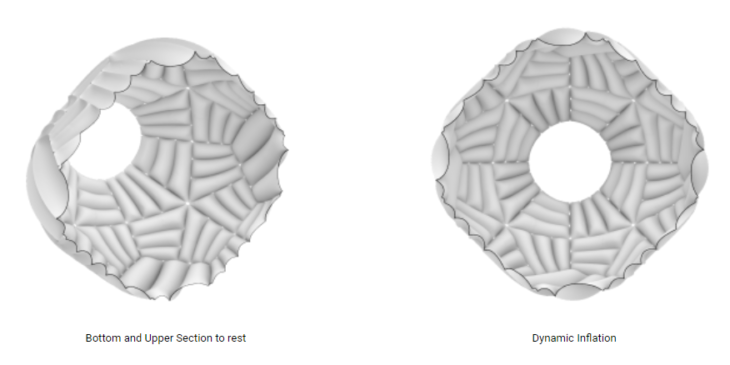
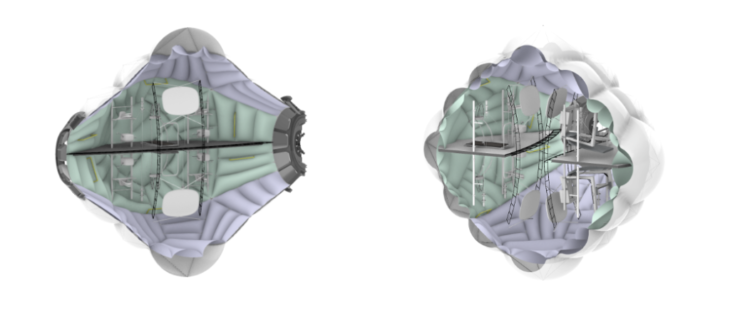
The Exercise Module has the necessary equipment to maintain the shape of the Astronauts. The interior pattern mimics a dynamic and fluid environment. The interior configuration is mirrored, using both sides of the module. The colour of the patterns divides the ground and sky perspective by introducing colours to the patterns.

MEDITATION
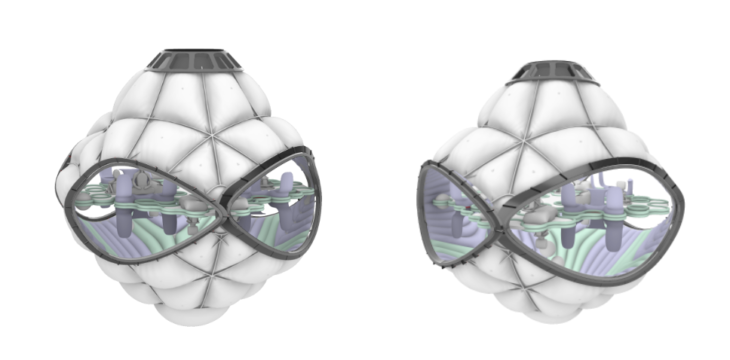
The Meditation Module presents a calm structure with soft meditation and yoga spaces suitable for microgravity. The interior pattern mimics a fluid and calm environment. The interior configuration is mirrored, using both sides of the module. The colour of the patterns divides the ground and sky perspective by introducing colours to the patterns, representing a warm environment. It is based on the isolation module with bigger openings for space interaction.
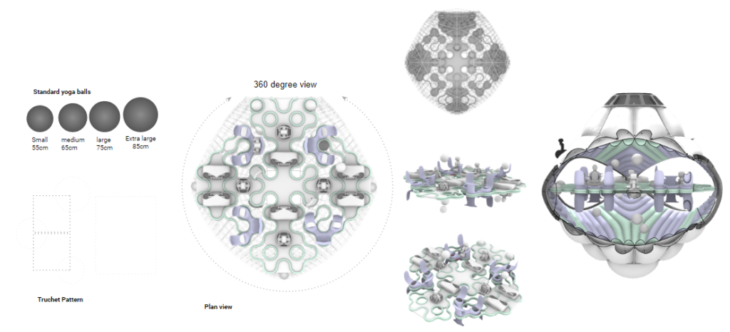
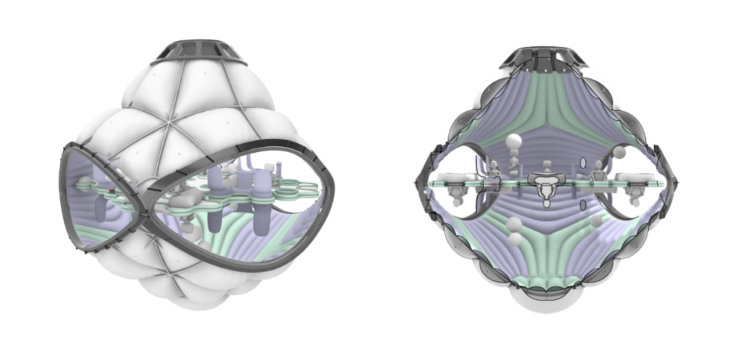

CASINO
The Casino Module presents a noisy structure with inflatables as seating and table-like furniture. It incorporates space bottles with beverages and food trays designed for space. The interior pattern is fluid, dynamic and colourful. The interior configuration is mirrored, using both sides of the module. The colour of the patterns divides the ground and sky perspective by introducing colours to the patterns, representing a cold but vivid environment. It is based on the night module.


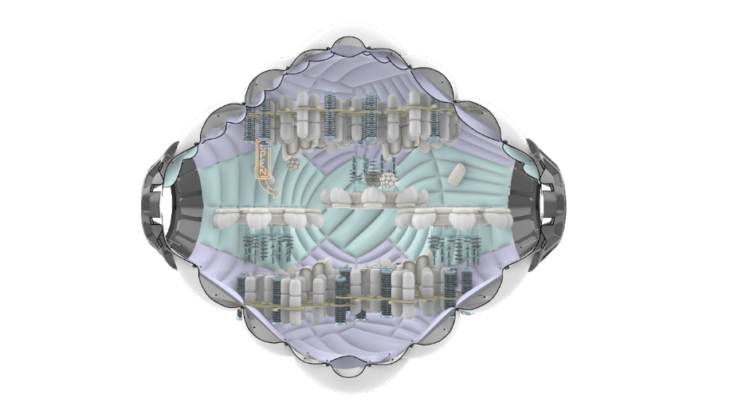


MODULES AGGREGATION
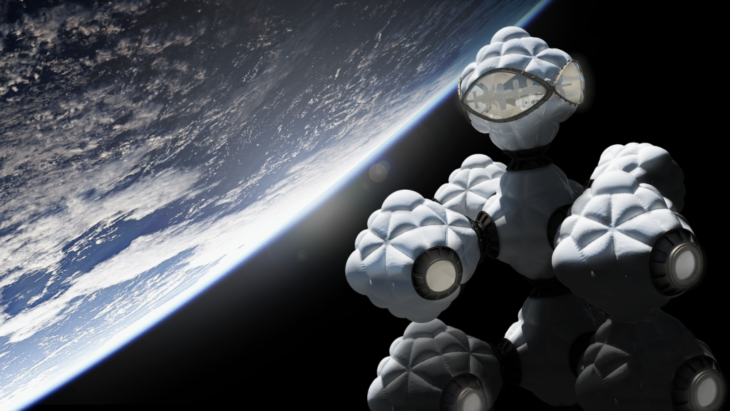
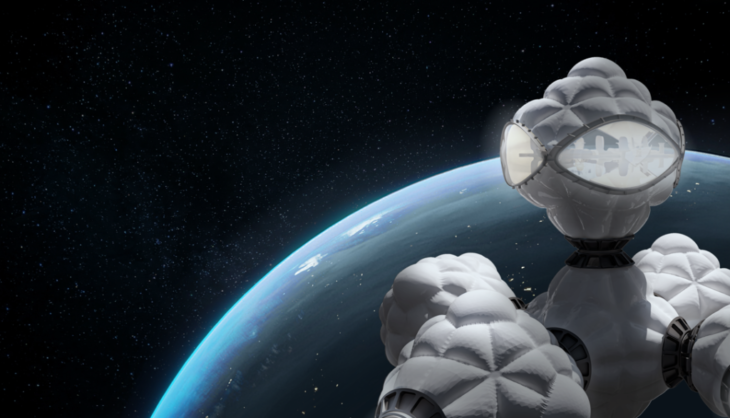
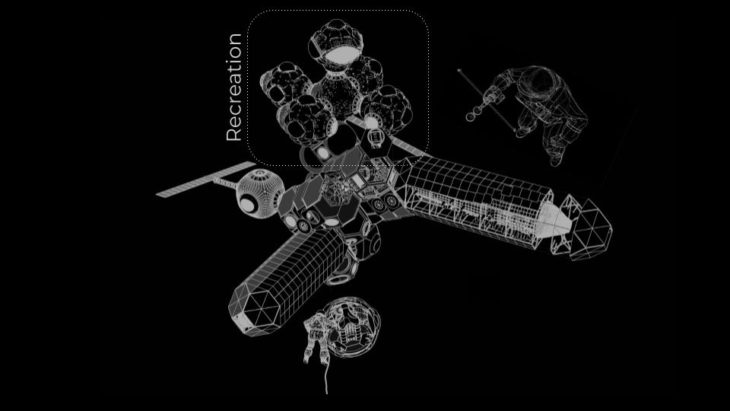


CREDITS
NEBULAE: ORBITAL SPACE HABITAT – INTEGRATIVE MODELING is a project of IAAC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at Masters in Advanced Computation and Design (MaCAD) in 2020/2021 by students: Jumana Hamdani // Irene Martín // Pablo Jaramillo and faculty: Xavier De Kestelier // Joanna Maria Lesna // Levent Ozruh