The main objective of this coursework was to design a mass timber project that was responsive to the climate conditions of a specific location, in this case, Rio de Janeiro.
Climatic Data
Rio de Janeiro is located at 22.9 south latitude and 43.17 longitudes. Therefore it is between the tropic of Capricorn and the equator, meaning it is in the tropical zone. If we take a look at the temperature range, in average the warmest month would be January with an average of 26.9 while the coolest month is July, with an average of 20.8.
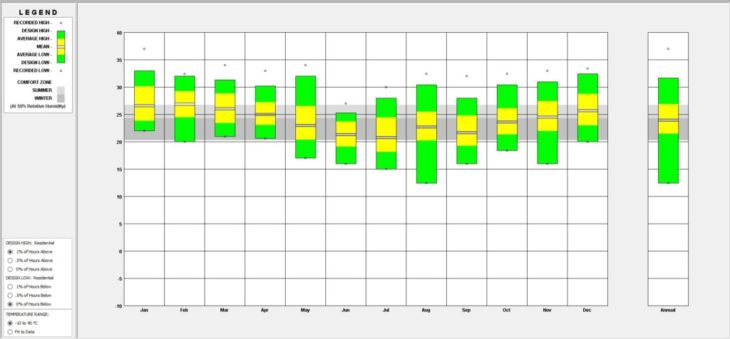
Temperature RangeAs seen in the graphics the temperature fluctuations year long and also night to day are at a minimum. A strong characteristic of the tropical climate, is that the humidity is quite high, year long.
Almost every month, the dry bulb temperature has to be lowered in order to reach the indoor comfort zone. Therefore it is crucial to reduce the heat load of the building.
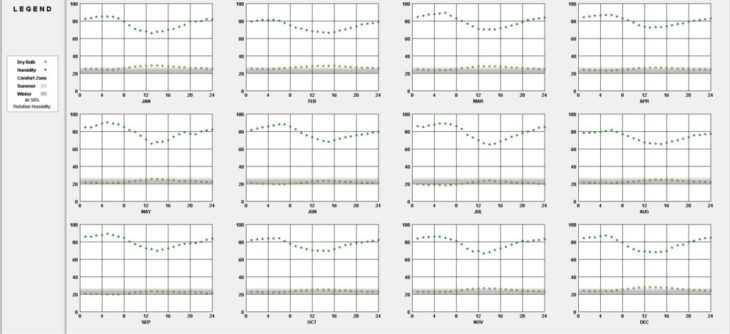
Dry Bulb and Humidity
Materials that transfer minimum heat from outside to inside like wood is a smart choice of material for walls, ceilings, and windows to provide a cool interior.
Solar radiation is generally very high, and sky cover is usually low.
This indicates the importance of shading. Solar protection from the sun is very essential in Rio’s climate. Along with solar shading, passive ventilation is also very vital when designing a building in such a climate.
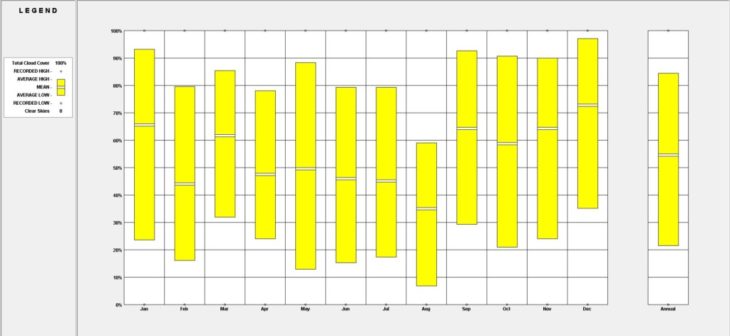
Sky Coverage
The prevailing wind from the North and the South East is what determines the sizes and positioning of the openings.
As to the form of the structure, a compact form and a low perimeter to area ratio mean minimizing the heat gain and therefore is a key to design for a hot and humid environment. Shaded outdoor buffer zones like patios and courtyards help extend the living and working areas in warm and humid weather.
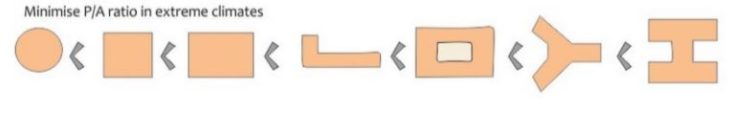
Varieties of Typology
Also considering some examples of Brazilian vernacular architecture, the Bandeirista houses, we thought the most suitable form for this house was a compact square with almost equally distributed indoor spaces. The Bandeirista houses were mostly 1 story high structures, usually elevated from the ground, with pitched roofs.

Bandeirista House
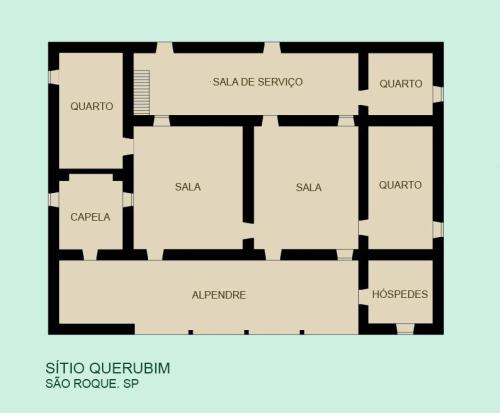
Bandeirista House Floor Plan
Design Strategies
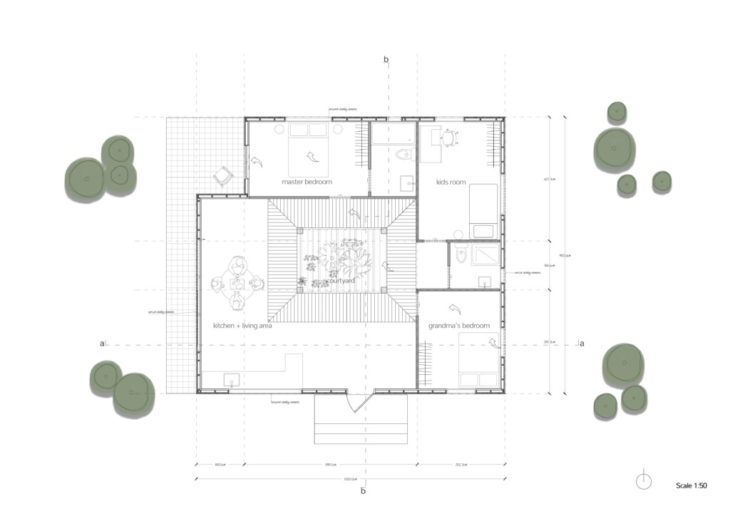
Floor Plan
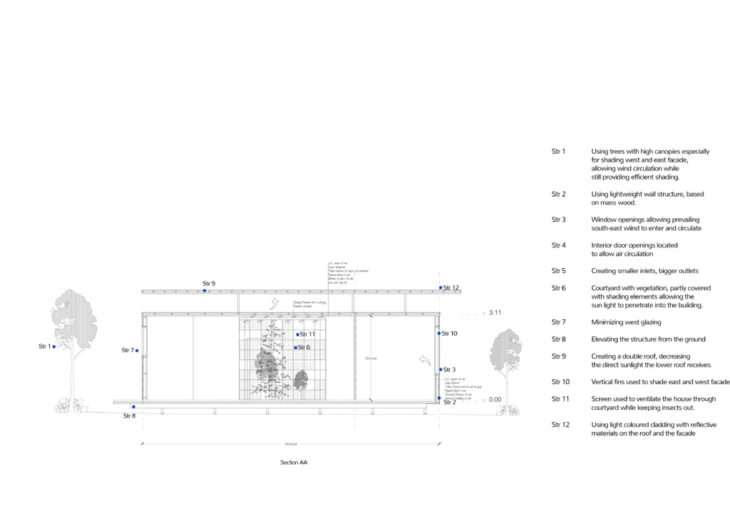
The house has a square floor plan with evenly distributed 2 bedrooms. The bedrooms were aimed to face east as much as possible, while the kitchen and living area received sunlight from the south, west, and through the courtyard. The key aspect of the house is the courtyard, creating a shaded area with vegetation, and allowing the hot air to escape through the openings in the roof.
While the north and south facades are protected from direct sunlight by the roof overhangs, the east and west walls are shaded with high canopied trees and vertical fins integrated into the windows. The windows and interior doors are located so that the prevailing wind from the north and the southeast can circulate through the building.

Section
The building is elevated from the ground to protect the wood from the humidity and to allow natural ventilation underneath. The northern-facing windows are shaded with horizontal shading elements that have four different settings.
The perimeter around the courtyard is covered with wood decking that has a sloped floor underneath, allowing any rainwater to flow towards the soil of the courtyard.
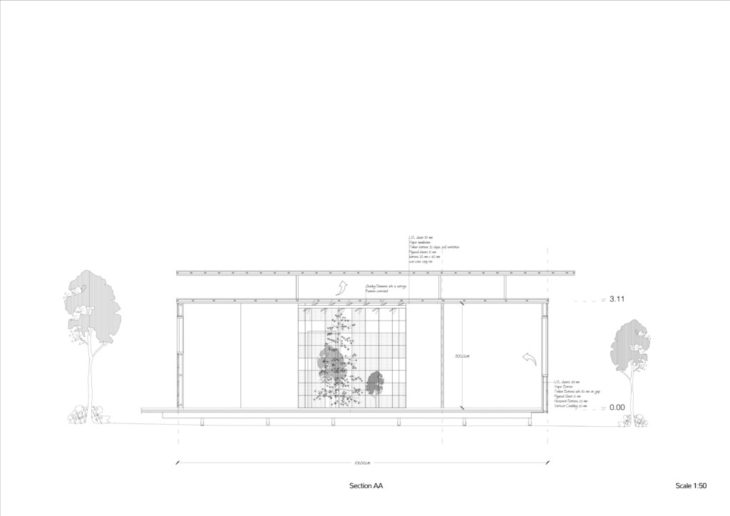
Section
The courtyard is surrounded by a screen, keeping the courtyard visible while stopping any insects from entering the house. The courtyard is also shaded with horizontal slabs that can be used in different angles. There is a double roof system that reduces the lower roofs solar gain, therefore, preventing the building from overheating.
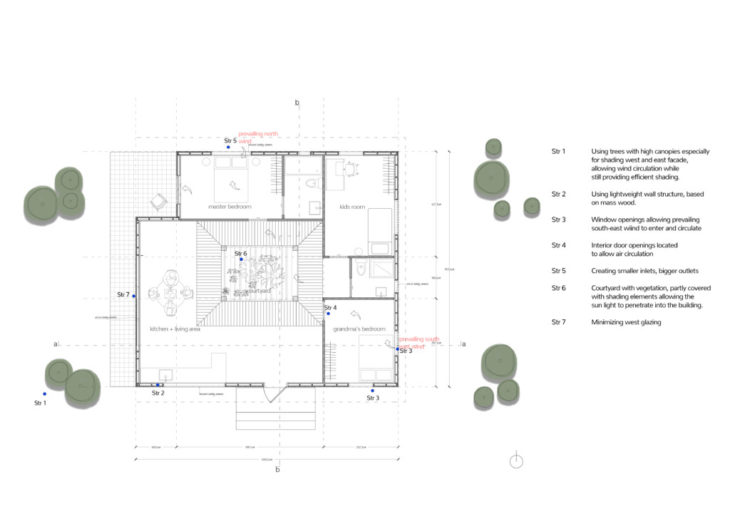
Design Strategies I
Design Strategies II
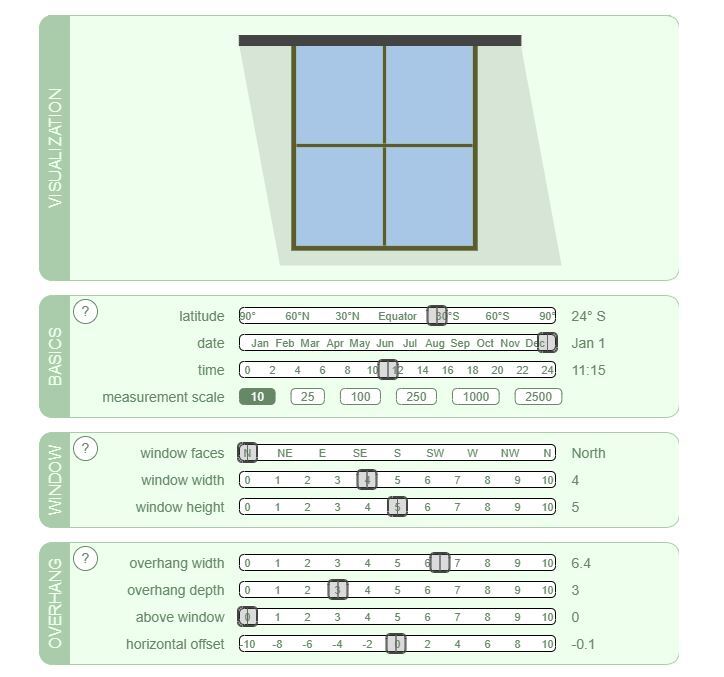
Calculations of the Overhangs
The horizontal shading elements were designed to have 4 different settings, adjustable to the angle and amount of sunlight that will be received.
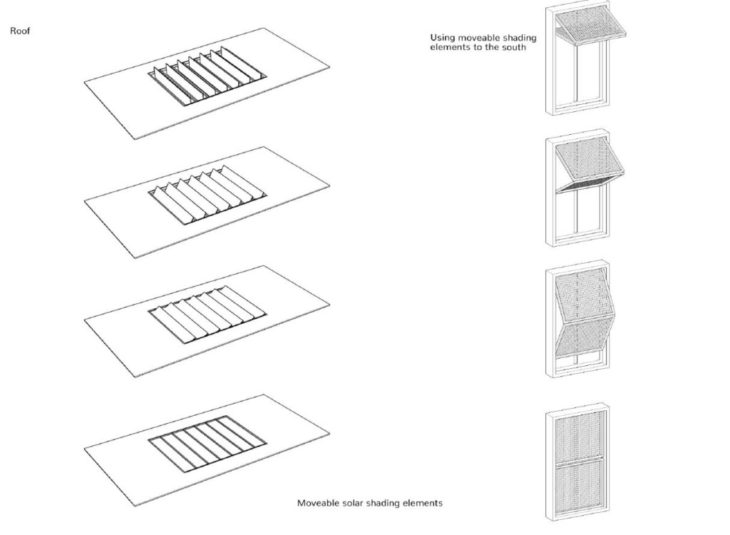
Shading Elements
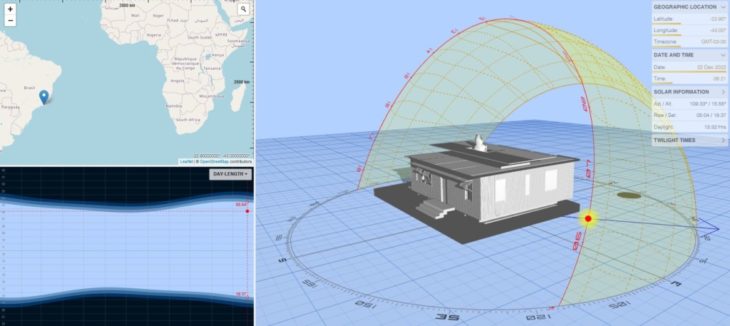
Sun Path 9 a.m.
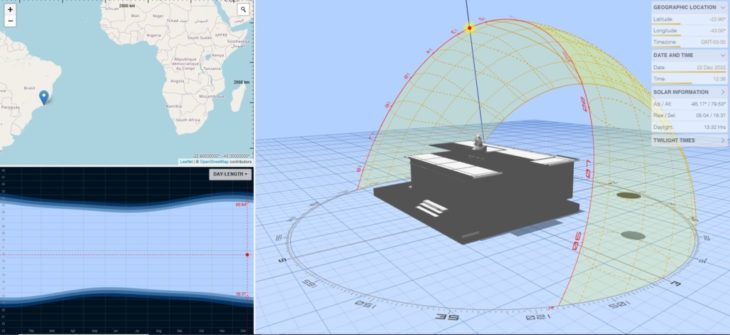
Sun Path 12 p.m.

Exterior Wall Detail
45 mm thick LVL panels are used in the exterior walls. Depending on the shading elements orientation (either vertical or horizontal) the wood cladding is also designed accordingly. Therefore, in the north and south facade the cladding runs horizontally and flush with the shading planks, and in the east and west, the cladding is done vertically.
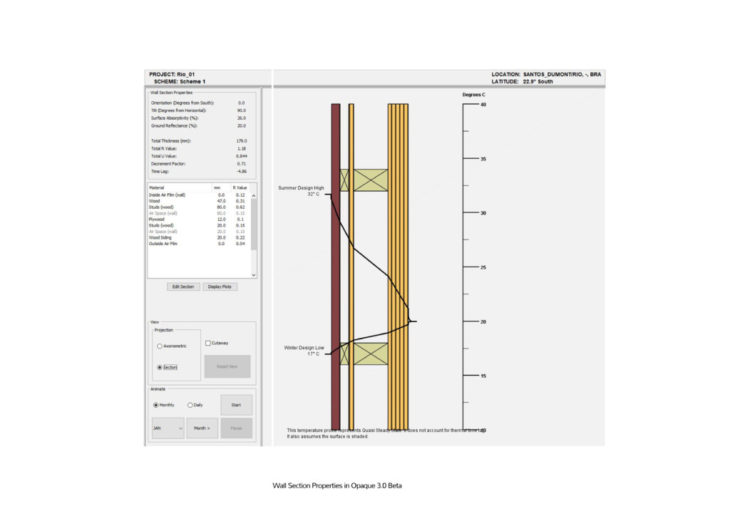
U Value Calculation
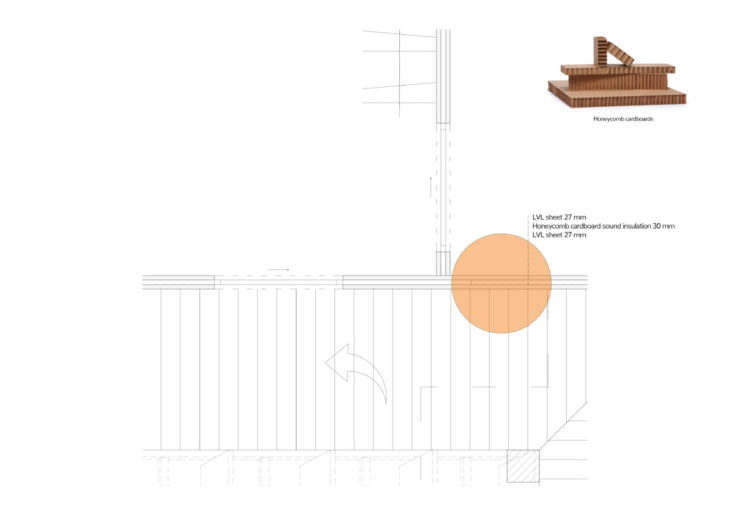
Interior Walls consist of 2, 27 mm thick LVL sheets with honeycomb cardboard insulation between, providing sound insulation.
The window overhangs in the south and west run through the facade as one single element. The upper roof extends beyond the lower roof towards the east to create shading.
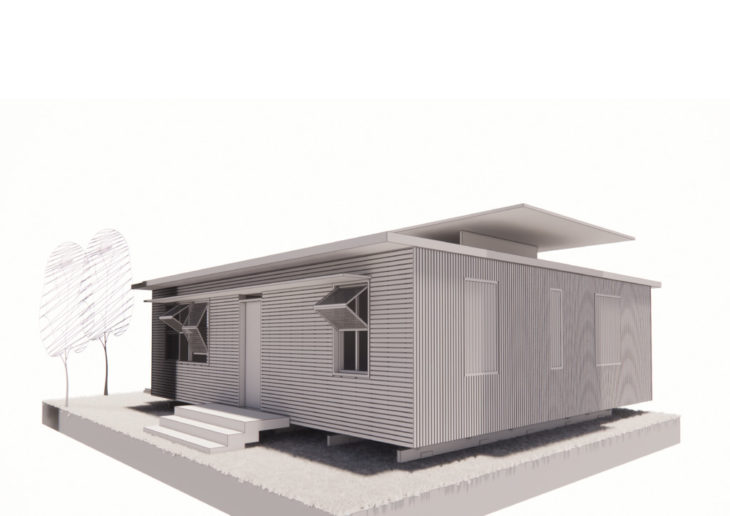

Exterior Image
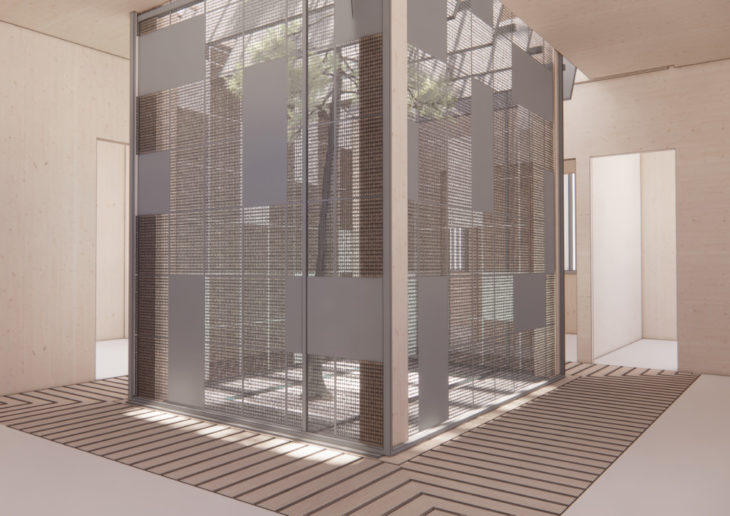

Interior Image
This 100 m² house located in Rio de Janeiro was designed to accommodate four people aiming to use the most efficient passive design strategies in order to create comfortable indoor conditions. By creating shaded outdoor areas such as a courtyard and a patio, allowing natural cross ventilation and mainly controlling the solar radiance via shading elements and vegetation, the intention was to meet this goal.
Mass Timber House in Rio de Janeiro is a project of IaaC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at Master in Mass Timber Design in 2021 by:
Students: Esin Aydemir, Suzane Kteich
Faculty: Patrick Spencer