
Gallery of Lightweight Structures: What They Are and What They Can Be – 6
Opportunity
With an interest in saving energy and reducing costs, I researched some information related to building energy consumption. It shows that buildings use about 30% of the world’s energy and in Europe, 40% of the total primary energy used is in buildings. Two thirds of the energy consumption in buildings can be used by heating and cooling, and between 25 – 35% of electricity costs result from the use of artificial light.

The shading can drastically reduce the need for active cooling and, through the optimization of daylight, also impacts on the use of artificial lighting. Studies have shown that the use of dynamic solar shading can reduce energy costs for cooling and heating in buildings by up to 70%. The EPBD (European Performance Building Directive) recommends the use of dynamic solar shading as an energy-efficient solution.
Market & Validation
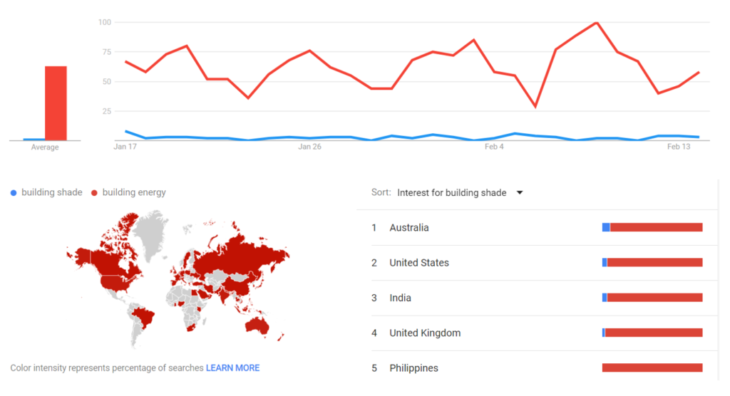
Based on all the data we have on the Internet, we can confirm that there is a huge market for building shading and energy.Google trends shows the considered of building shade and building energy in the worldwide.
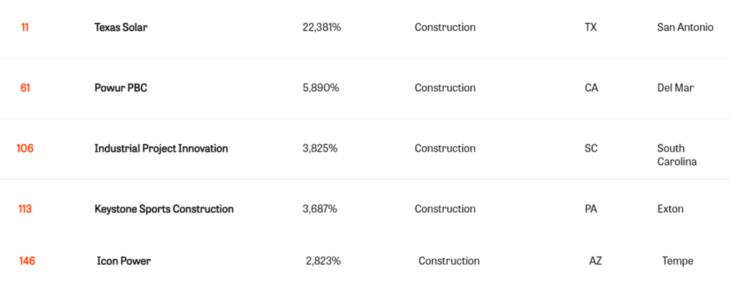
2021 Fastest-Growing Private Companies in America shows that in the top 5 companies of construction, 3 of them are related to solar and energy.
Analysis
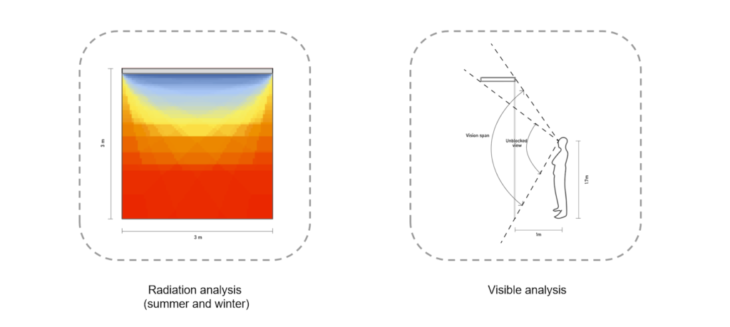
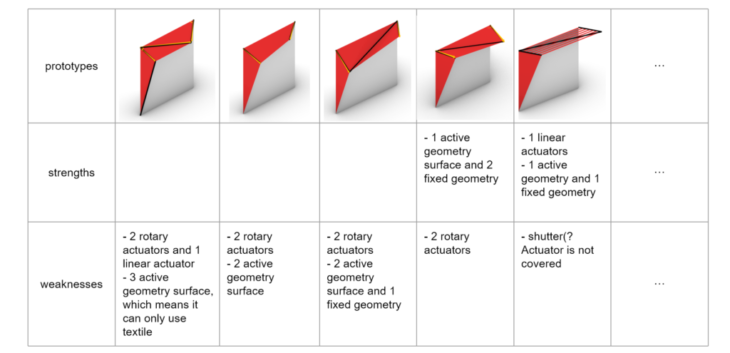
In order to study the various shading devices available, I classified them according to fixed and active, as well as different geometries. I made a list to show their name, architect, location, height, shading geometry, shading size, material and transparency. And analysis them with a 3*3m south facade, test the radiation with and without shading in summer and winter, and also test how much view is blocked.

Solution
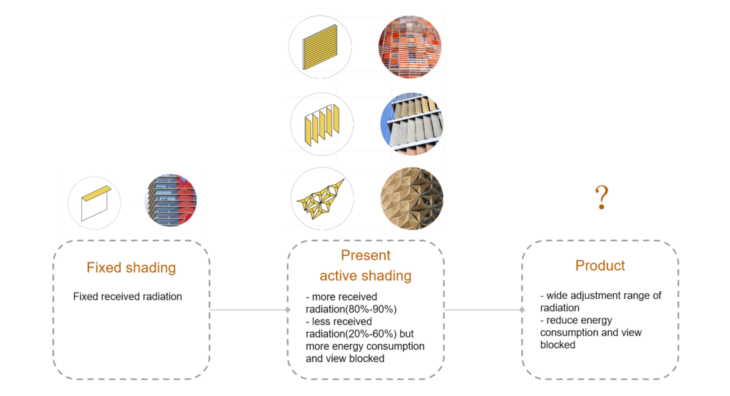
Through analysis, we can find that both fixed sunshade and existing active sunshade still have certain limitations:
- Fixed shading devices: have only fixed received radiation.
- Present active shading devices: some of them have more received radiation(80%-90%) and ome of them have less received radiation(20%-60%) but more energy consumption and view blocked.
comparing with these shading, my target is to have product which can have a wide adjustment range of radiation and can reduce energy consumption and view blocked.
Now I’m working on the prototypes to test how to make a lightweight structure active with less actuators, and try to add solar panels on the facade to provide energe for the shading systems. Collectively, these initiatives are expected to reduce energy consumption by 30-50%.

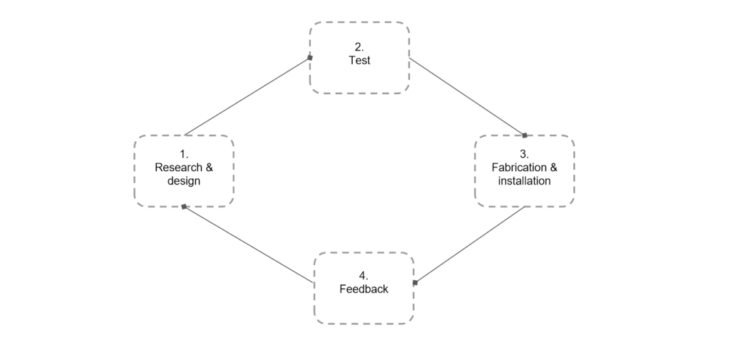
Implementation
The process start with research and design, then go to test the radiation, energy consumption and other parameters. Thirdly, the next step after the product is determined is mass production, put into the market, get feedback and then turn back to the research and upgrade the product.
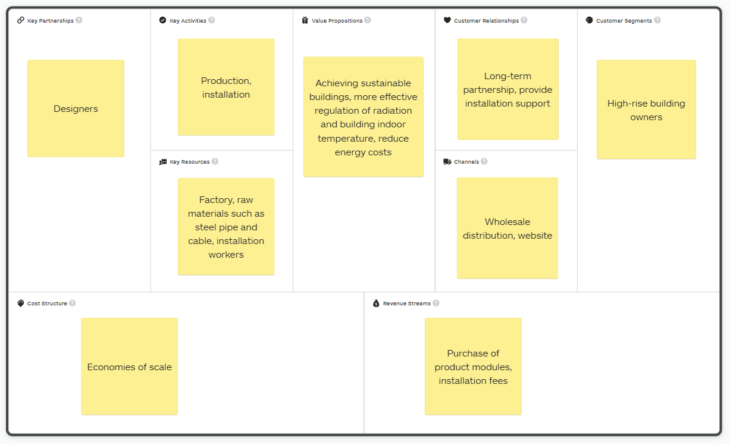
Business Model Canvas
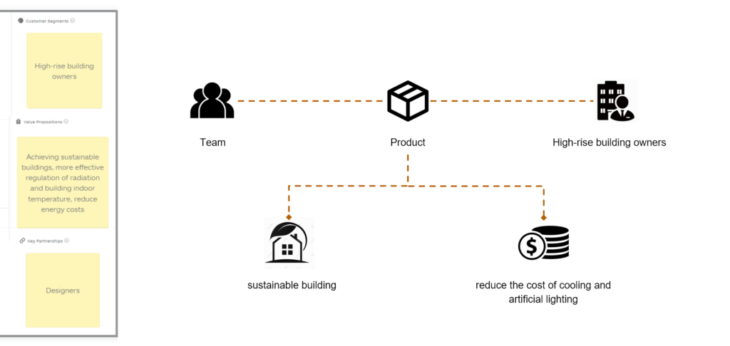
Customer & Value Proposition
Our target customers are high-rise building owners. With our product, the building owners can achieve sustainable buildings, more effective regulation of radiation and building indoor temperature, and reduce their energy costs.
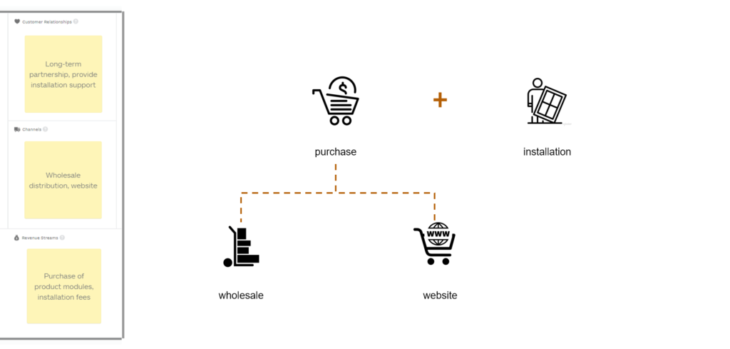
Customer Relationship & Channels
It can be a long-term partnership with our customers through wholesale and online sales.
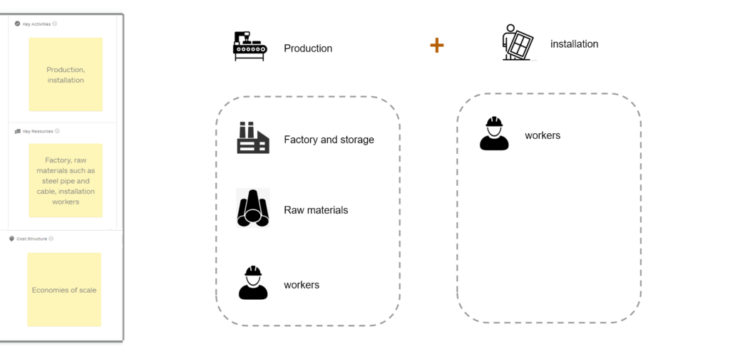
Key Activities & Key Resources
Our key activities are production and installation. To accomplish these two steps, we need factories, raw materials such as steel pipe and cable, installation workers.
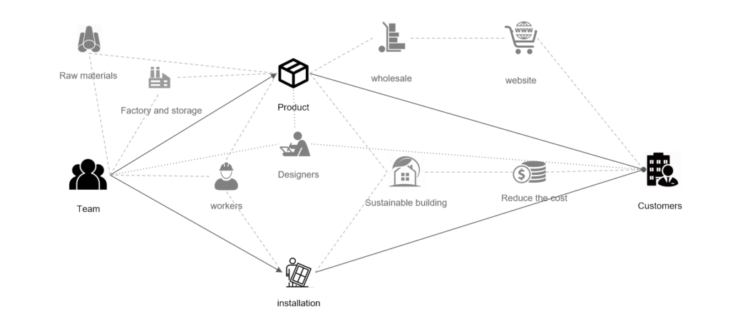
Final Diagram
Lightweight Active Shading is a project of IAAC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at MAA02, Business Innovation in 2022 by Student: Jiaqi Sun. Faculty : Davide Rovera