GREEN SQUARE ENVIRONMENTAL ANALYSIS
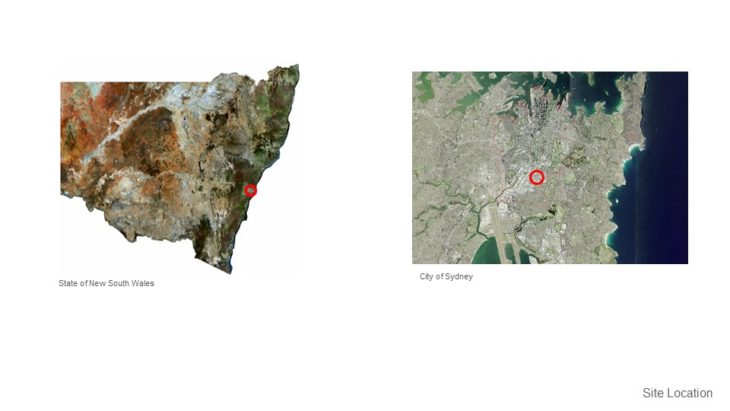
SITE DATA AND ANALYSIS – GREEN SQUARE, SYDNEY, NEW SOUTH WALES, AUSTRALIA
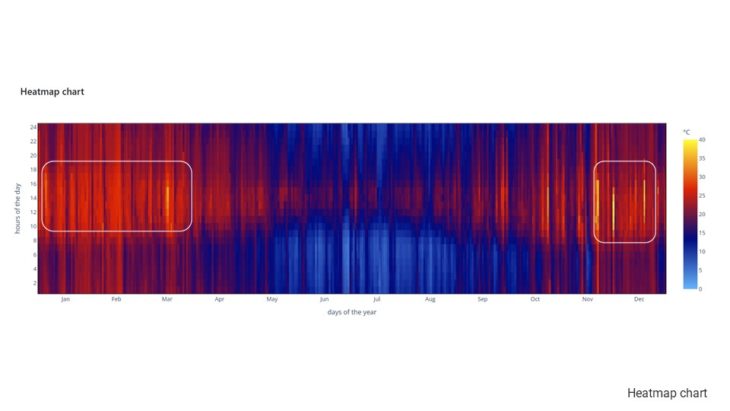
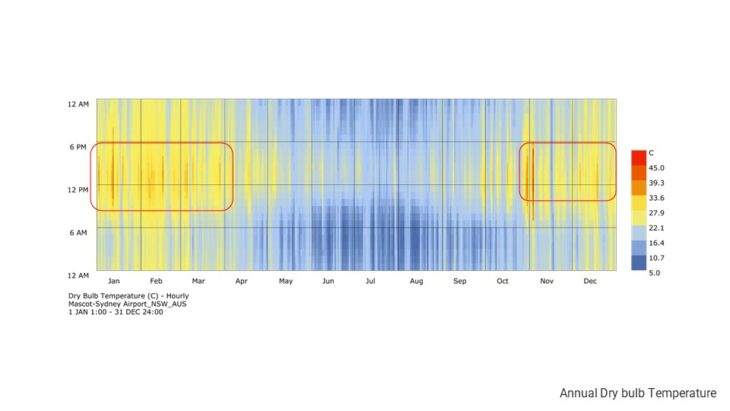
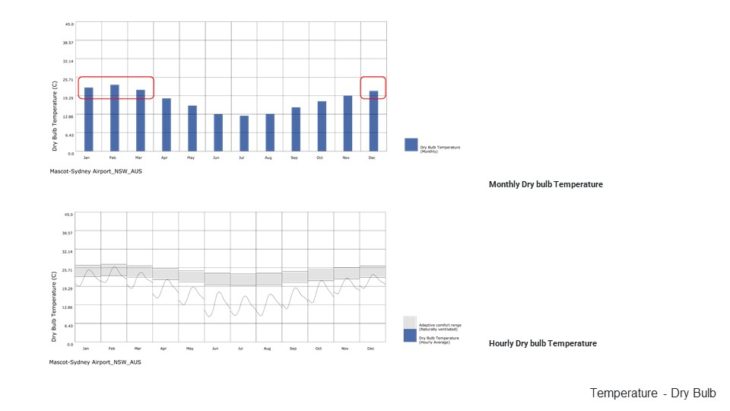
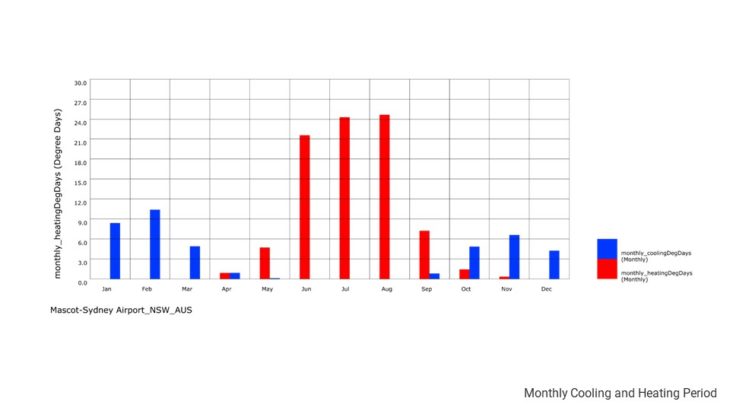
The climate of Sydney is humid subtropical, shifting from mild and cool in winter to warm and hot in the summer, with no extreme seasonal differences as the weather is moderated by proximity to the ocean, although more contrasting temperatures are recorded in the inland western suburbs. Despite the fact that there is no distinct dry or wet season, rainfall peaks in the first few months of the year and is at its lowest just around the middle of the year, though precipitation can be erratic throughout the year
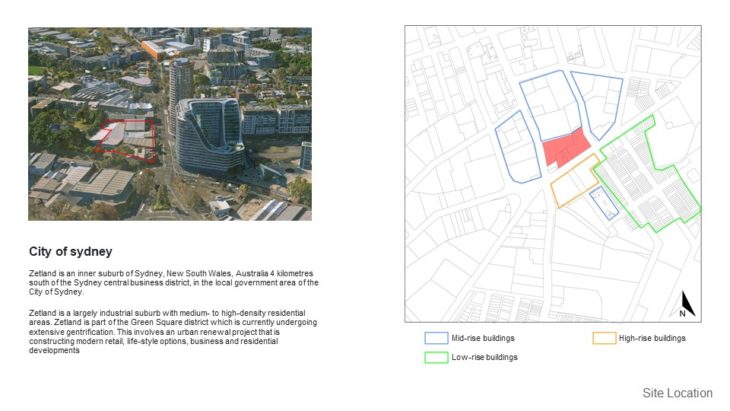
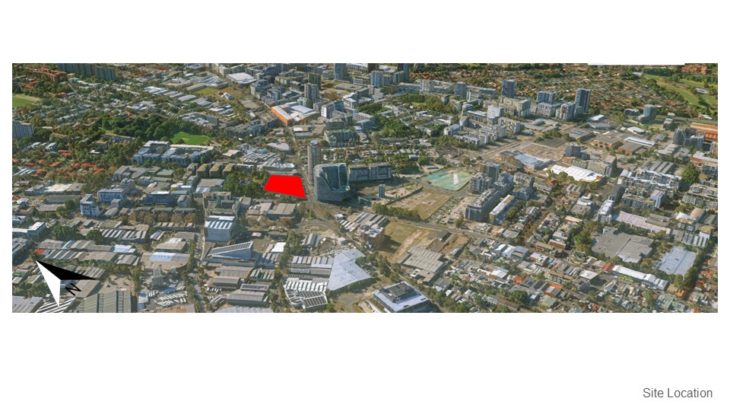
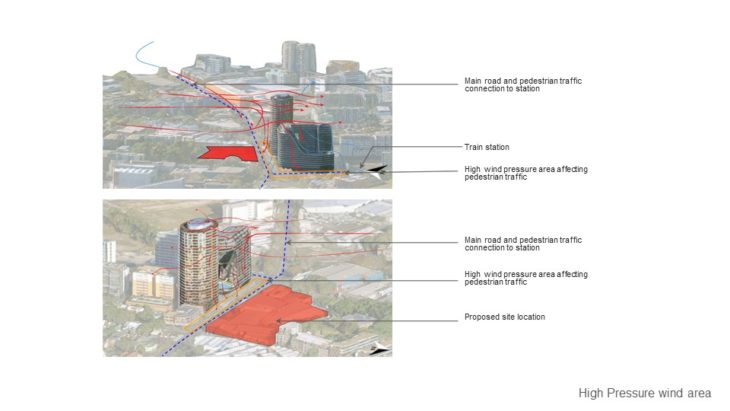
Zetland is an inner suburb of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia 4 kilometres south of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the City of Sydney. Zetland is a largely industrial suburb with medium- to high-density residential areas. Zetland is part of the Green Square district which is currently undergoing extensive gentrification. This involves an urban renewal project that is constructing modern retail, life-style options, business and residential developments

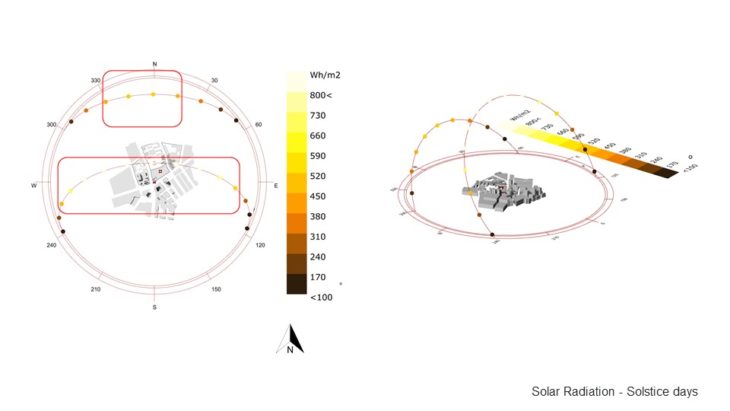
SITE SOLAR RADIATION ANALYSIS
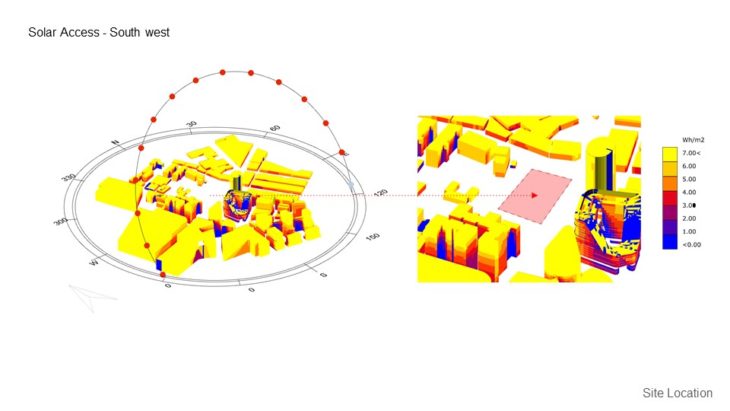
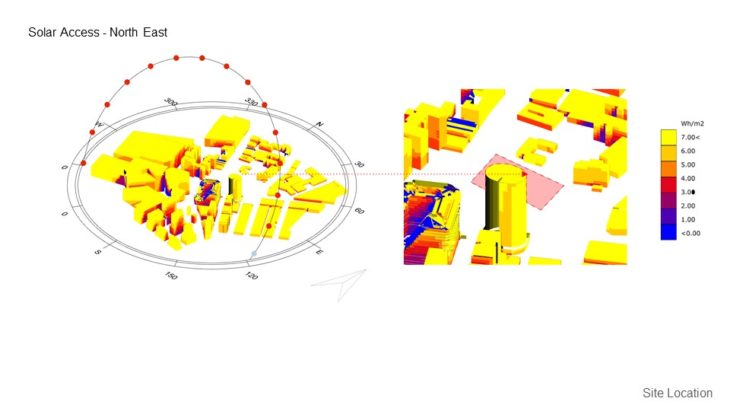
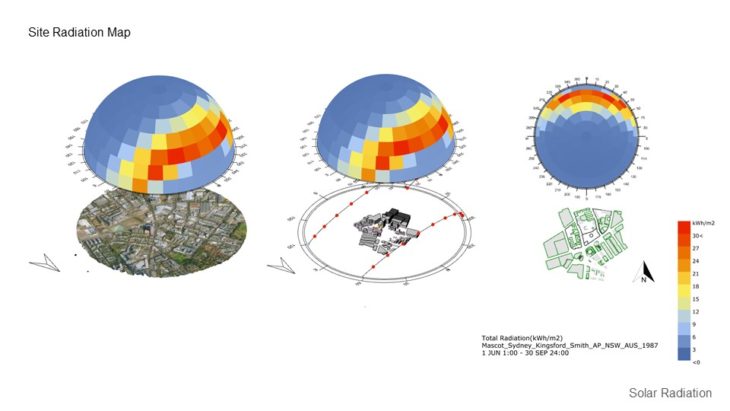
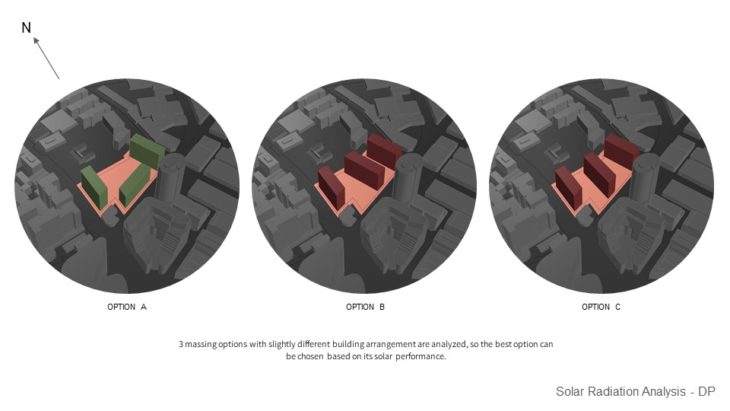
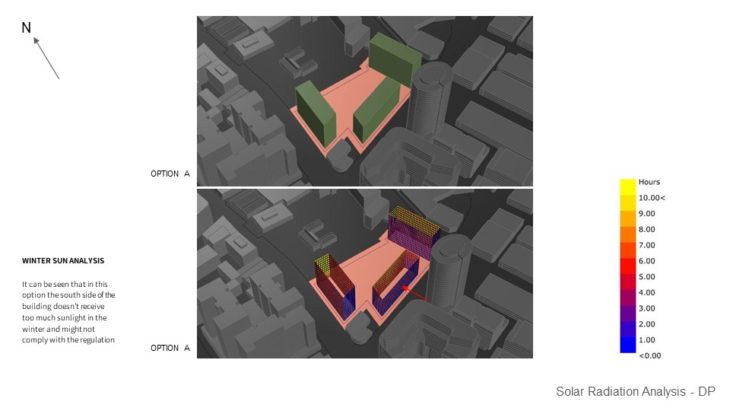
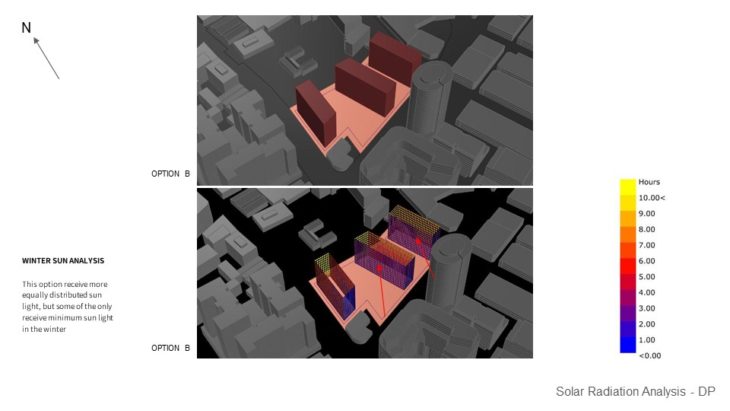
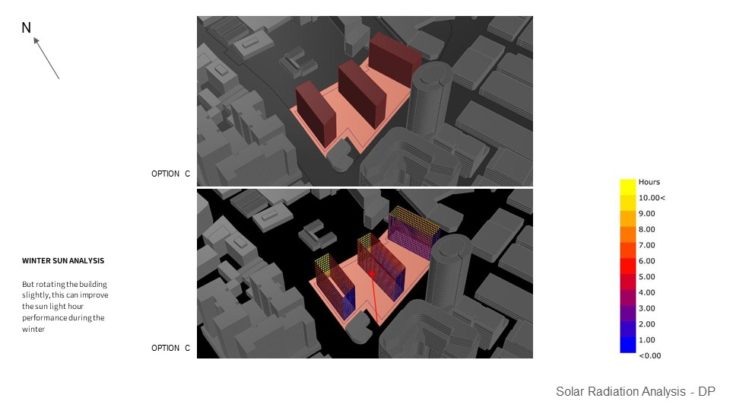
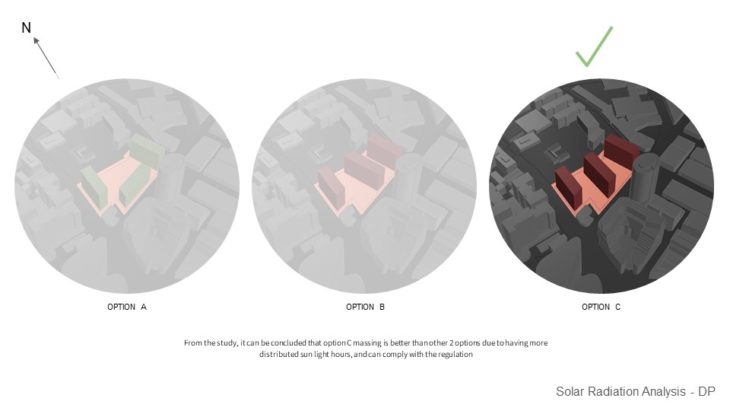
MASSING STUDY – SUNLIGHT HOUR ANALYSIS IN HEATING PERIOD / WINTER
For this study, 3 massing options with slightly different building arrangements are analyzed, so the best option can be chosen based on its solar performance. It can be seen that in option A, the south side of the building doesn’t receive too much sunlight in the winter and might not comply with the regulation. Option B massing receives more equally distributed sunlight, but some of them only receive minimum sunlight in the winter. But by rotating the building slightly ( option C ), can improve the sunlight hour performance during the winter. From the study, it can be concluded that option C massing is better than other 2 options due to having more distributed sunlight hours, and can comply with the regulation.

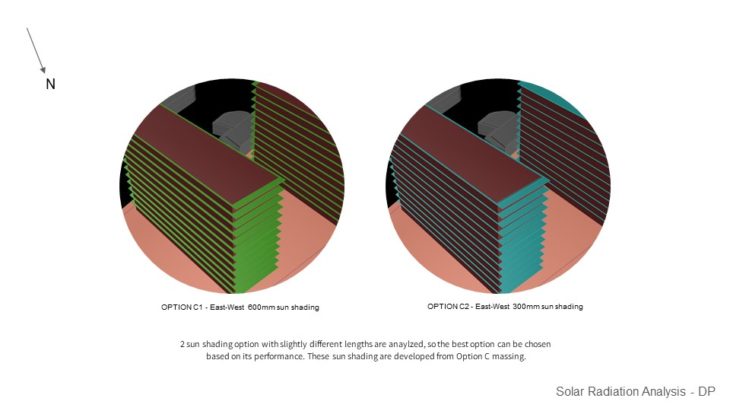
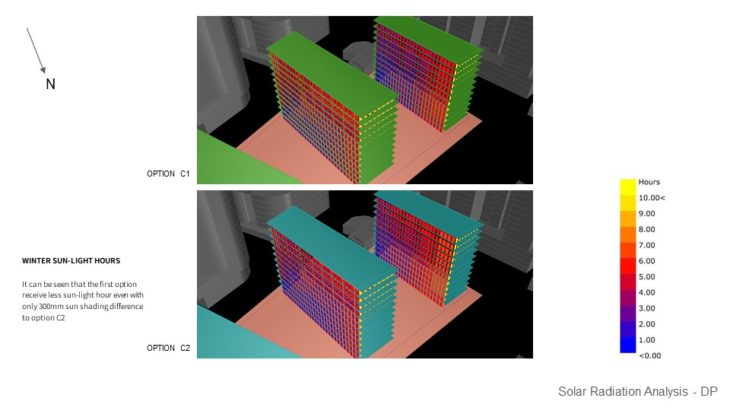
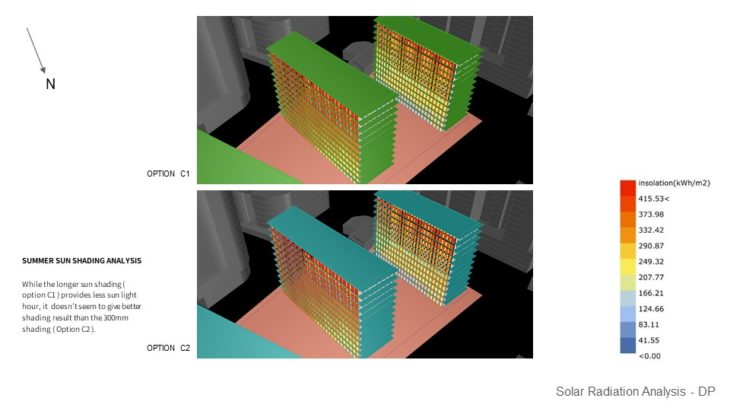
SHADING DEVICE STUDY – WINTER SUNLIGHT HOUR ANALYSIS VS SUMMER RADIATION ANALYSIS
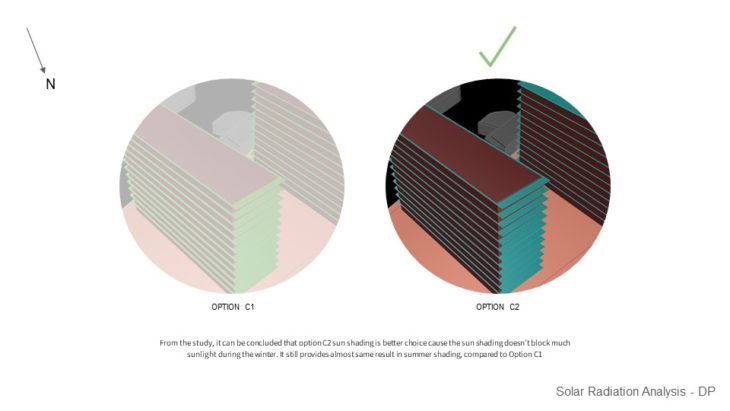
For this study, 2 sun shading options with slightly different lengths are analyzed, so the best option can be chosen based on its performance. These sun shading are developed from Option C massing. It can be seen that the first option receives less sun-light hour even with only 300mm sun shading difference to option C2. While the longer sun shading ( option C1 ) provides less sunlight hour, it doesn’t seem to give better shading results than the 300mm shading ( Option C2 ). From the study, it can be concluded that option C2 sun shading is a better choice because the sun shading doesn’t block much sunlight during the winter. It still provides almost the same result in summer shading, compared to Option C1.
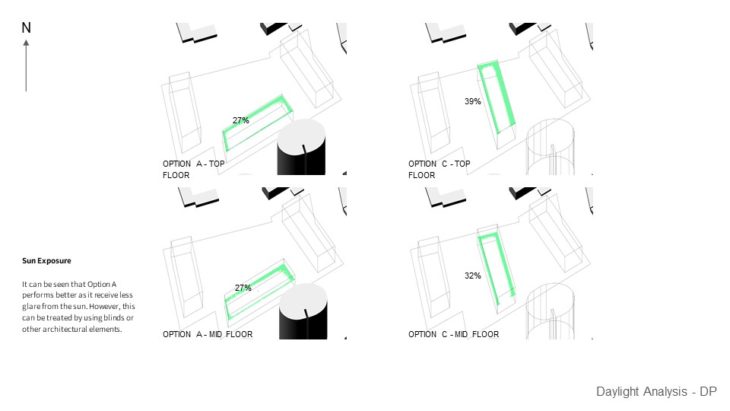
DAYLIGHT ANALYSIS
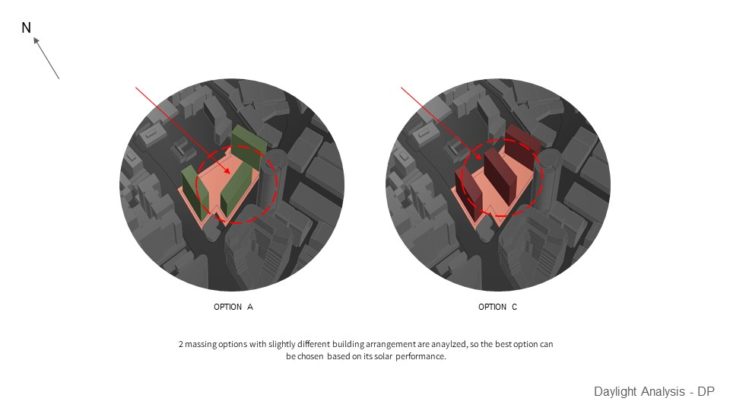
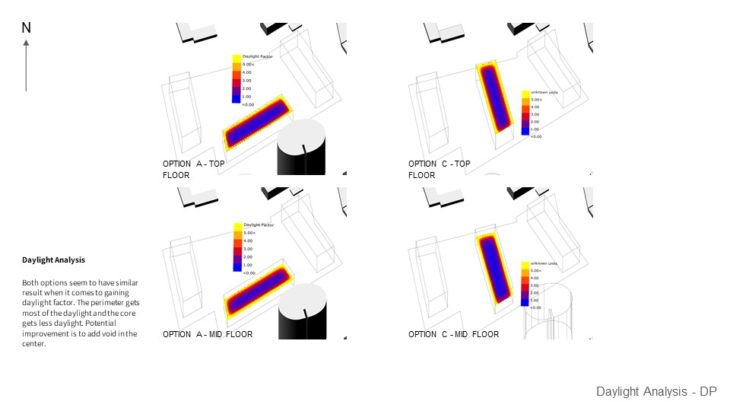
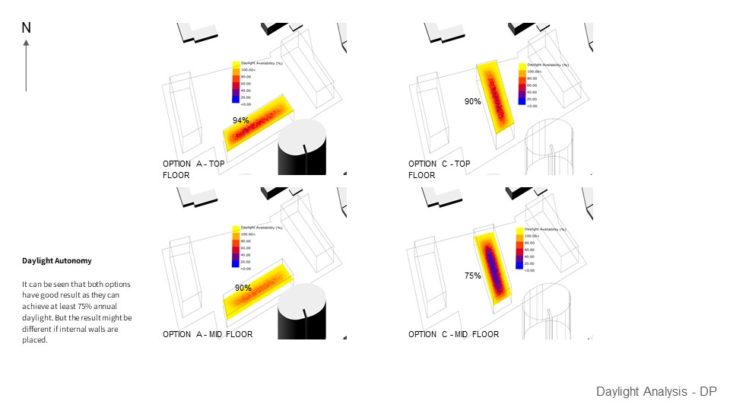
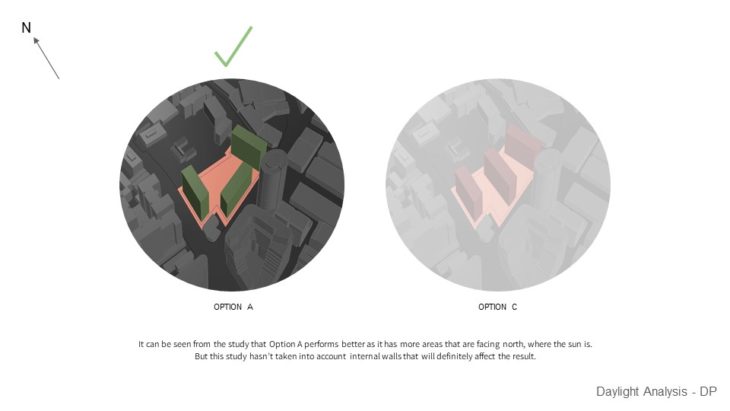
For this study, 2 massing options with slightly different building arrangements are analyzed, so the best option can be chosen based on its solar performance. Both options seem to have similar results when it comes to gaining daylight factor. The perimeter gets most of the daylight and the core gets less daylight. Potential improvement is to add void in the center. And when daylight autonomy was analyzed, It can be seen that both options have good results as they can achieve at least 75% annual daylight. But the result might be different if internal walls are placed. When it comes to Sun exposure, It can be seen that Option A performs better as it receives less glare from the sun. However, this can be treated by using blinds or other architectural elements. It can be seen from the study that Option A performs better as it has more areas that are facing north, where the sun is. But this study hasn’t taken into account internal walls that will definitely affect the result.
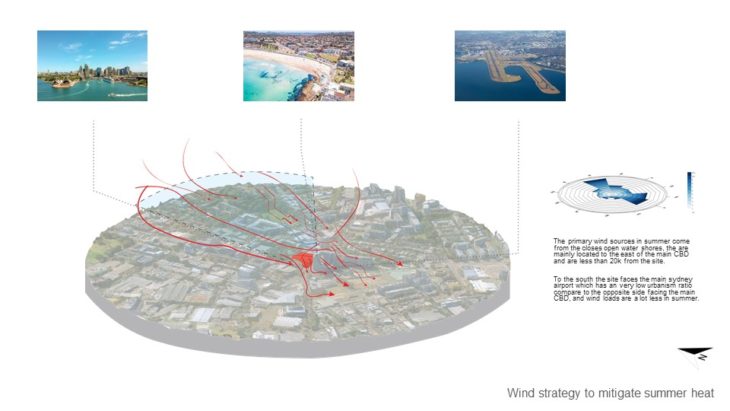
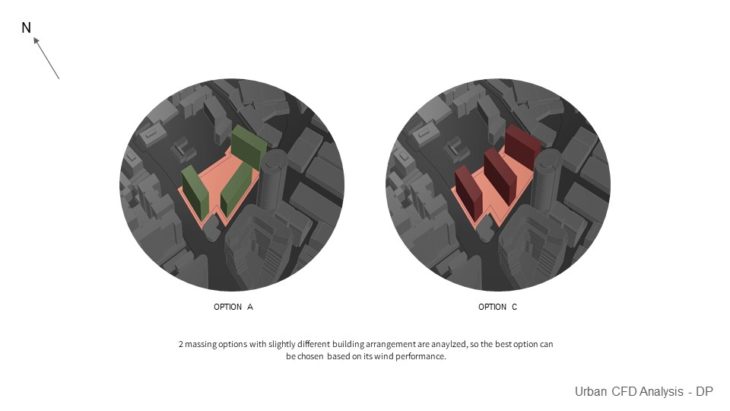
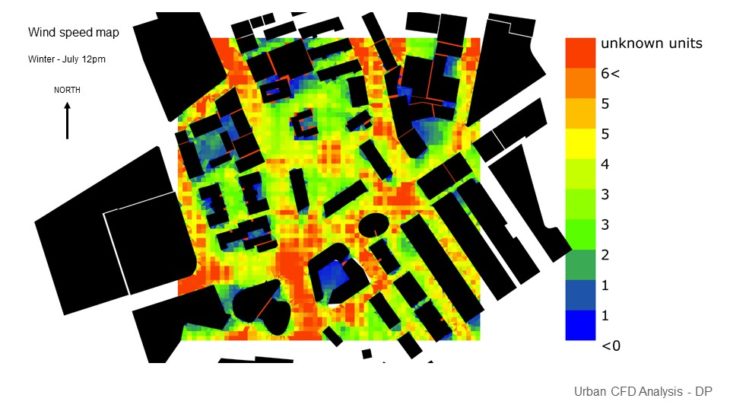
URBAN CFD ANALYSIS
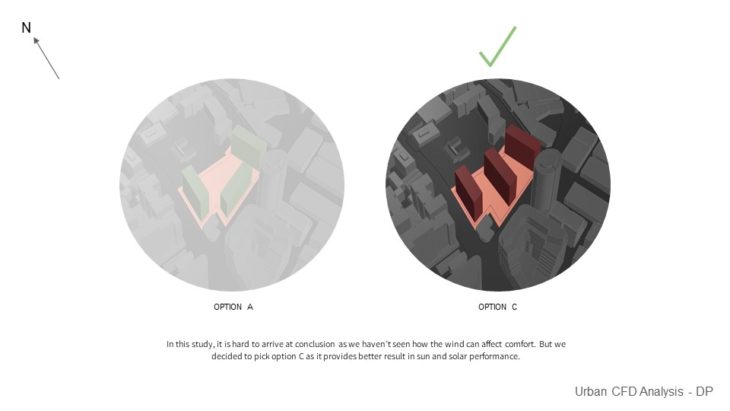
For this study, 2 massing options with slightly different building arrangements are analyzed, so the best option can be chosen based on its wind performance. In this study, it is hard to arrive at a conclusion as we haven’t seen how the wind can affect comfort. But we decided to pick option C as it provides better results in sun and solar performance.
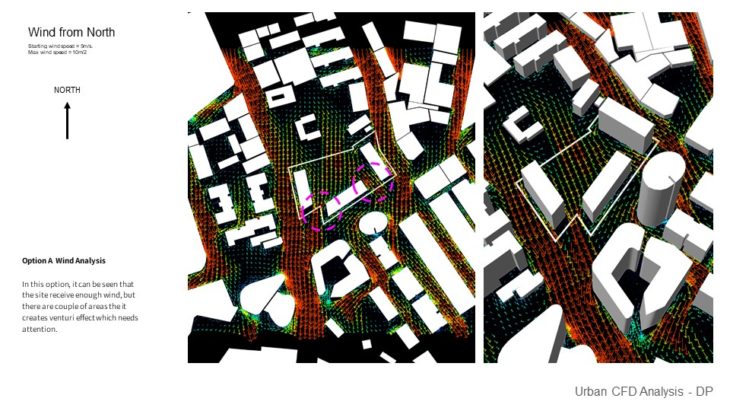
Option A Wind Analysis – In this option, it can be seen that the site receives enough wind, but there are a couple of areas where it creates a Venturi effect which needs attention.
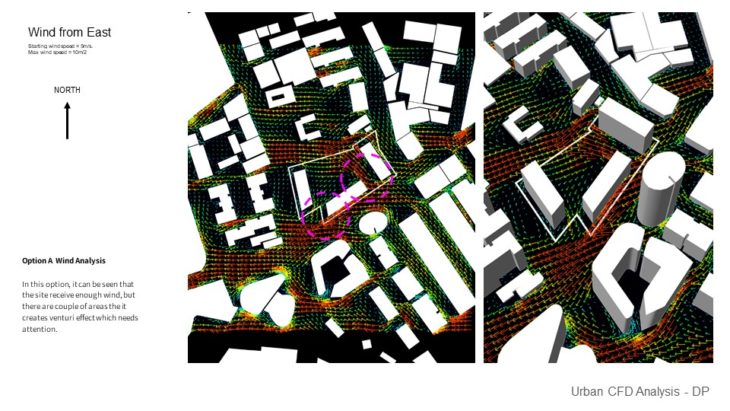
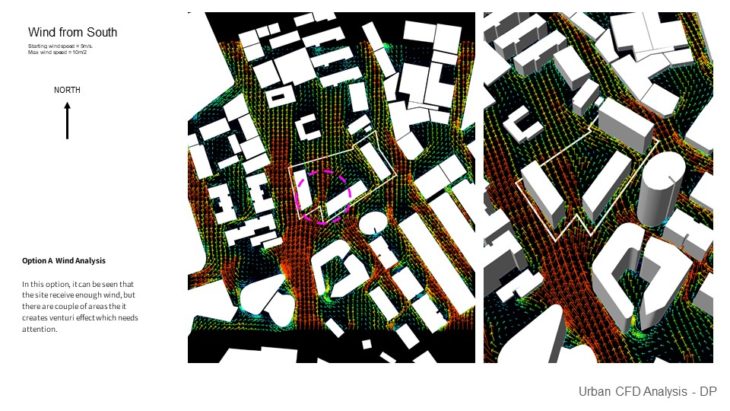
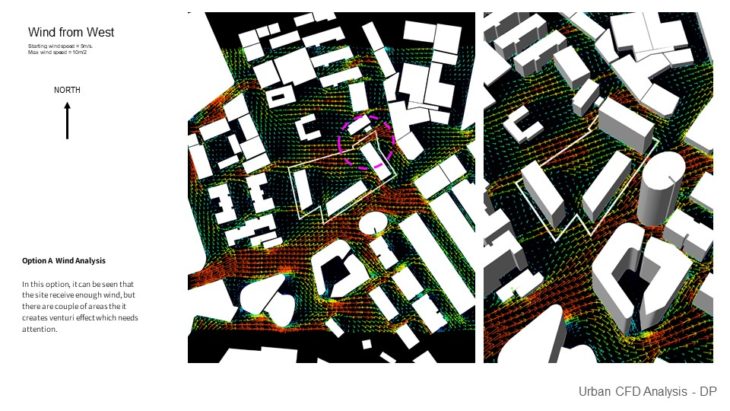
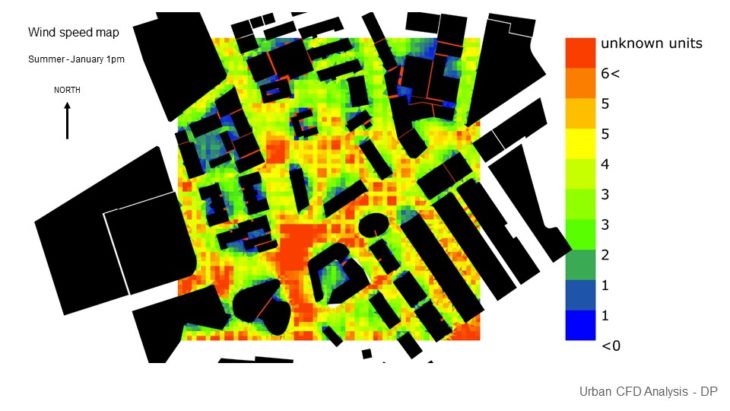
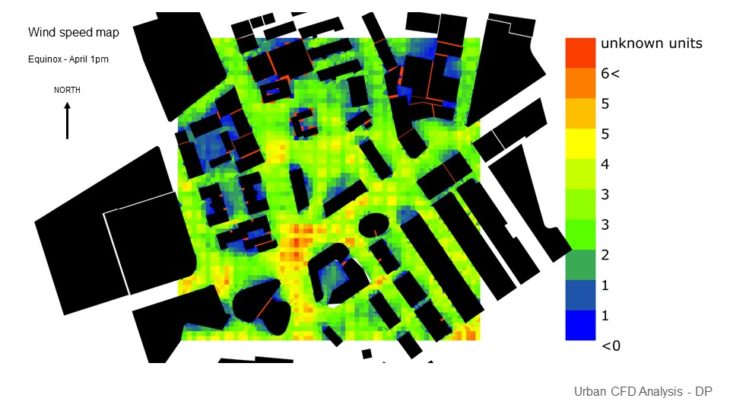
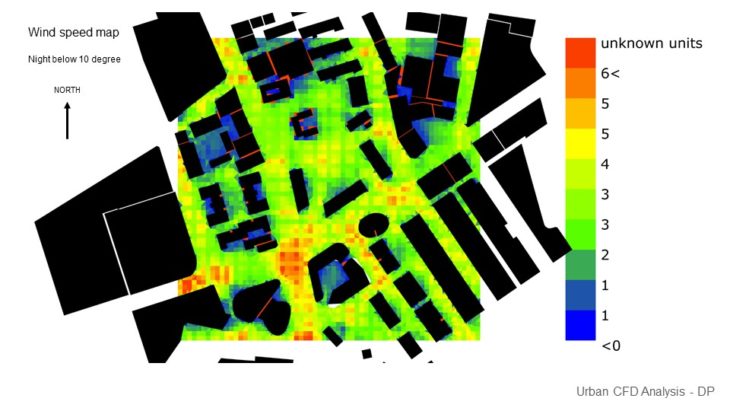
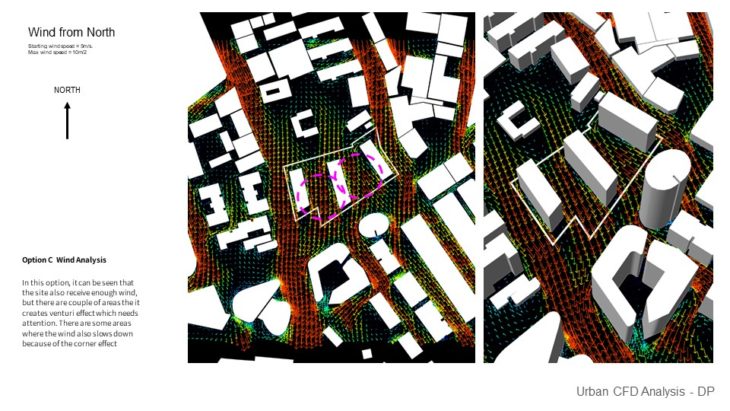
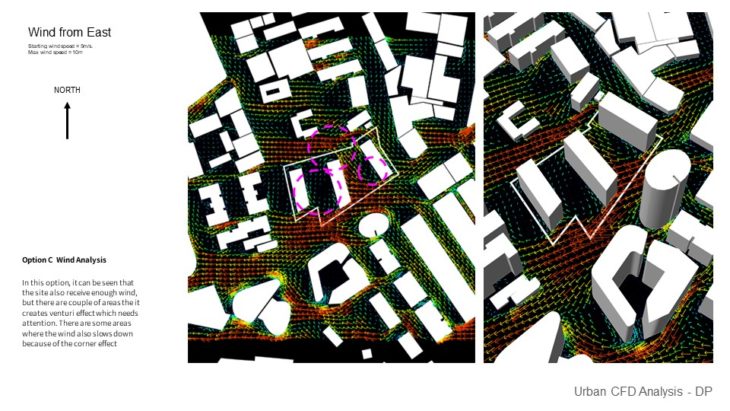
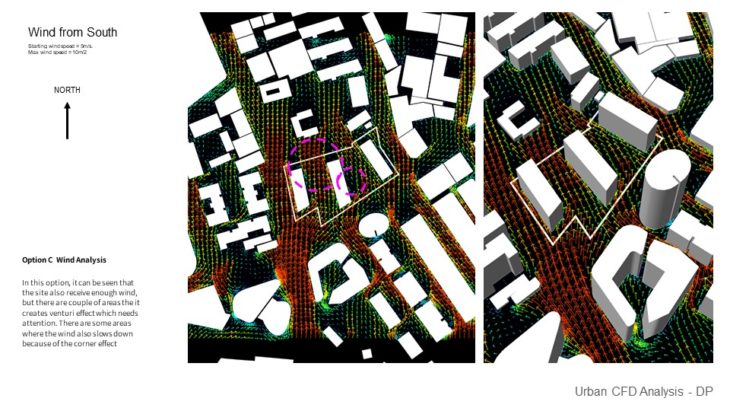
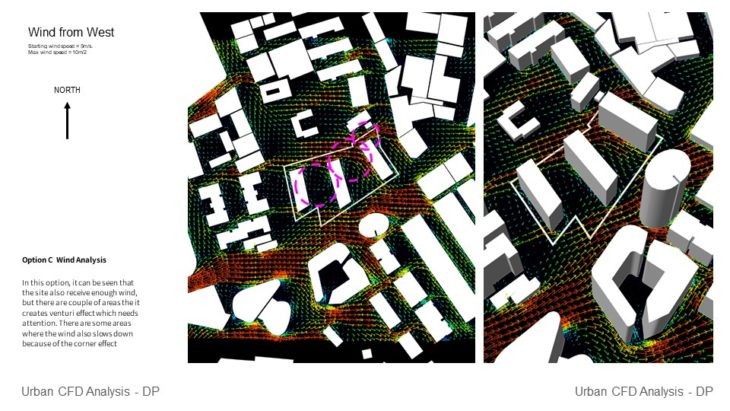
Option C Wind Analysis – In this option, it can be seen that the site also receives enough wind, but there are a couple of areas that it creates a Venturi effect which needs attention. There are some areas where the wind also slows down because of the corner effect
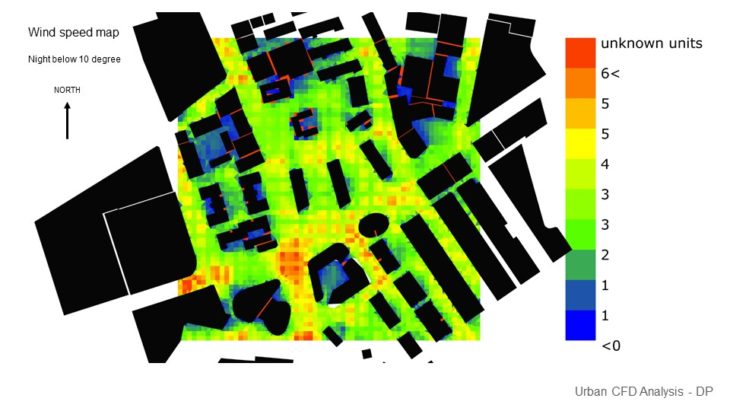
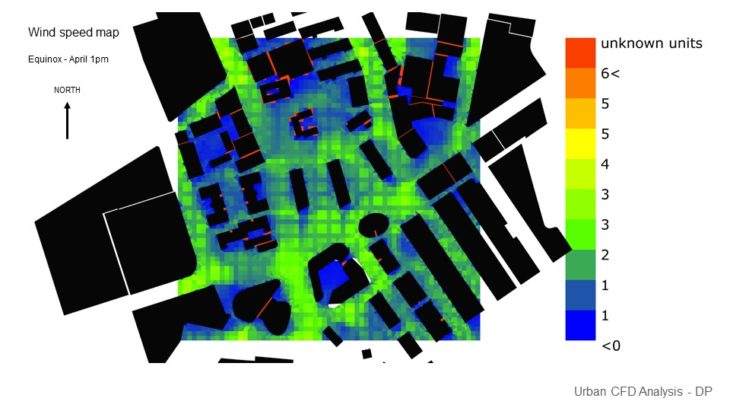
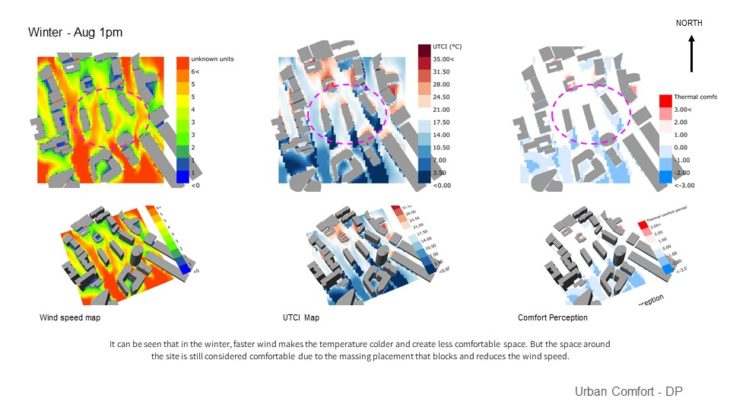
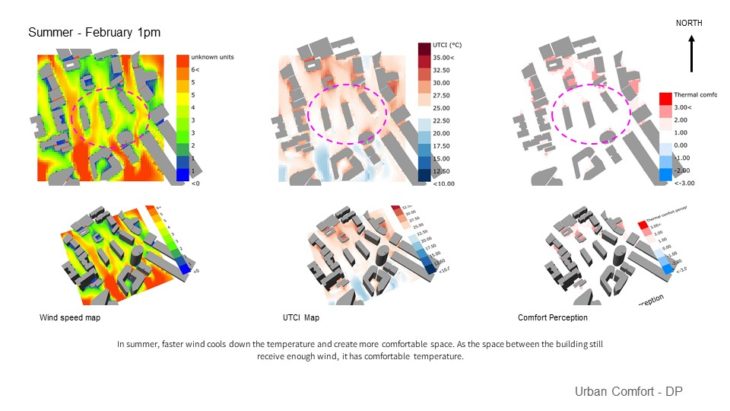
URBAN THERMAL COMFORT
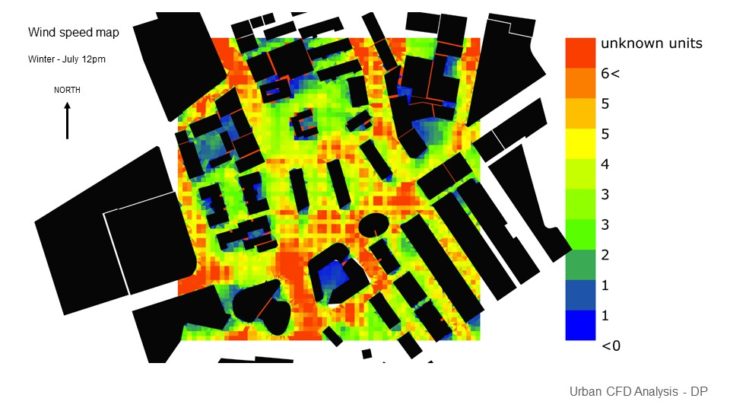
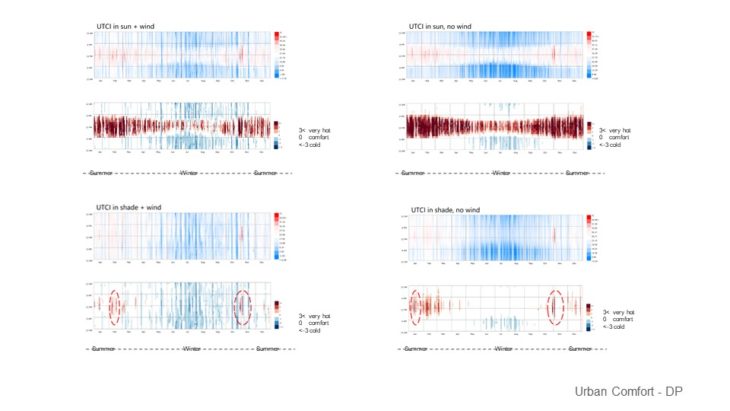
At this stage, only 1 massing option is analyzed and developed further as a previous study showed that this massing has better performance than other options. It can be seen that in the winter, faster wind makes the temperature colder and creates less comfortable space. But the space around the site is still considered comfortable due to the massing placement that blocks and reduces the wind speed. In summer, faster wind cools down the temperature and creates more comfortable space. As the space between the buildings still receives enough wind, it has a comfortable temperature.

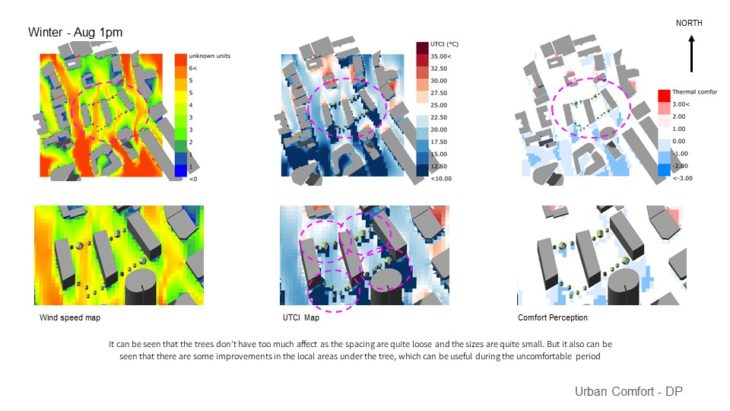
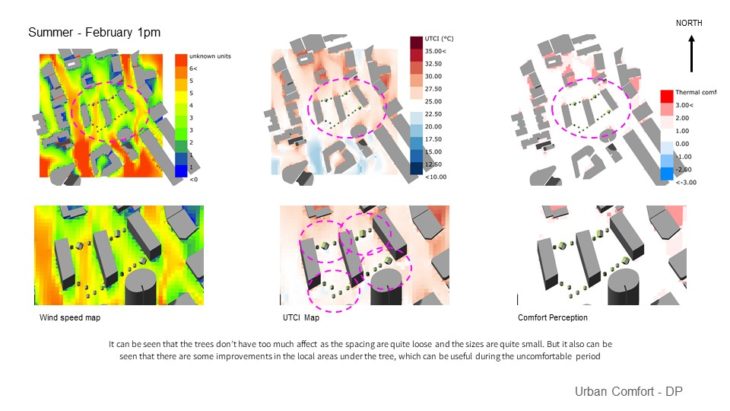
Landscape Optimization – For this study, landscape elements are added to optimize the micro climate control. It can be seen that the trees don’t have too much effect as the spacing is quite loose and the sizes are quite small. But it also can be seen that there are some improvements in the local areas under the tree, which can be useful during the uncomfortable period. It can be seen that the trees don’t have too much effect as the spacing is quite loose and the sizes are quite small. But it also can be seen that there are some improvements in the local areas under the tree, which can be useful during the uncomfortable period. It is also important to note that local areas under the tree can be quite cold during the winter, so it is critical that tree selection is considered carefully to ensure it allows sunlight to penetrate in the summer, for example, selecting trees that the leaves can fall.
INFRARED ANALYSIS
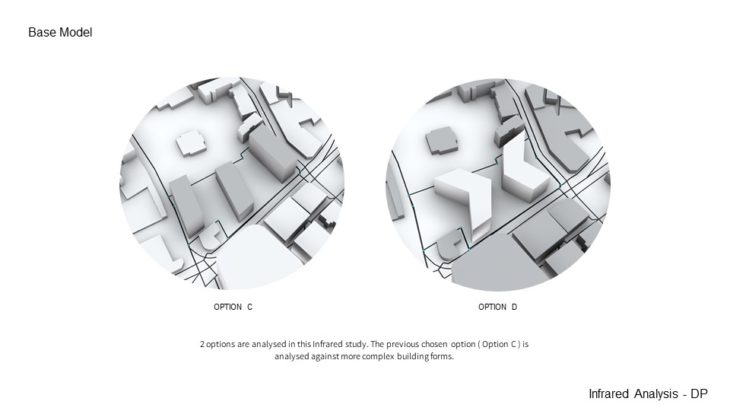
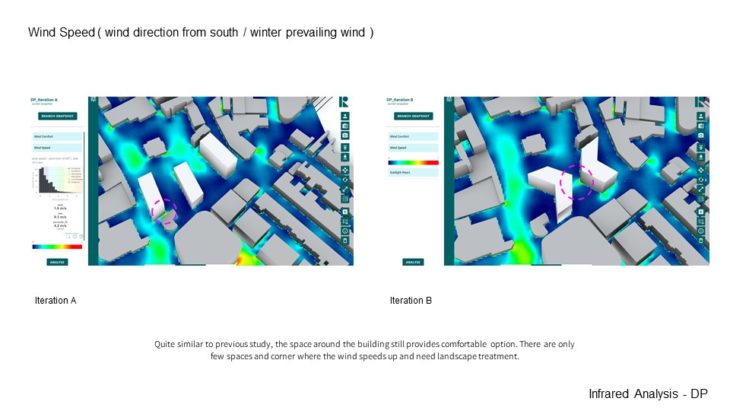
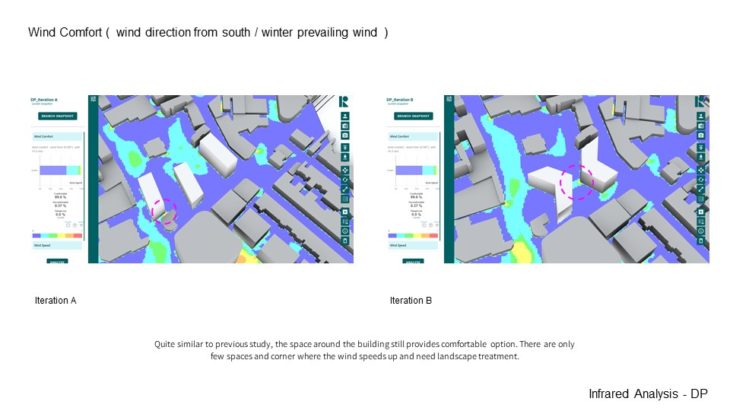
2 options are analysed in this Infrared study. The previous chosen option ( Option C ) is analysed against more complex building forms. Quite similar to the previous study, the space around the building still provides a comfortable option. There are only a few spaces and corners where the wind speeds up and needs landscape treatment. And when it comes to sunlight hour analysis, It can be seen that those around the site receive enough sun-light and shading. There are only some spaces that receive too little sun-light.

TAKEAWAYS
Sydney’s climate in general is quite favourable. The temperature almost never gets below 0 degrees in the winter, which makes the city very liveable. There are only some periods where the temperature can get above 40 degrees in the summer. From the study it can be seen that wind, especially breeze, can help cool down temperature and increase the comfort level. This can be done by placing trees in the arrangement of the building blocks.
Building orientation and openings are always better to face north to reduce the necessity of cooling in the summer. When the building has internal corridors like residential, east-west facing can be considered, but the opening should have treatment against east and west sun, and it should have enough space in front of it to ensure the opening can catch north sun as well.
Credits
Green Square Environmental Analysis is a project of IaaC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia
developed at Master in Advanced Computation for Architecture and Design in (2021/2022) by:
Students: Danna Priyatna, Alexander Lopez
Faculties: Angelos Chronis, Aris Vartholomaios, Hager El-Sokaily
