Freeform distinction explores a method of appropriate clustering of a series of freeform structures in order to cluster these surfaces in similar batches that can be systematically and efficiently fabricated or mass produced.
Freeform distinction is a part of the computational analysis process in METAform, a project of IAAC, Insitute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed in the Masters in Advanced Architecture 02 2019/20 by Student: Ankita Alessandra Bob, Faculty: Areti Markopoulou and Faculty Assistants: Nikol Kirova and Eduardo Chamorro Martin.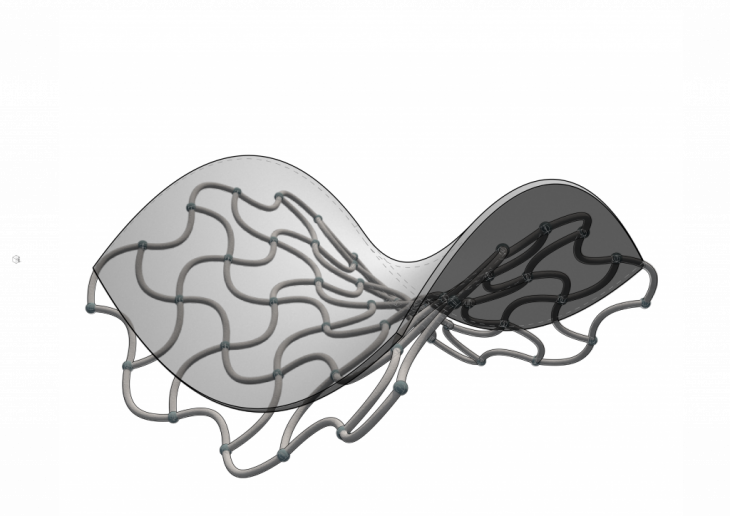
METAform is a component based system that uses reconfigurable formworks to produce a variety of freeform structures. The computational analysis determines the number and size of components needed for the formwork of the target surface, simultaneously optimizing it for least time and cost of production and maximum structural efficiency. This information is given to the fabrication stage so as to efficiently produce the required formwork through a systematic fabrication protocol.
Freeform Distinction uses a Machine Learning algorithm develepoed on OWL – A plug in developed by Mateusz Zwierzycki in order to cluster a variety of surfaces into existing fabrication protocols determined by the above shown algorithm.
Freeform structures or surfaces can be split into categories based on
SHAPE:
- High curvature
- Medium curvature
- Low curvature
and
SIZE:
- Big
- Medium
- Small
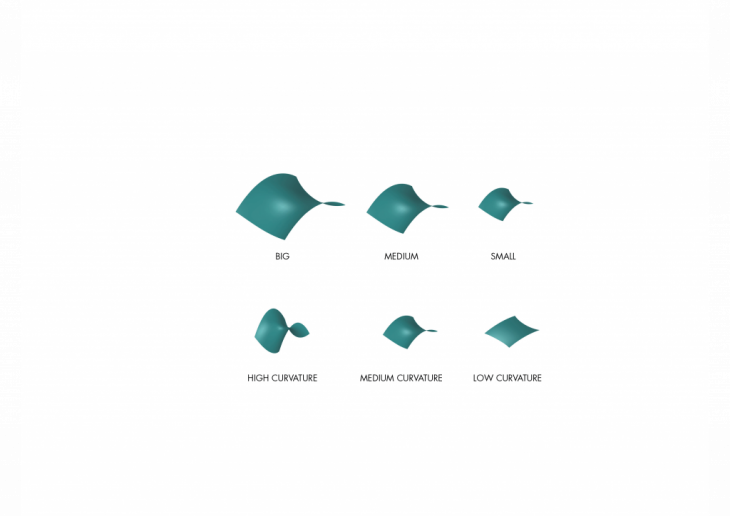
These categories can be analysed seperately or together in combination based on the user’s needs and an algorithm can be run to categorise them into select fabrication protocols. The algorithm requires the user to add certain output shapes that can undergo the categorisation.
EXAMPLE 1:
In this example, the input surfaces are the following:
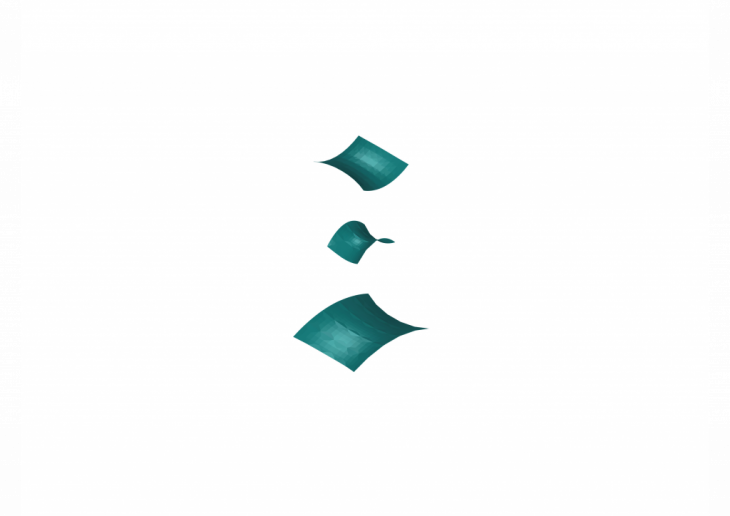
Producing this categorisation by the algorithm for the following output shapes
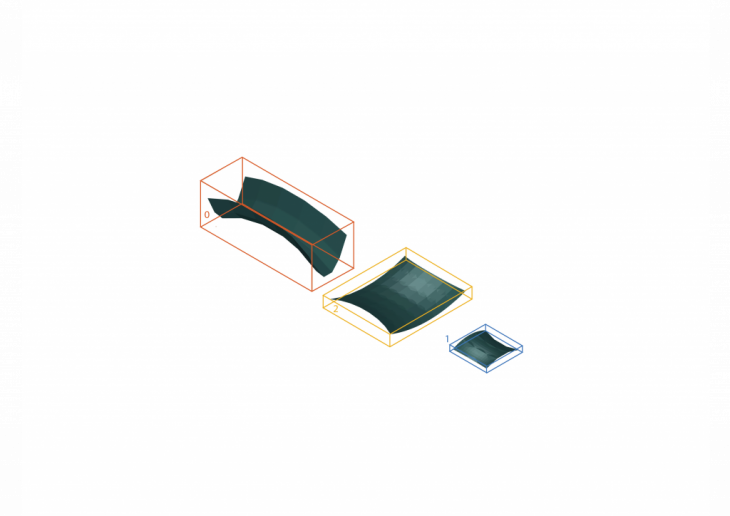
EXAMPLE 2:
In this example, the input surfaces are the following:
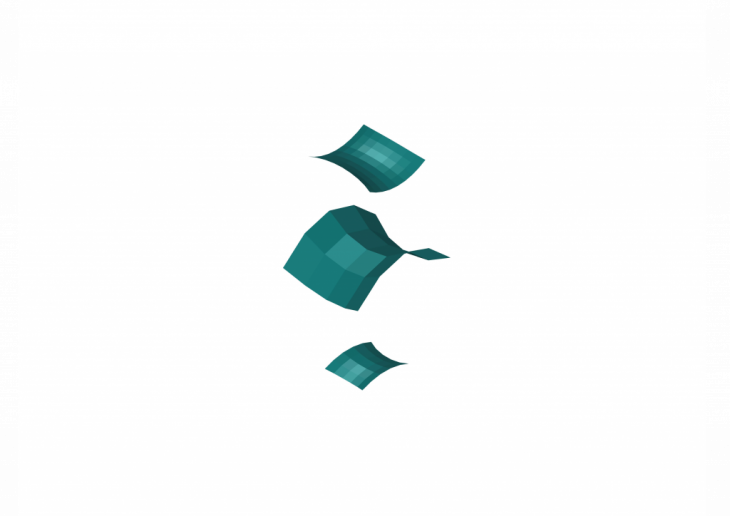

Producing this categorisation by the algorithm for the following output structures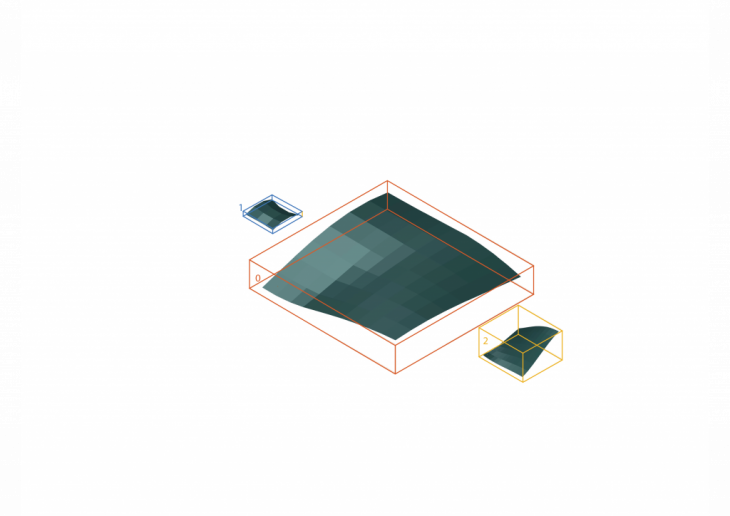
Hence by varying the types of the input surfaces, a variety of freeform structures can be fed into the algorithm that will categorise them into the appriate groups for further stages of fabrication.