Environmental Driven Design in Plaza Mayor, Madrid, is an experimental project where the environmental tools have been applied on an architectural project. We began this adventure using a box module as our initial case to study our site and building parameters. During this investigation you will see that every new environmental condition added changes a lot the design of the project.
Site Introduction
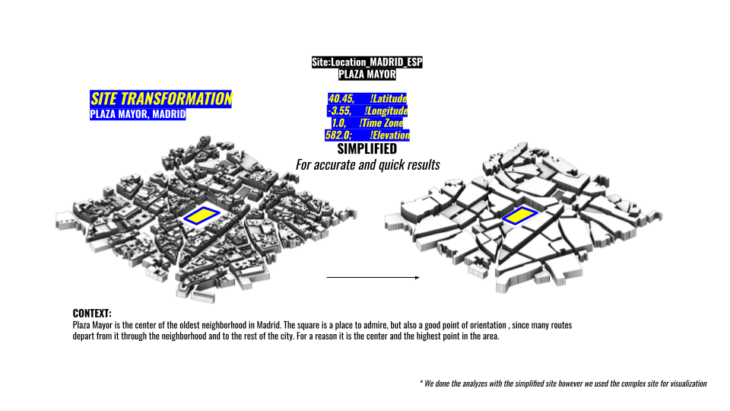
We have chosen Plaza Mayor of Madrid because of its history and its high density of tourists per year. Plaza Mayor is the center of the oldest neighborhood in Madrid. The square is a place to admire, but also a good point of orientation , since many routes depart from it through the neighborhood and to the rest of the city. For a reason it is the center and the highest point in the area.

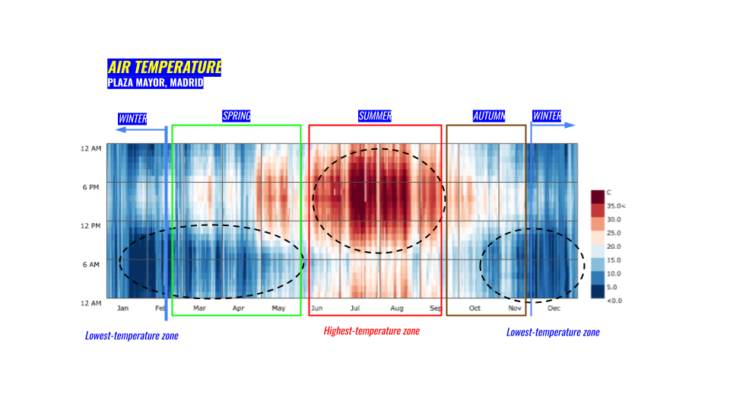
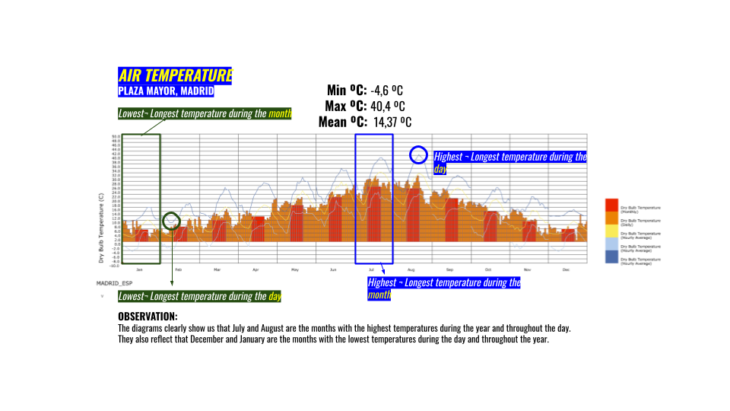
After analyzing the site, we decided to focus on summer:
- High radiation, temperature, wind speed and sunlight hours during the summer.
- Low shading zones and uncomfortable thermal data.
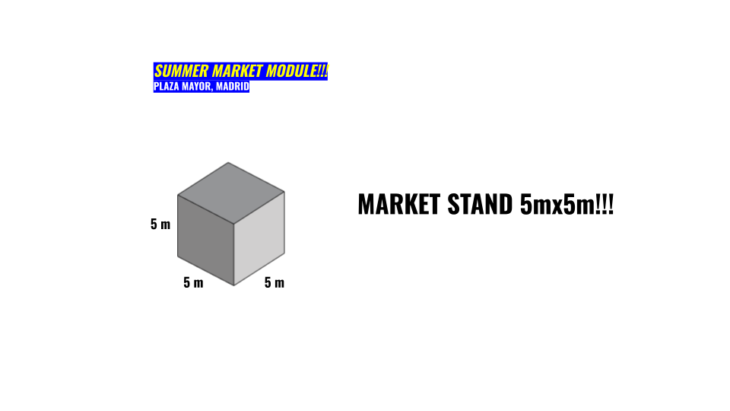
So we decided to design a voxelized market for the community which will be use as a shelter and to recover economically the neighborhood.
First of all we began simplifing our context to obtain quicker and accurate results.
Our premise was to work with a 5×5 meter voxel.
Solar Study
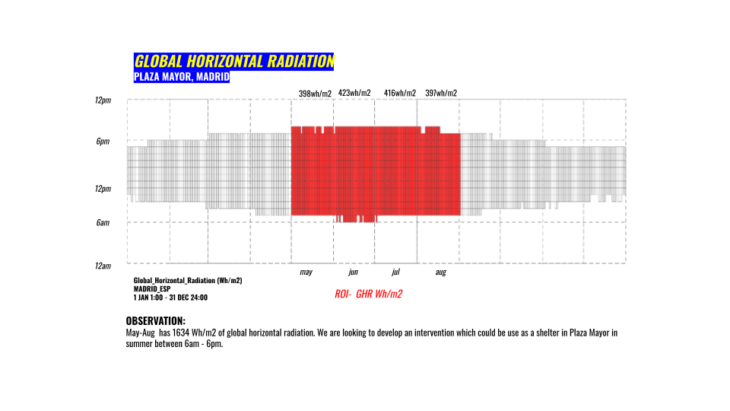
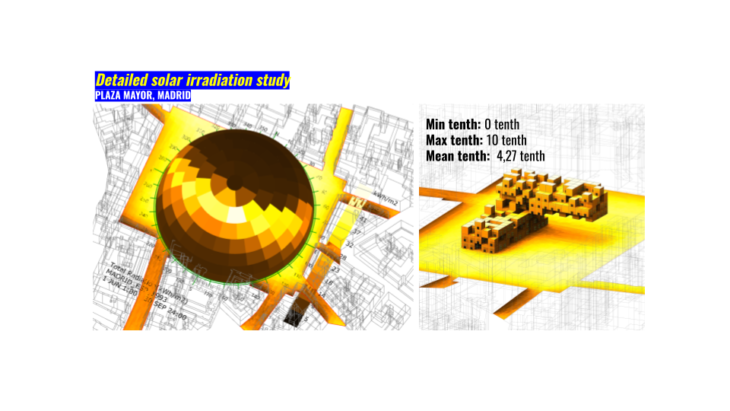
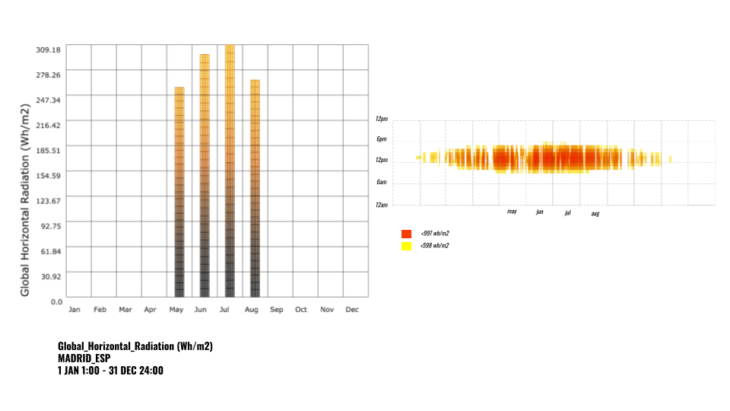
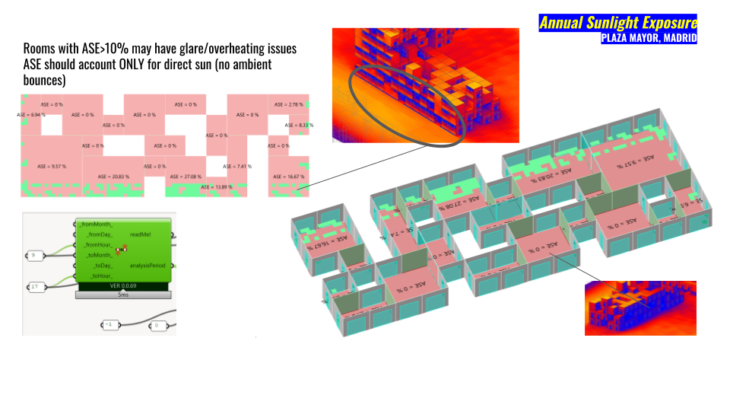
The following analysis helps us to understand the specific time we are interested in our intervention in Plaza Mayor. Between May and August, results point out a minimum of 397wh/m2 during August, 423wh/m2 during June and an average of 408.5wh/m2. These values were generated from 6am to 6pm. Basically this gives us a starting point for our design intention in order to handle these values for a comfortable experience with the different actors that will be part of the intervention.
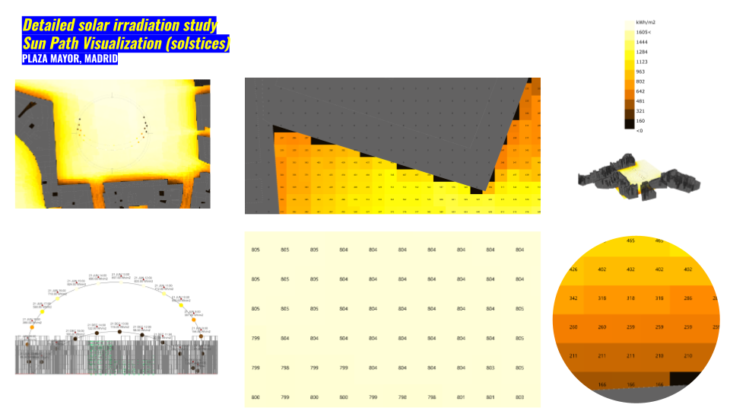
We used solar irradiation analysis to map with a grid 5×5 meters the main surface of Plaza Mayor. By this process we were able to understand the interaction between the main surface and context buildings. How these values increase in the center of the Plaza and help us to understand the consideration for hour design. These Considerations are for example if some modules are for a market or sales we suggest to avoid artefacts/devices that can melt, by this protect the merchandise from users and avoid losses on their revenues during this season.
First we began with a lineal distribution however we noticed that half of the stands where exposed to low radiation.
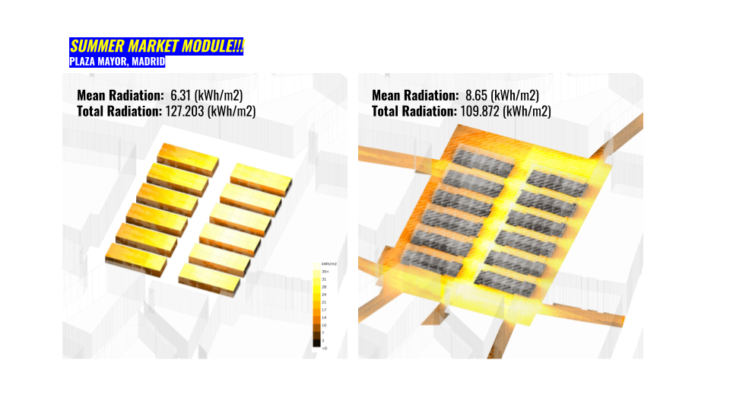
So we began experimenting in diferent locations of the Plaza with the objective of maximizing the radiation that reaches to our market stands.

Not only we stop on the location by radiation and sunlight hours that we done some experimenting on resizing windows to see how it affects inside the market. We transform a mass appearance to a lighter design.
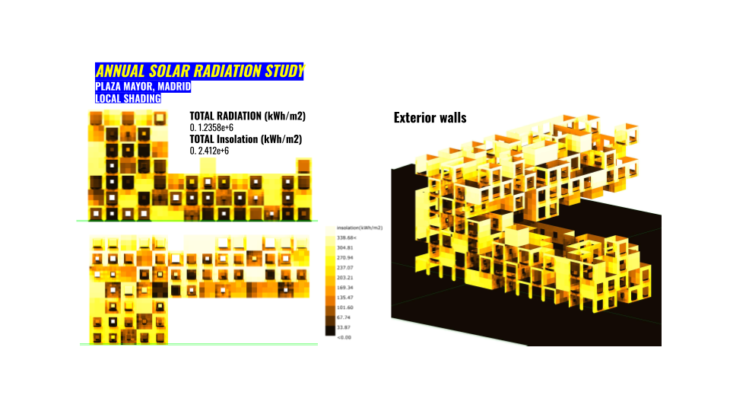
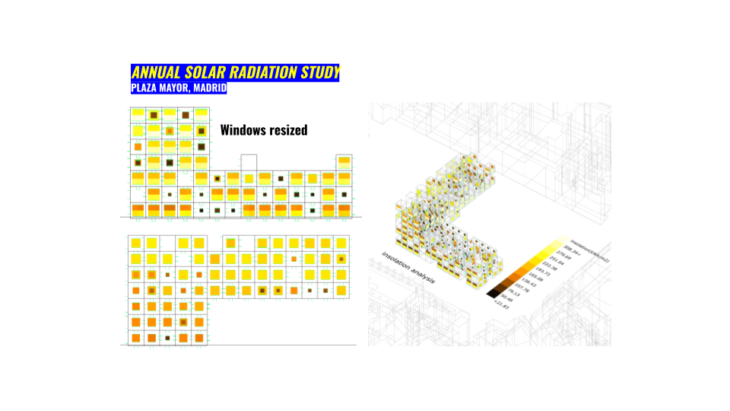
In the following section will explain different options from our design intention for reach this comfort level.
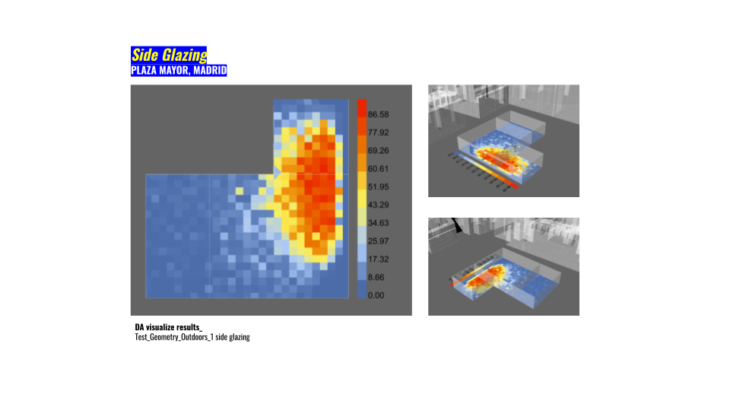
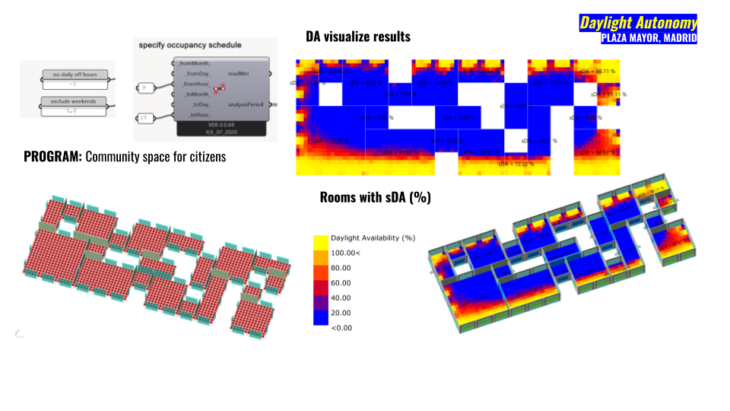
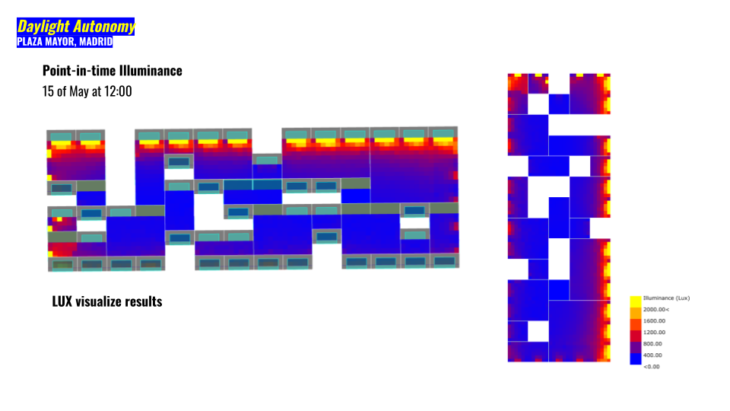
In this section we started to explore how Daylight Autonomy could affect indoors. Which are our options with a basic primitive geometry and then how we could increase the density of our voxelize shape for the next steps. In the image above basically we started with one side glazing and how we will integrate these studies in our decision making based on using more natural light and avoiding as much artificial light as possible to decrease the energy consumption inside of the building. The image above shows a grid in which represent each point where a sensor (point in the middle of the grid) receive an specific threshold of DA in lux.
We use the typical illuminance levels to understand our working areas and design program to add apertures and shades. In this case we are interested in activities like Public areas with dark surroundings (between 20-50 lux, lumen/m2) but at the same time simple orientation for short visits (between 50-100 lux, lumen/m2).
Source:
https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/light-level-rooms-d_708.html
Wind Study
Then we reached to our wind study, for this occasion we decided to study the heating and coolong periods of Madrid. We will obtain our prevailing wind directions and speed. This will configure again our project.


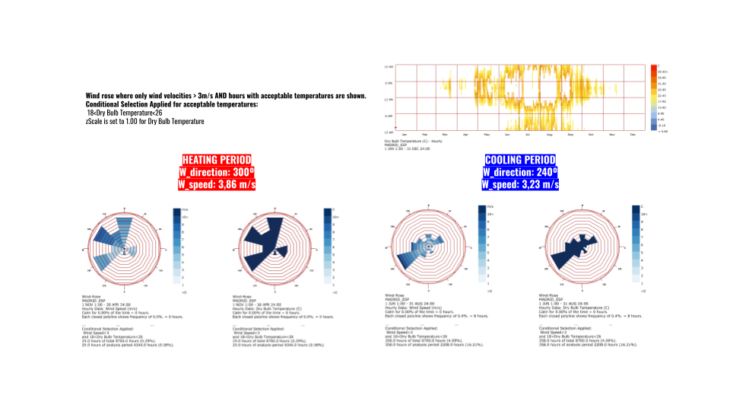
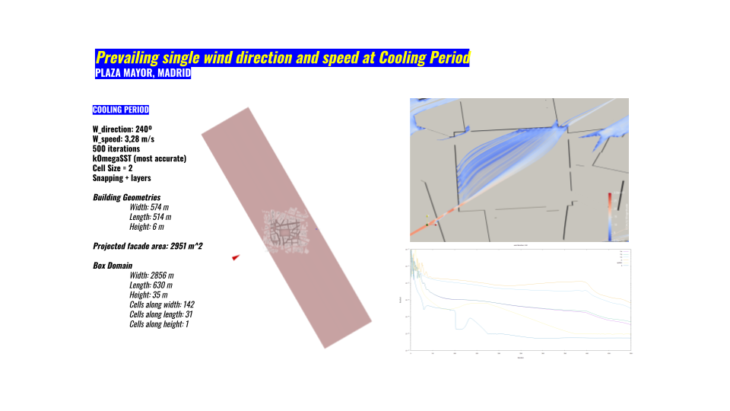
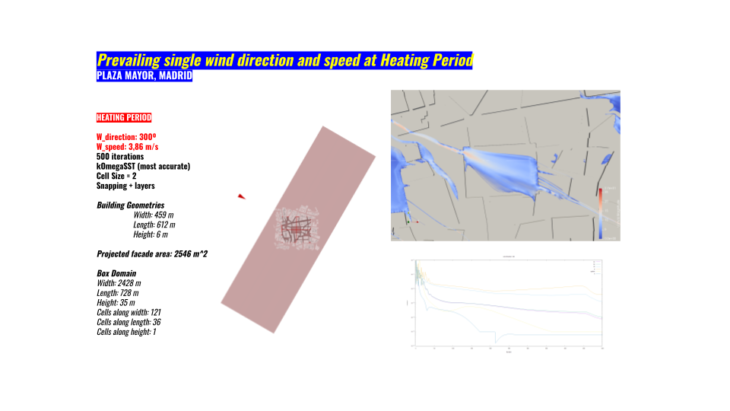
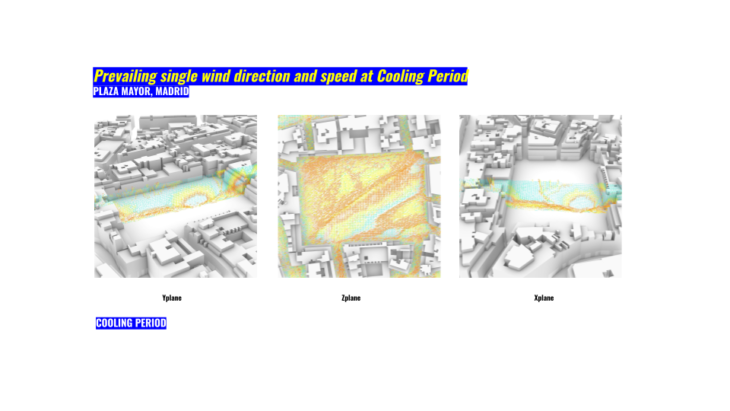
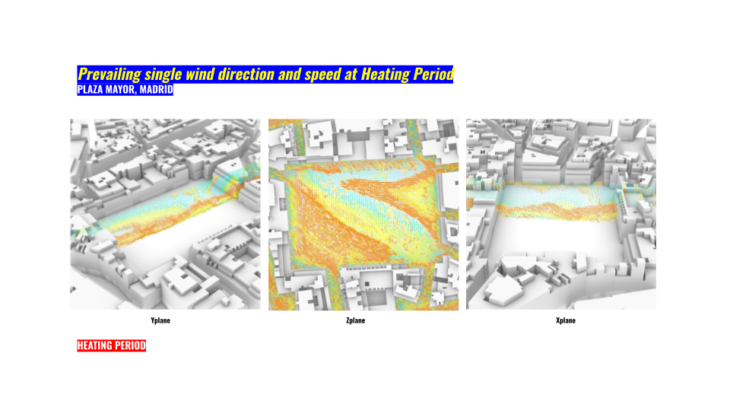
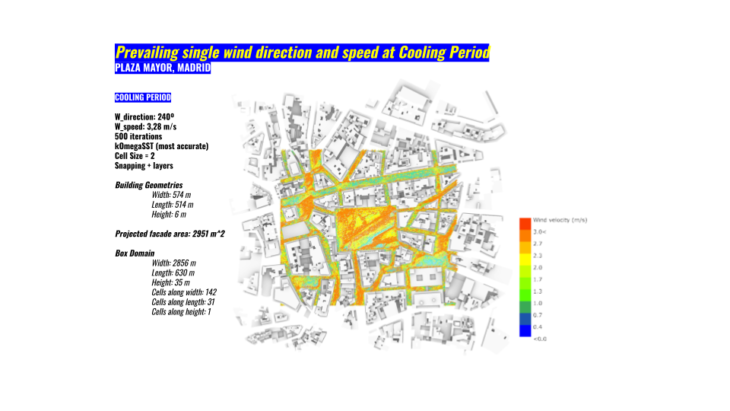
The results determined high wind speeds because of a highly urban density. This creates great streams of wind that reaches the Plaza Mayor and generate high wind tunnels. We will try for sure to locate the market at the centered and rotated to take advantage of the spaces of less wind speed.

This is a funny example of how an hurricane appears in our site!
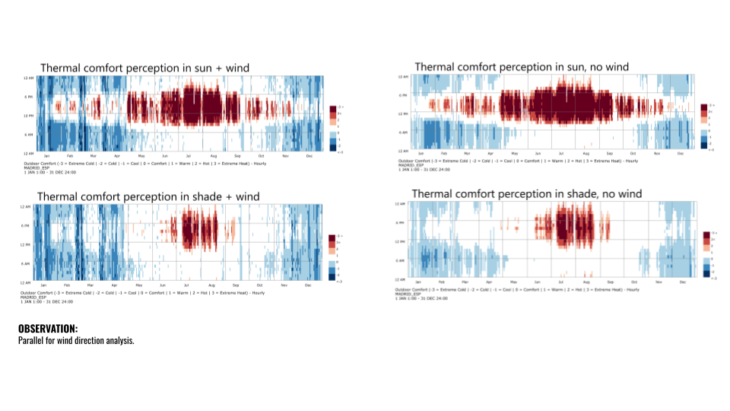
Comfort Study
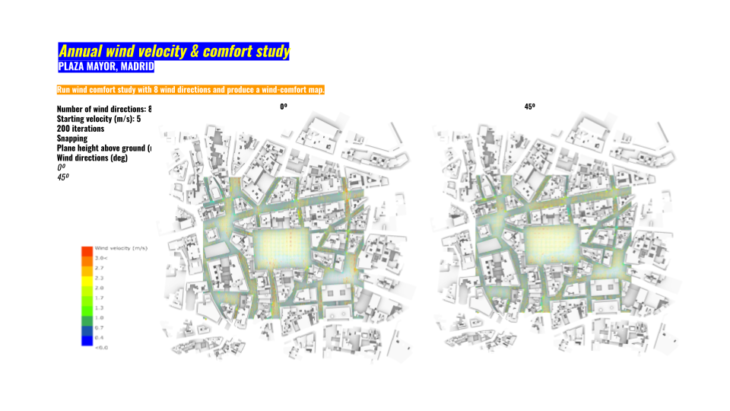
For ou comfort study first of all we run 8 wind directions during a whole year and obtain for eah a comfort map. Later we will overlap them to detect the areas where our building can be use for comfort issues.

Example of comfort maps without the project. Urban first analysis.
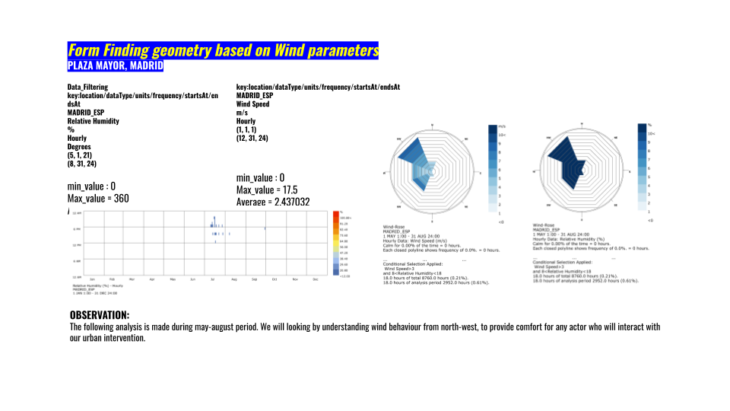
Then we focus on our form finding in summer:

During wind analysis we could visualize 10.50 m/s as the first bound during summer. From May to July this is the highest speed we will experience in the afternoon. In August is a little bit higher like in a couple of days and again during afternoon but with 17.50 m/s.
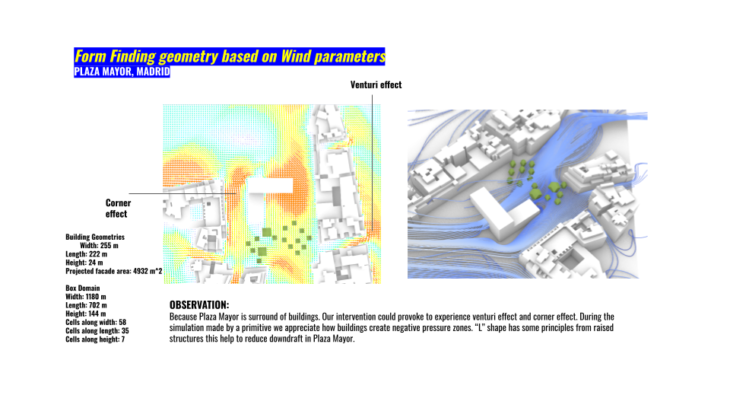
In our form finding process we worked with shapes/geometries that will allow us to adapt to the simulation process. The following L shape could be our level 2 shape. Was a great opportunity for exploration. We played with the density of polygons of our context buildings and also in the image above you can see how for our design intention, decrease the amount of polygon in our geometry.
First we observed wind speed behaviour only by placing the simple geometry and where could be critical points for corner and venturi effect. One option could be that the low polygons which represent trees could be pots that help us to drive our wind direction and wind speed intensity.
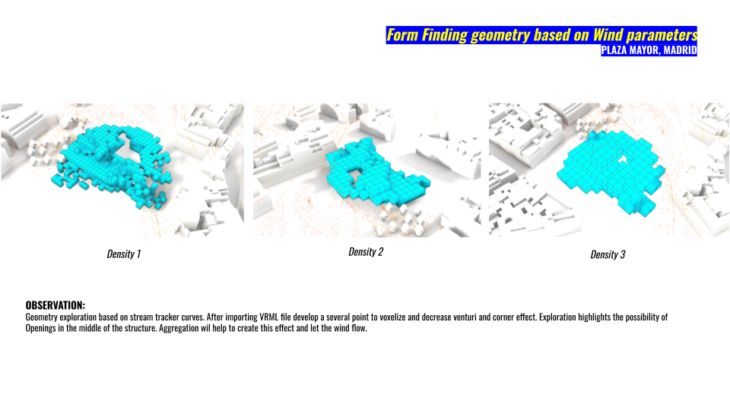
Next we explore wind speed and the interaction between our voxelize shape. 3 splitted options for voxelize exploration. Trying to avoid a massive geometry that could affect the surroundings of the plaza. We increase the density of voxels and random seeds in tree steps. But didn’t find any specific improvement the 3 of them develop pressure that will affect any actor walking beside the intervention. For this density step we runned the simulation for the voxelize geometry without context building.
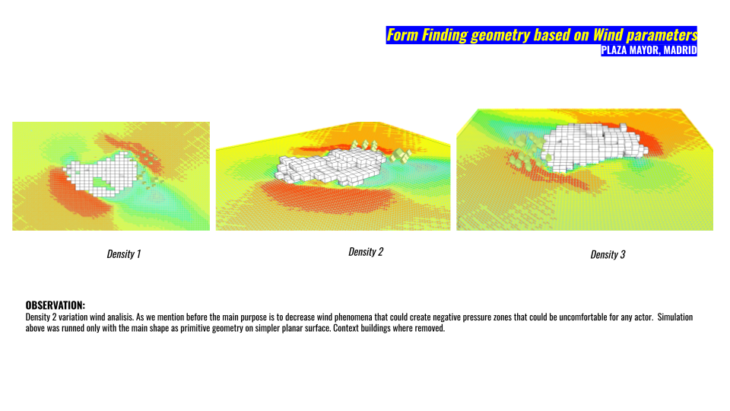
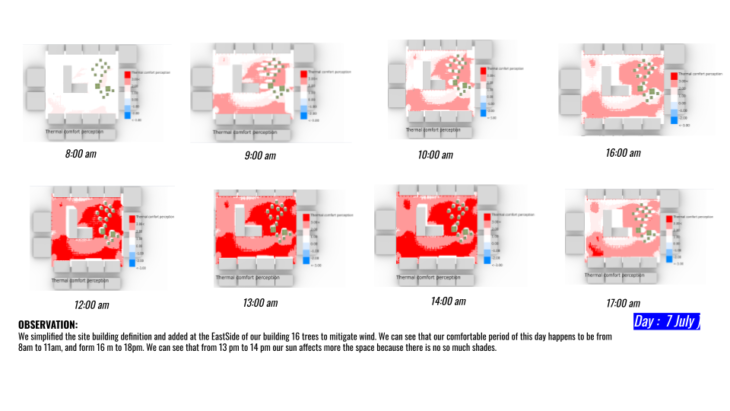
Now for the following simulation we go back with our L simple geometry and also decrease the amount of polygons again for the context buildings of Plaza Mayor. During this simulation the results shows that during morning in Plaza Mayor will experience no thermal stress 8:00 am and will incrementally increase to very strong heat stress until 14:00 then will partially decrease at 16:00.
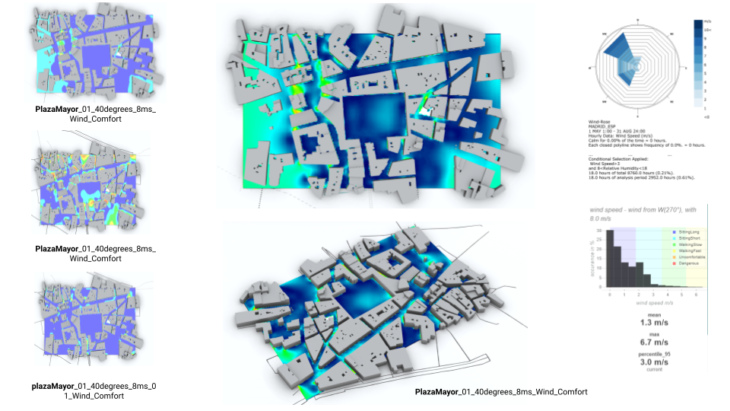
Finally just for exploration we tried to change from small scale geometry to urban scale. How we could improve new cities in development? What could happen if we tried to replicate the same wind comfort in new cities? How could we replicate the same features extracted from any initial analysis? The intention of the following exploration is run in Infrared Platform wind comfort analysis in Plaza Mayor. Then create a series of urban prototypes to run the same simulation and find the most likely geometry that could improve wind comfort in new cities. Extracting the kpi values to get the most comfortable score was really useful to understand the goal for our design intention and setup.
After running the simulation again with the new geometries if the setup is fine basically we could have results of conformity between 69% to 100%.
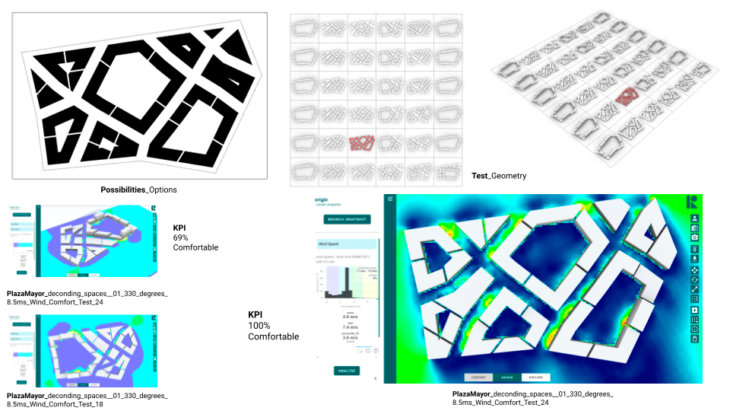
No doubt the future exploration for improving the experience by environmental analysis could be accelerated by the right conversation between data interpretation and tools. Basically to be able and have more options for our informed decision making. This will be vital to understand how we improve our energy consumption from small buildings to large urban developments.
Environmental Driven Design in Plaza Mayor, Madrid is a project of IAAC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed in the Master In Advanced Computation For Architecture & Design 2021/2022 by Students: Salvador Calgua and Jacinto Moros Montañés; Lead Faculty: Angelos Chronis; Faculty Assistant: Aris Vartholomaios