In order to understand how the various Digital Fabrication tools enable us to create shapes and forms that surpass the capabilities of usual manual design techniques, we were introduced to three different tools: Laser Cutting, CNC Milling and 3D Printing.
We used Laser cutting to successfully enable the kerfing of a wooden panel in both the X and Y axes by increasing the path of material that flows horizontally, as well as vertically, by cutting a diagonal pattern into the wooden panel.
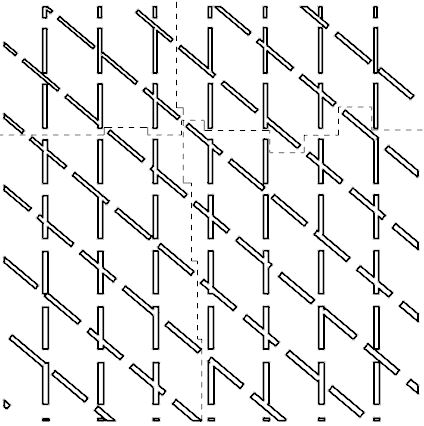
The curfing pattern
In order to achieve the required two-dimensional kerfing I wanted to increase the path of material in the X and Y axes by introducing a diagonal pattern. The way that this pattern was created, was by rotating the original series of rectangles by 50 degrees and by creating a union between the original and the rotated patterns. Much attention was paid on the thickness of the pattern as it was crucial that all the connecting patches of wood between the ‘’pattern cells’’ would surpass a certain dimension.

The wooden panel with the laser cut pattern
In addition to Laser Cutting, we were introduced to CNC Milling with which we made a proposal to mill a surface with undulations and waves in the foam, in order to have the desired 3D visual effect.
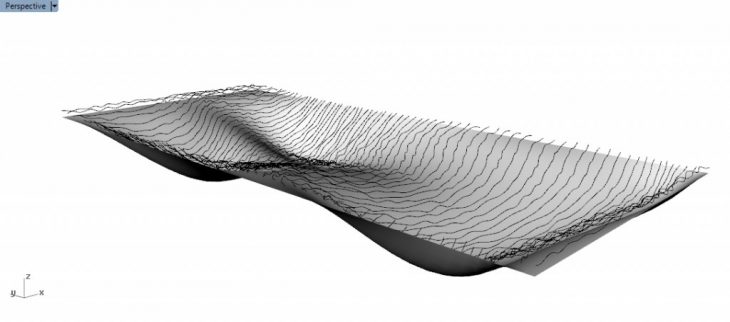
The form that was designed to be milled out of the foam.
In order to achieve the desired undulations and waves in the foam, I used a Grasshopper algorithm that allowed me to divide my surface in points. By connecting the points I created curves and I managed to create a series of horizontal undulations and waves by applying a random seed for vertical dislocation in the algorithm. In the end, I flipped the matrix of points, in order to flip my horizontal lines into vertical ones, thus creating the resulting 3D surface in the foam.

The final form of the foam.
Lastly, we were introduced to 3D Printing techniques that allowed us to use 3D Print a Cube of PVA material, that contained an organic form the combination of which is going to be used as a negative for the casting of resin inside the cube itself.

Two different iterations of a possible form that can be 3D printed inside the box
In order to achieve the desired shape of the model, an Icosahedron was transformed into a liquid and viscous geometry using the Grasshopper plugins Anemone and Boid. After the geometry has been generated I tried to isolate an organic shape, from the large variety of forms that the Liquidahedron was made of. The end result was a box that contained organic forms.
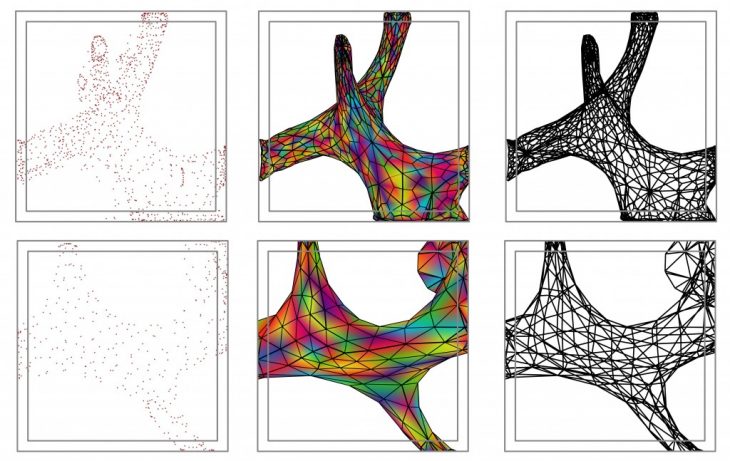
A diagramatic representation of the forms inside the box.
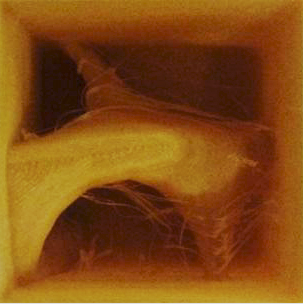
The 3D printed form ready to be resin casted
Digital Fabrication Tools is a project of Iaac, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia at Master in City and Technogy in 2016/2017 by:
Students: Alex Mademo
Faculty: Djordje Stanojevic, Kunal Chadha