In this experiment, we are investigating the viscocity of a non-newtonian fluid (cornstarch) and its response when stressed by sound waves. The resulting forms produced by the cornstarch are practically the visualisation of the static sound waves produced by the speaker.
A non-Newtonian fluid is a fluid with properties that are different in any way from those of Newtonian fluids. Most commonly, the viscosity (the measure of a fluid’s ability to resist gradual deformation by shear or tensile stresses) of non-Newtonian fluids is dependent on shear rate or shear rate history. Some non-Newtonian fluids with shear-independent viscosity, however, still exhibit normal stress-differences or other non-Newtonian behavior. In a Newtonian fluid, the relation between the shear stress and the shear rate is linear, passing through the origin, the constant of proportionality being the coefficient of viscosity. In a non-Newtonian fluid, the relation between the shear stress and the shear rate is different and can even be time-dependent (Time Dependent Viscosity). Therefore, a constant coefficient of viscosity cannot be defined.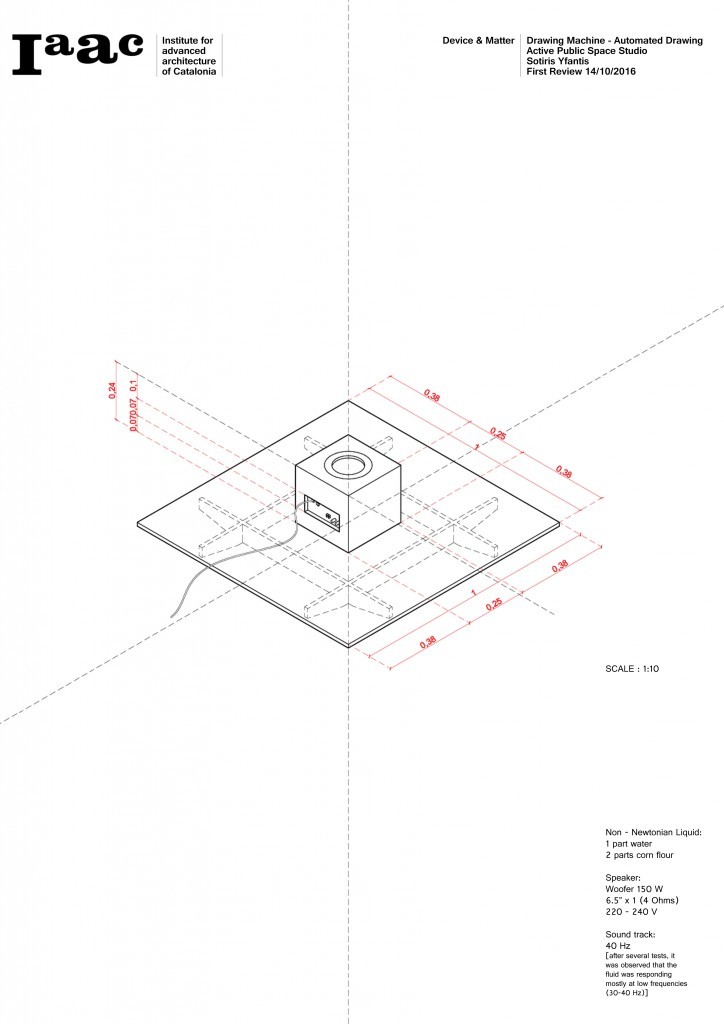
Device and matter is a project of IaaC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia
developed at Master in Advanced Architecture1 in 2016-2017 by:
Students: Sotiris Yfantis
Faculty: Edouard Cabay, Rodrigo Aguirre