Prognosis :
” Cities contribute to 75% of CO2 emissions whereas they occupy 2% of land”
The global challenge of global warming is finding cities as the major emitters of GHG gases and also major contributors to Urban Heat Islands. The study focuses on how we can utilize AI in tackling urban level issues. The context for the study is the City of Pune,Maharashtra.
The project aims to use the Supervised ,Unsupervised machine learning algorithms to evaluate the probability of finding commonalities in the spatial configuration further allowing to cluster them under common parameters.
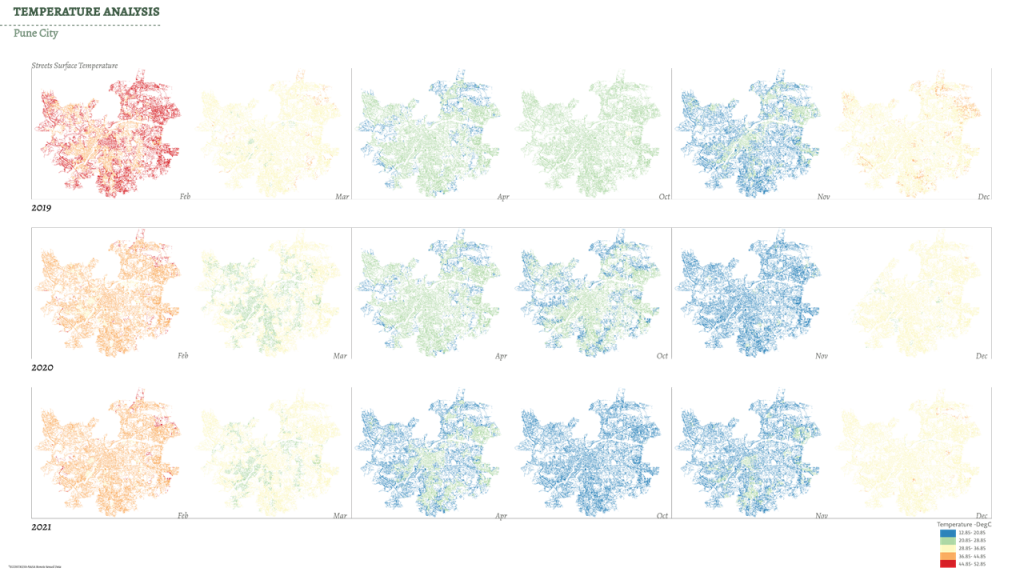
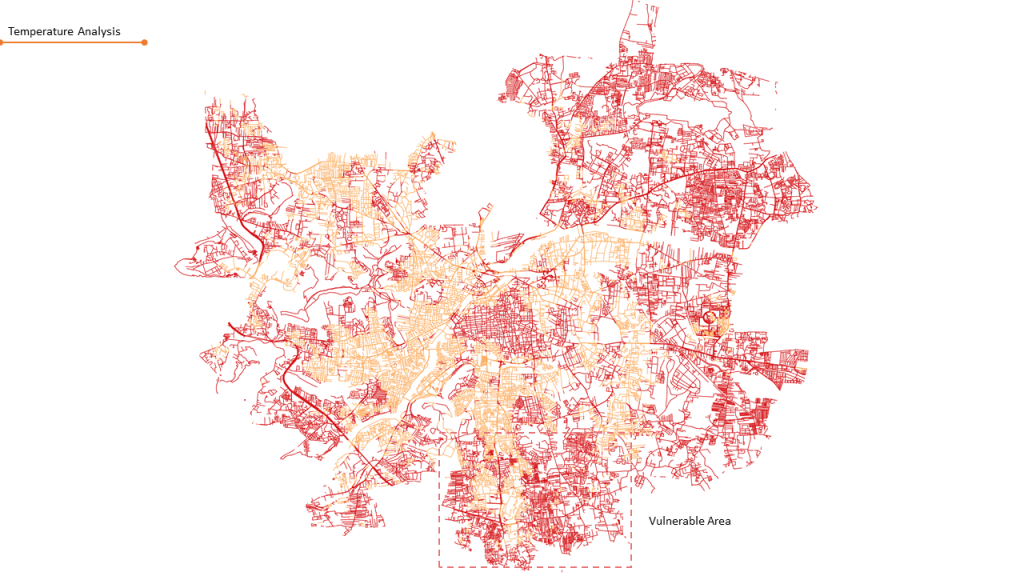
Climate action primarily involves impacts of Urban Heat Island effects in urban areas. Which arise from the built infrastructure and their radiative actions.The dataset is array of temperature values spatially collected of various Built spaces and other parameters.The study is defined in smaller part of the city prone to harsh temperatures noted.
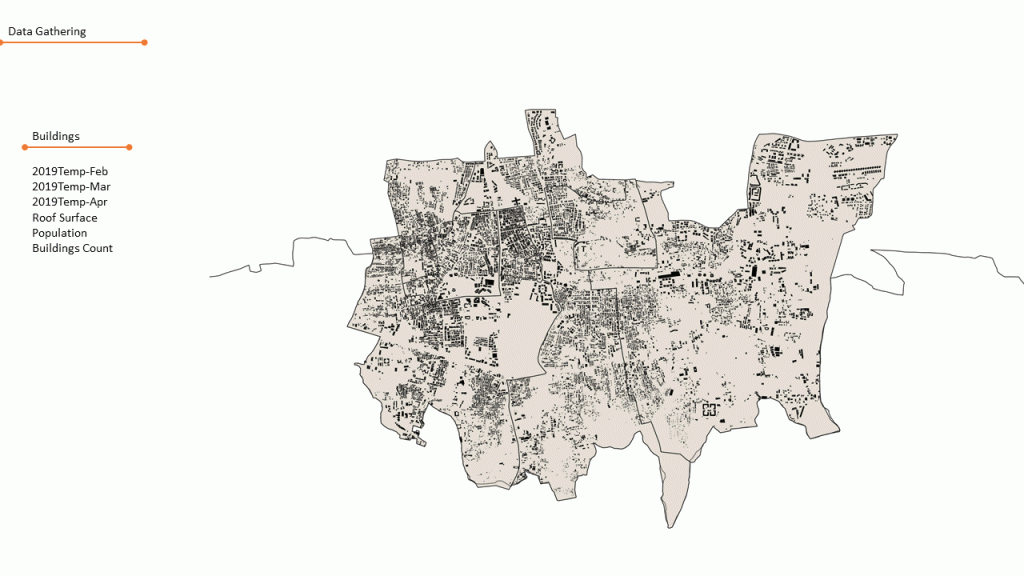
DataSet Parameters:
Methodology :
The spatial dataset is organised in the grid to process it further for analysis.

The data set with spatial co-ordinates is then further processed for co-rrelational study in between the parameters.
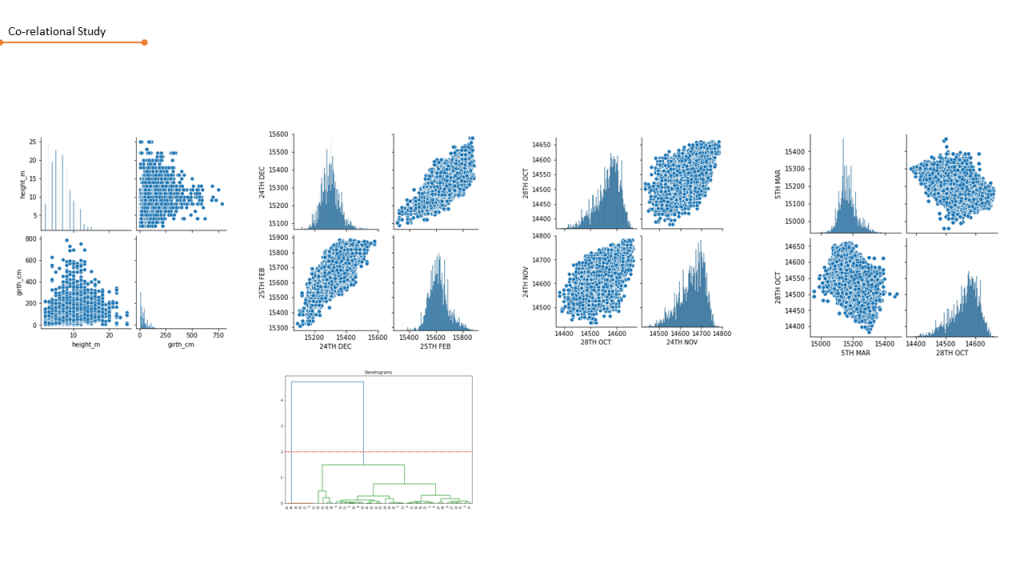
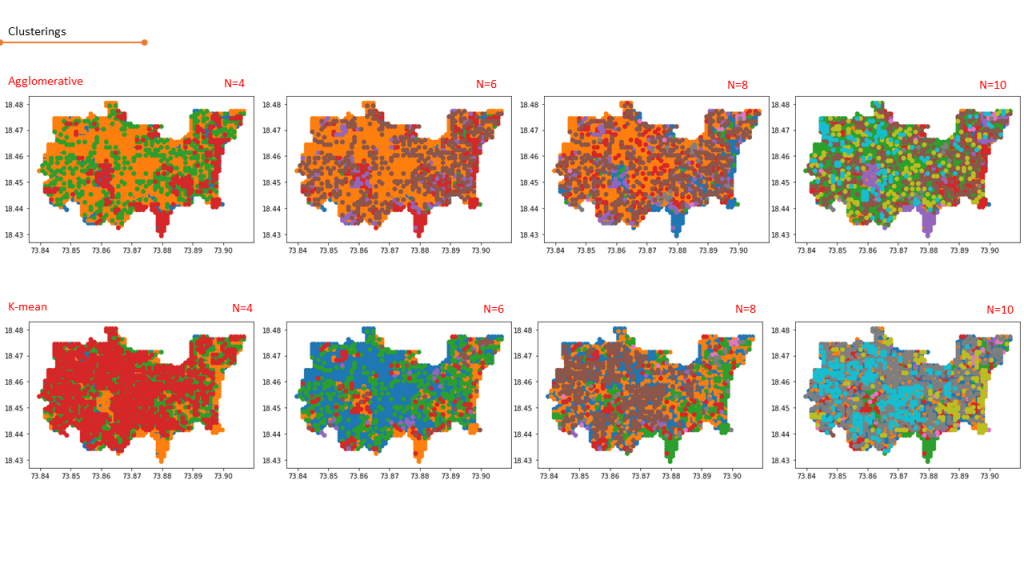
Agglomerative & K-means :
The unsupervised machine learning models were used on the above created datasets for finding the clustering pattern.
Conclusion:
The algorithm showed similarities in the clustering pattern while the number of clusters were small.With increase in number of clusters the clustering pattern for both models showed different patterns and clustering parameters.
This project is developed by: Kshama Patil
AI for Climate Action is a project of IAAC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at Master in City & Technology in 2021/22 by student: Kshama Patil and faculty: Angelos Chronis,Nariddh Khean,Serjoscha Duering