Advances in Wood Housing
Can fabrication methods increase the productivity and assist the labor workforce, to build more efficiently?
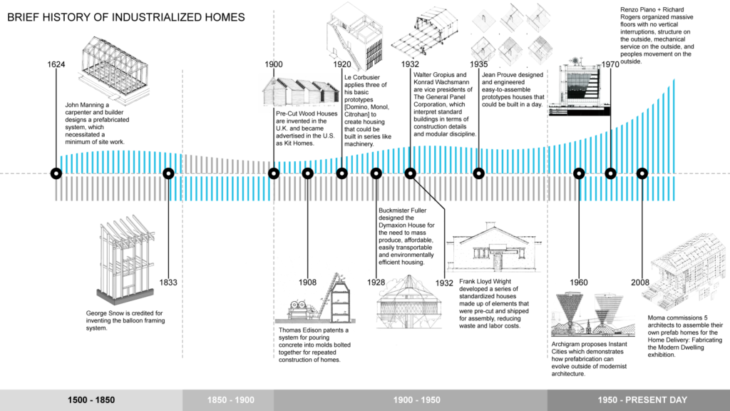
History of Industrialized Housing
A brief history of housing demands on industry and individuals that have yielded innovative results.
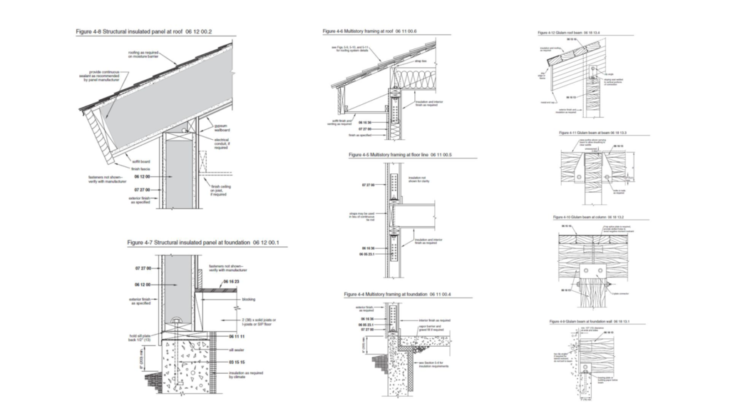
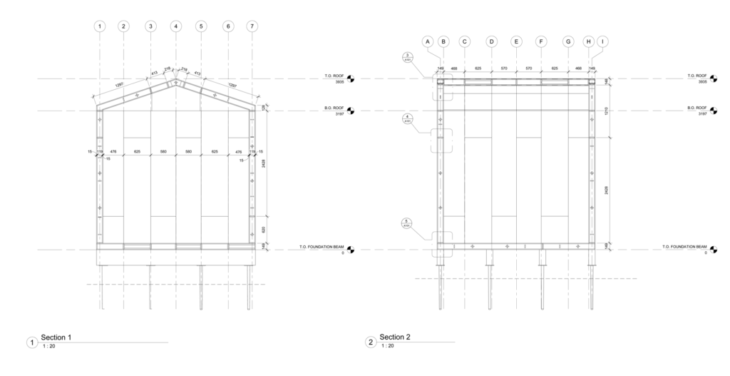
Three types of methods commonly accepted in wood housing construction are: A] SIP Panels B] Platform Framing C] Glulam Framing.
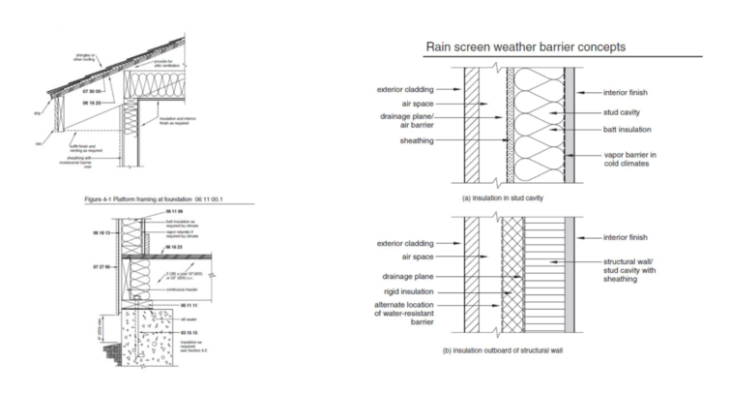
Platform Framing is the most commonly used construction system for wood housing.
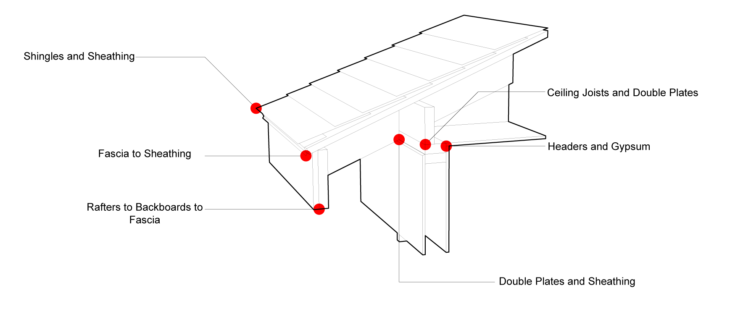
Platform Framing utilizes a large amount of demand of labor by constraints carried out in the methods of assembly.
Prior Study of Housing Tectonics
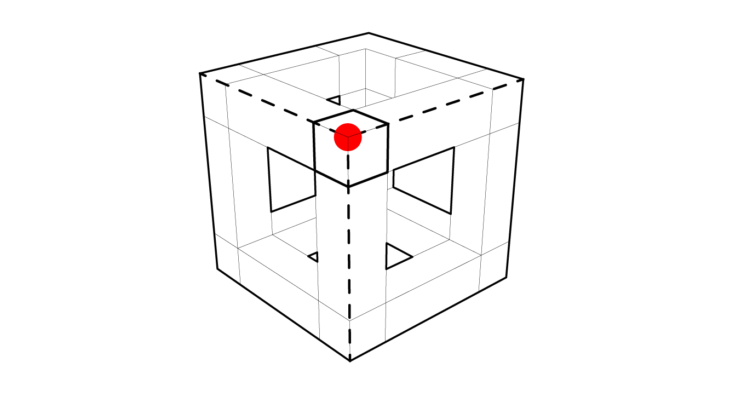
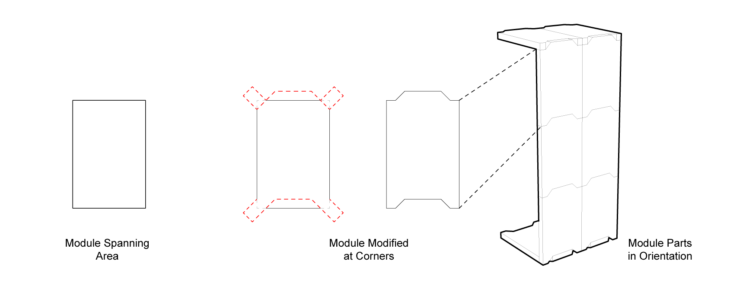
A node [red dot] represents a connectivity for valence. A connection [dashed lines] which extends is also a measure of valence. The red dot is depicting the centers, edges, corners,, and is dependent on various points as connecting nodes.


The corner conditions along with the extended connections make a volume. This volume yields a stable structural module and provides a continued entry point as a node for a new module. The node [red dot] should be able to adapt to angles in connections [dashed lines], where the node [red dot] logic allows for vertical, horizontal, and angled connections [dashed lines] to form a volumetric module.

A typical structural element of a beam or column can also be interpreted as a shell where the faces that compose a module are acting as the horizontal, vertical, and angled parts.
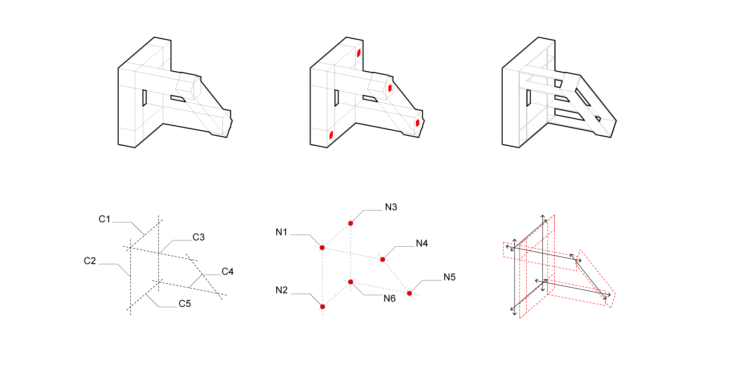
Geometric models express the application of these rules for simple edge rotation of nodes and connections in their horizontal, vertical, and angular conditions.

Space Frames and 3D Volumetric Models

In plane connections and fabrication study of joinery
Transitioning a module into a network of nodes as connections
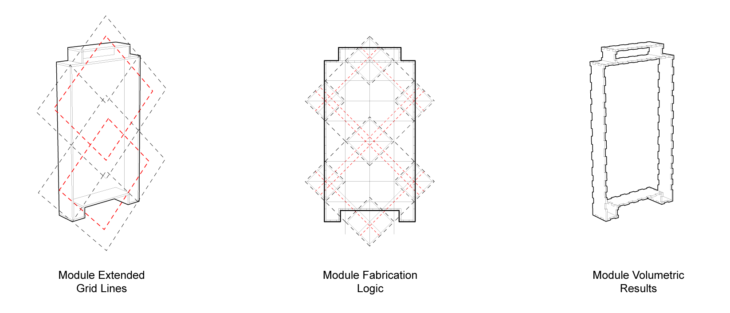
Transitioning a fabrication logic into nodes that connect in plane
Learning from Existing Case Studies
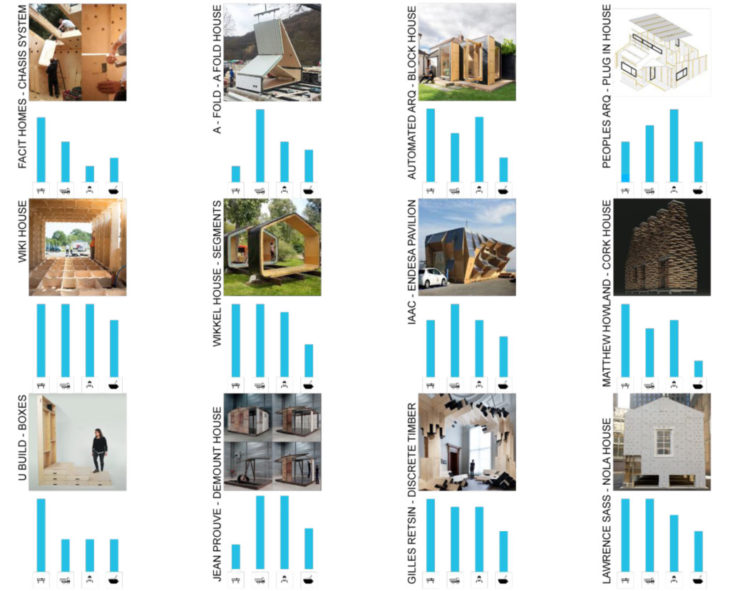
State of the Art Matrix
Evaluation of Hybrid Joinery Conditions
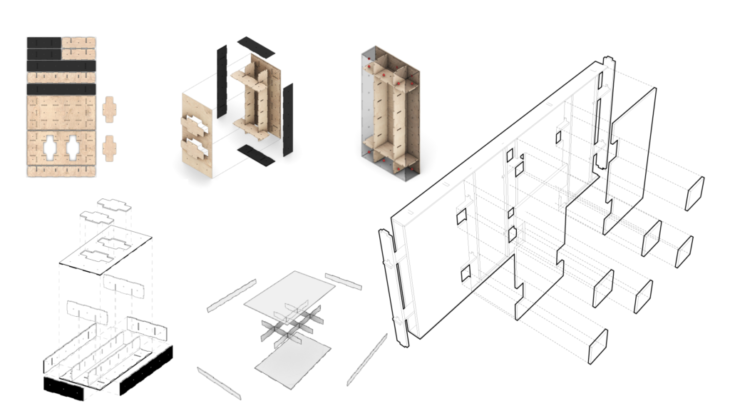
Learning from Existing Case Studies: Block House Cassette assembled partitions w/ access
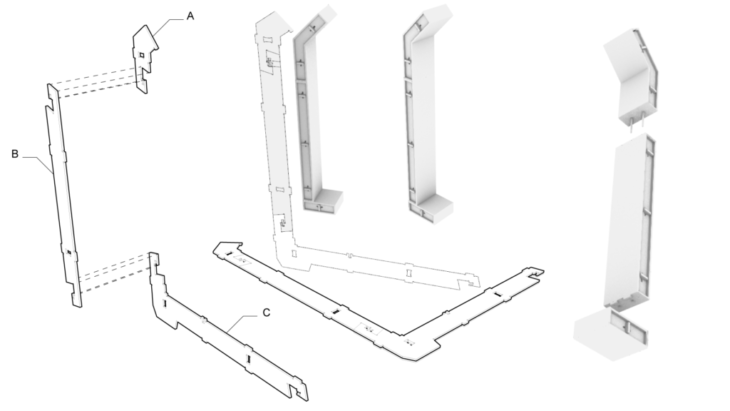

Learning from Existing Case Studies: Wiki House A] Roof Node B] Wall Node C] Floor Node
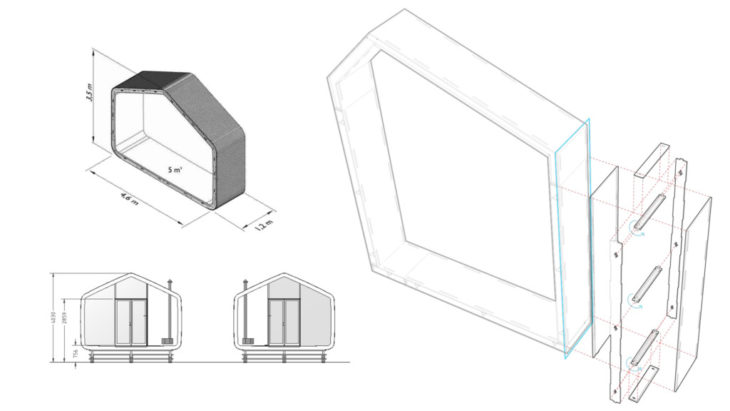

Learning from Existing Case Studies: Wikkel House – Creating Modular Planes
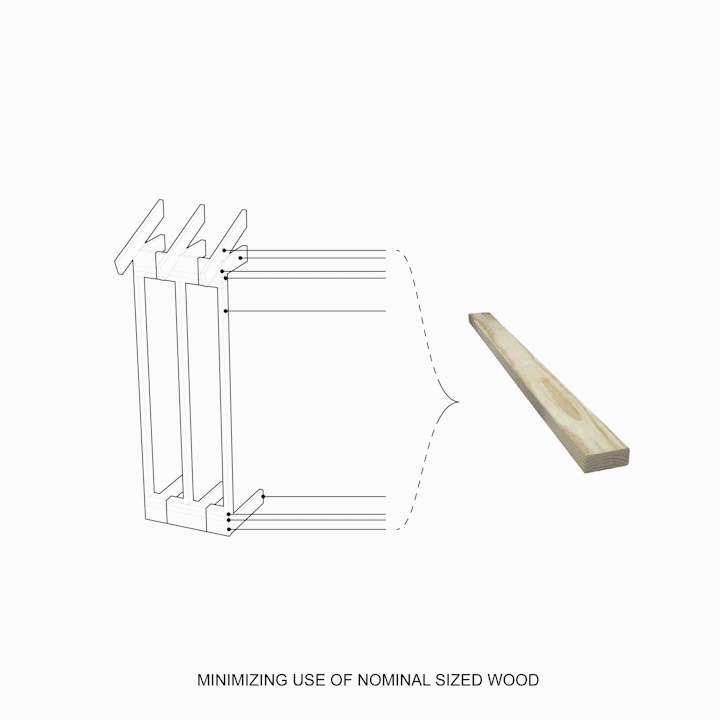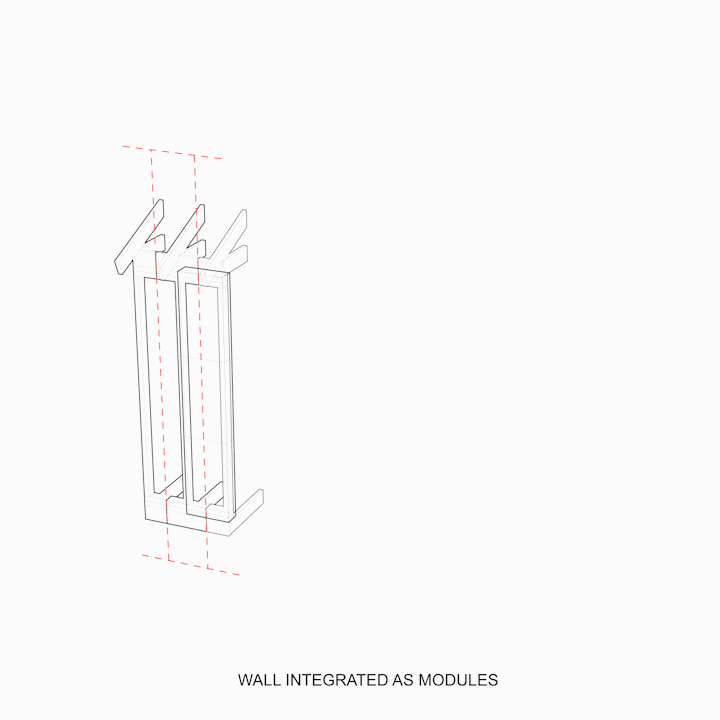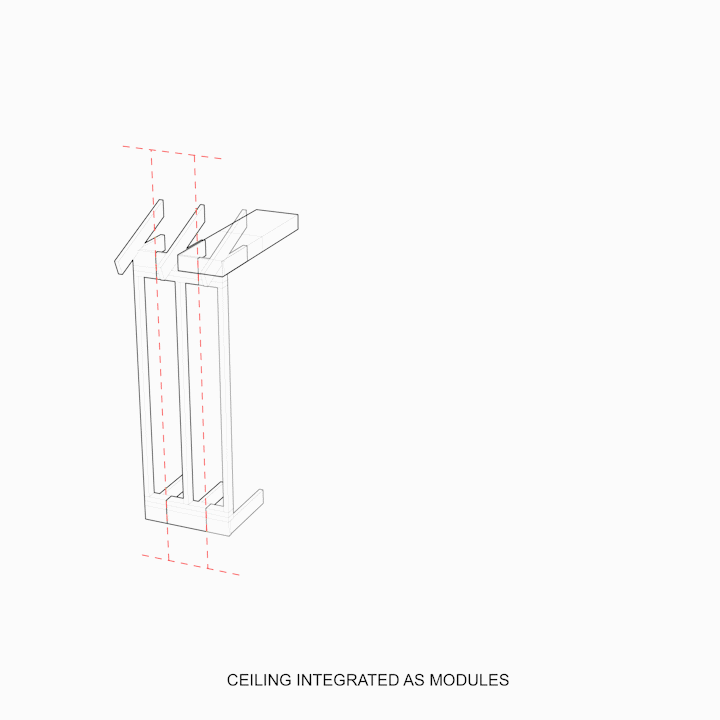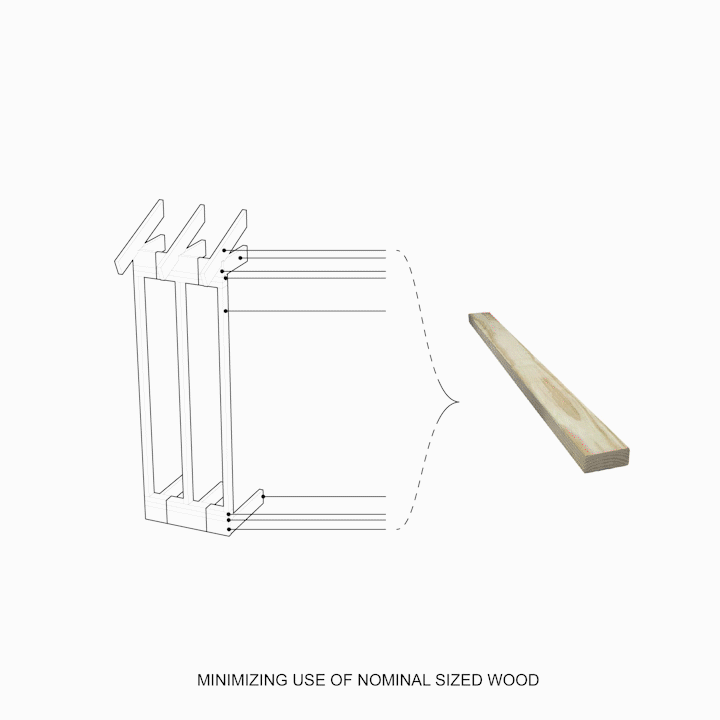
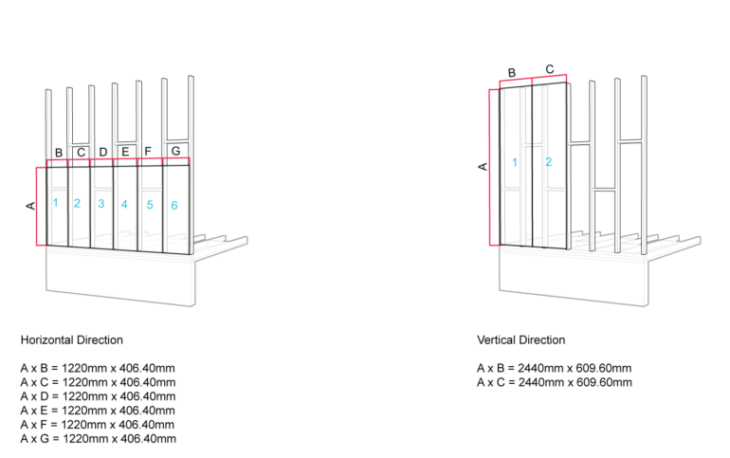
Learning from IBC Code: Minimum Spans for Modules Based on Material Sizing
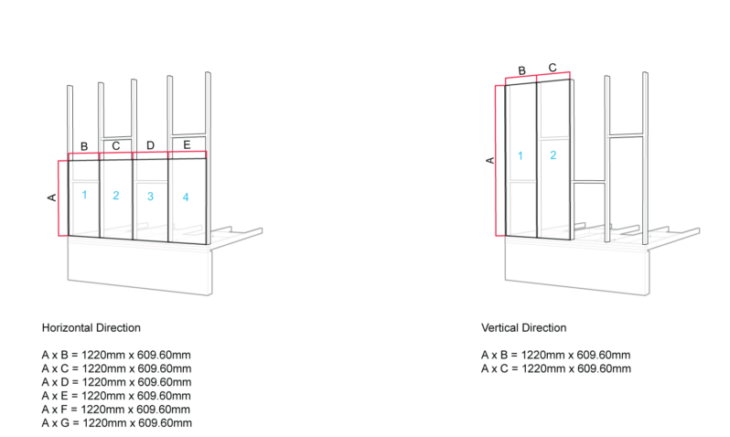
Learning from IBC Code: Maximum Spans for Modules Based on Material Sizing
3-Axis CNC Fabrication
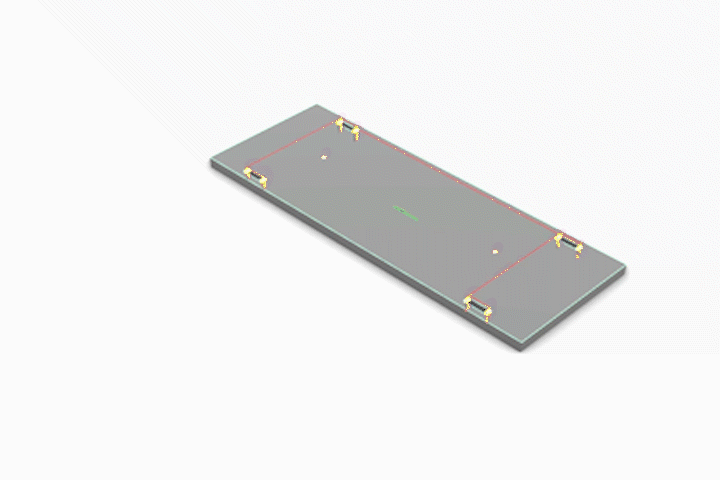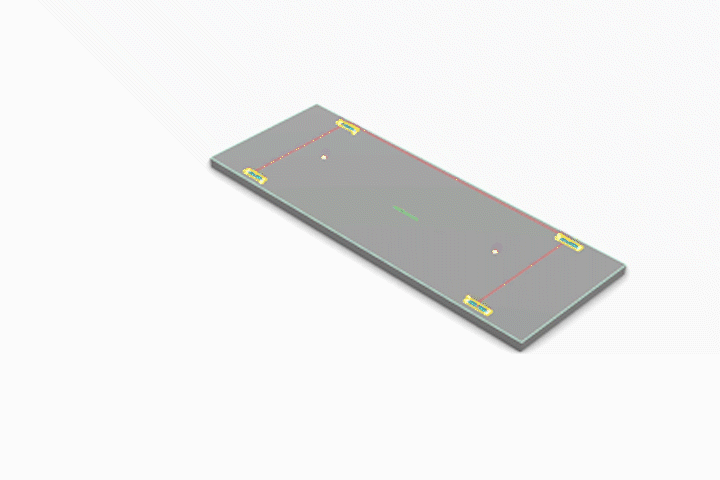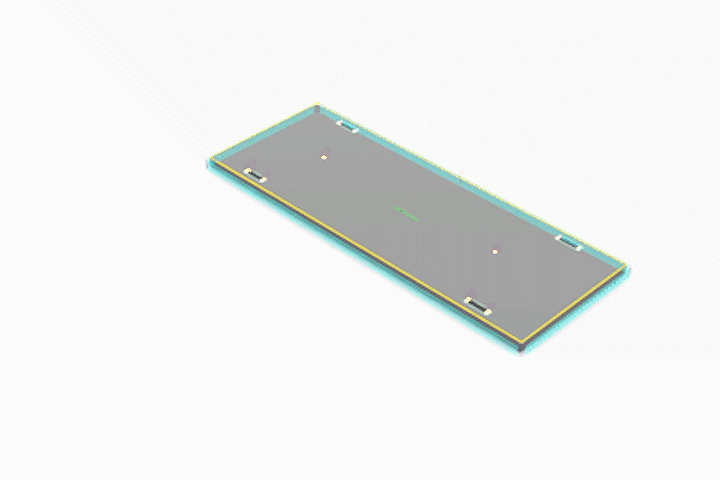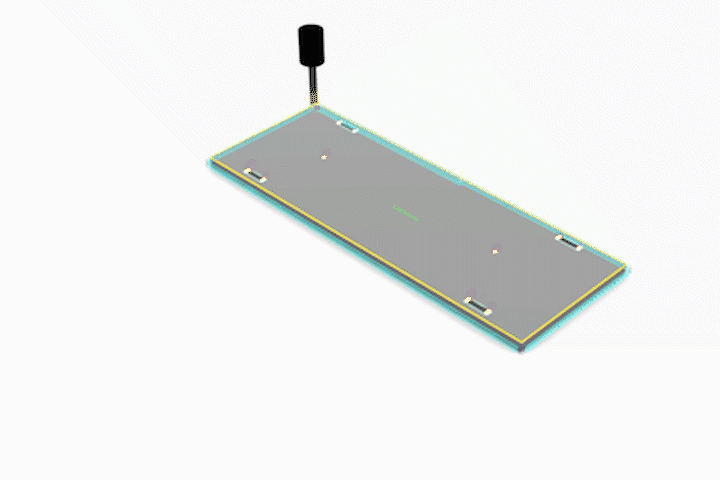

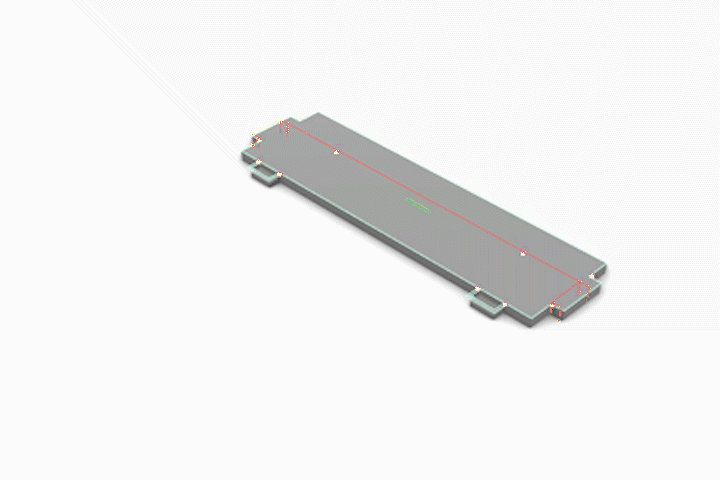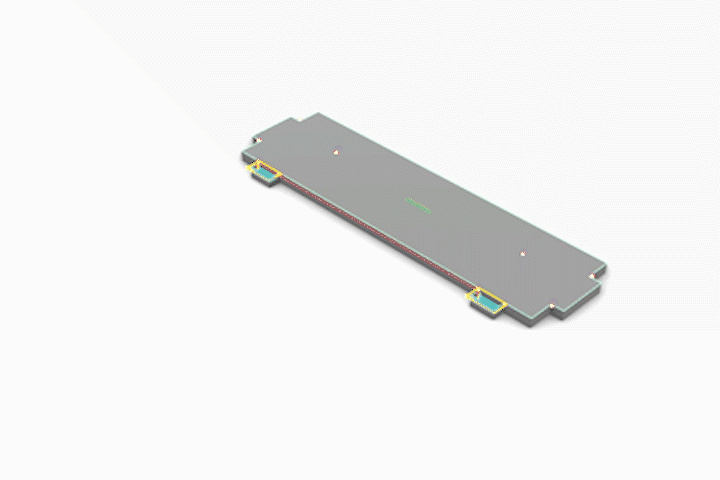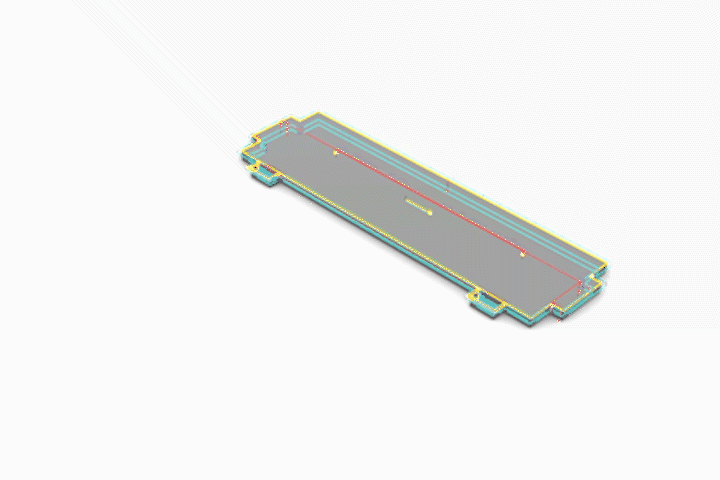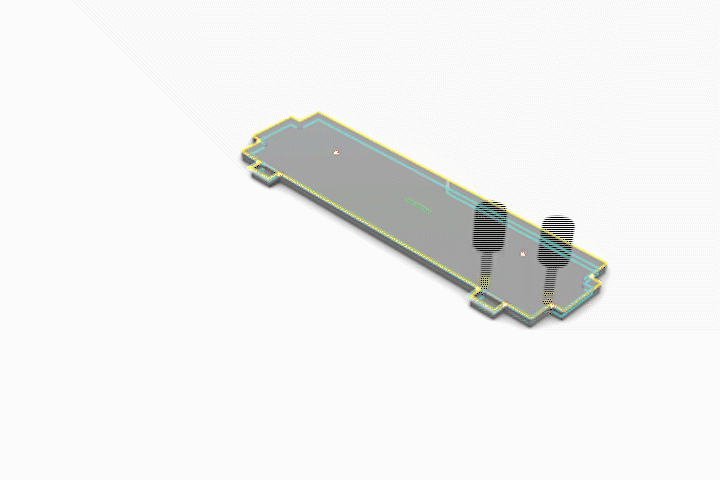
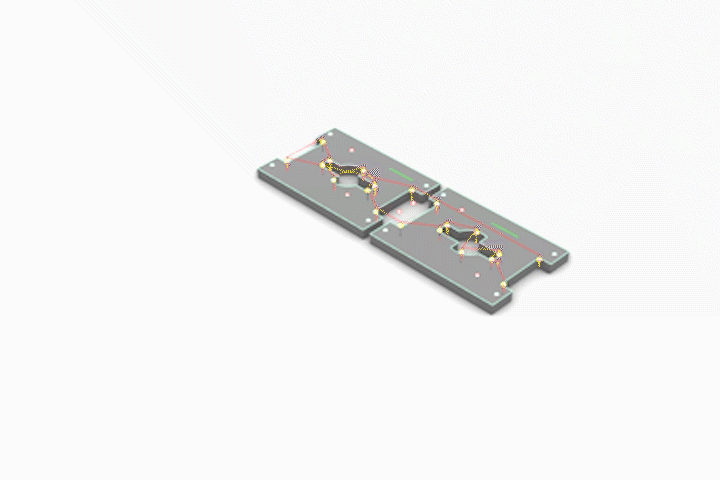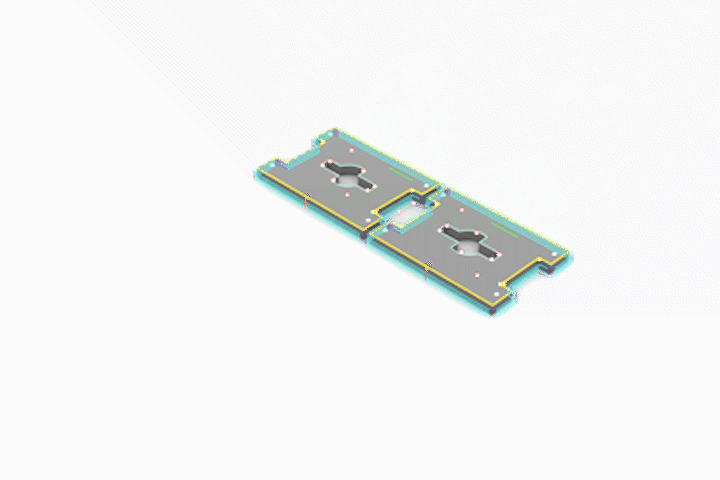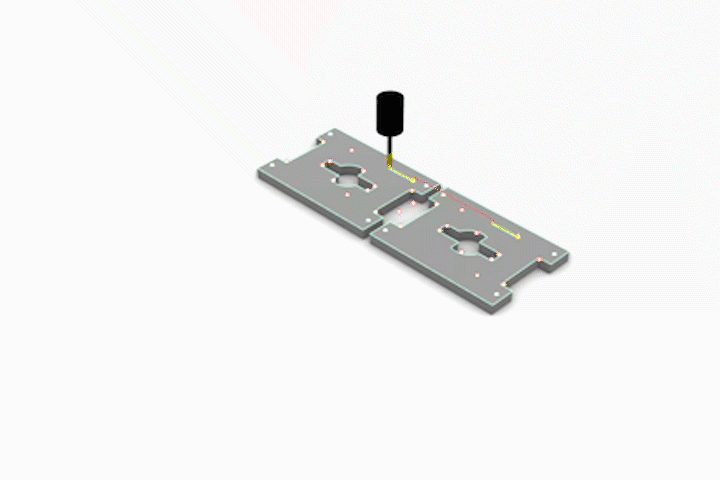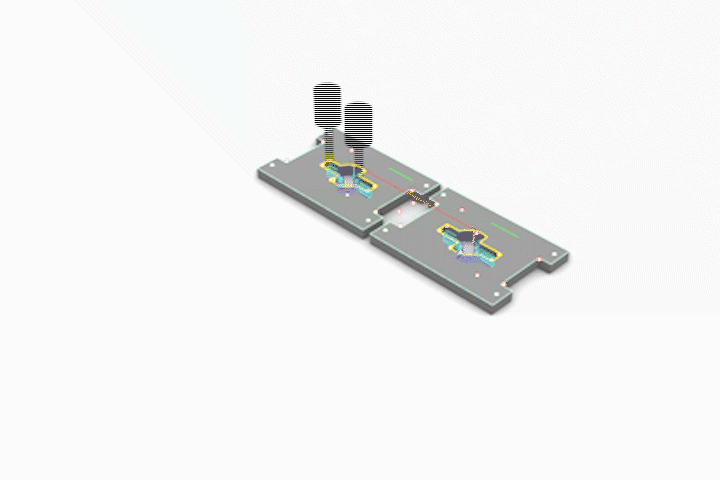
Simulated CNC Process: A] Engraving B] Pocketing C] Profiling
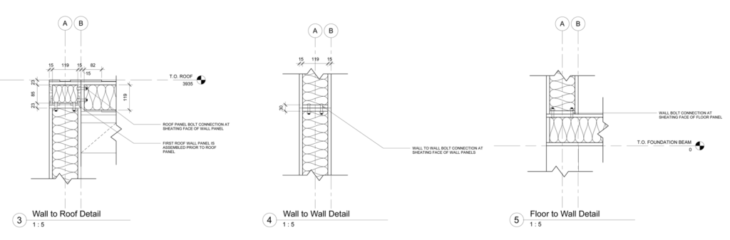
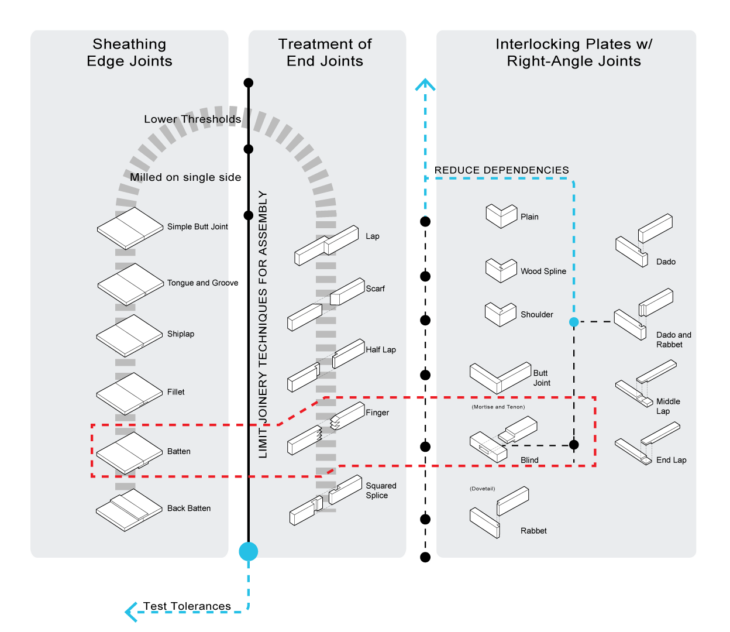
Joints for Plywood


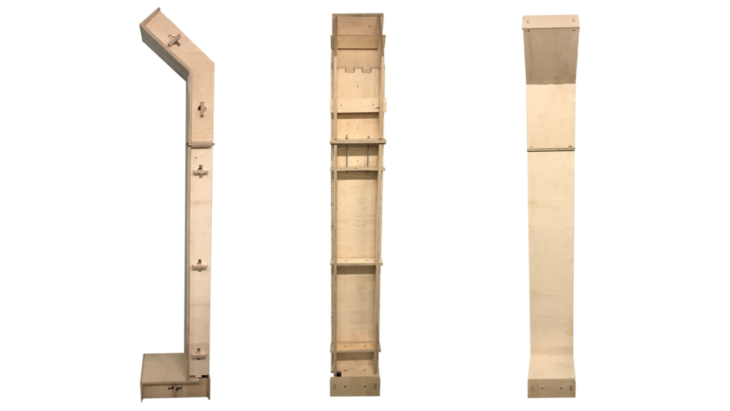
Sequence of Module Assembly




Assembly sequence of Module Types: Floor, Wall, Roof
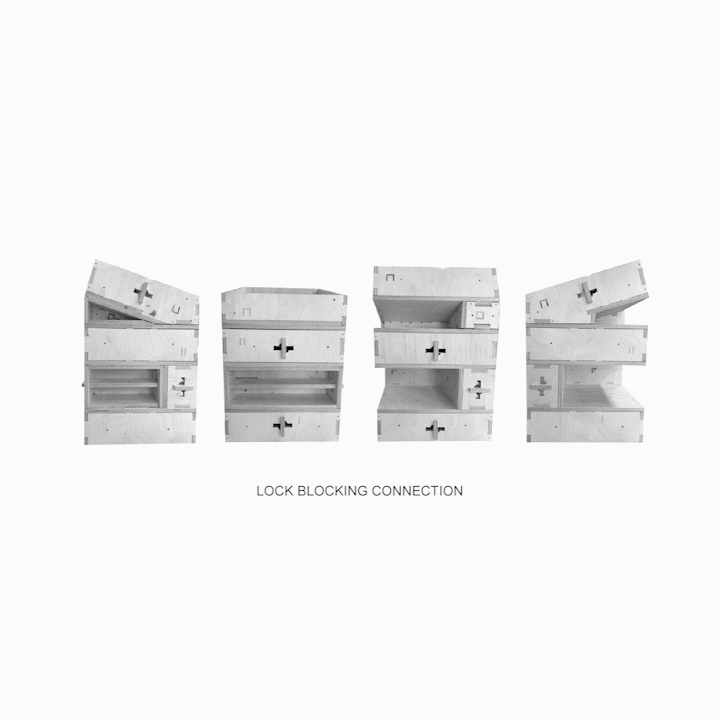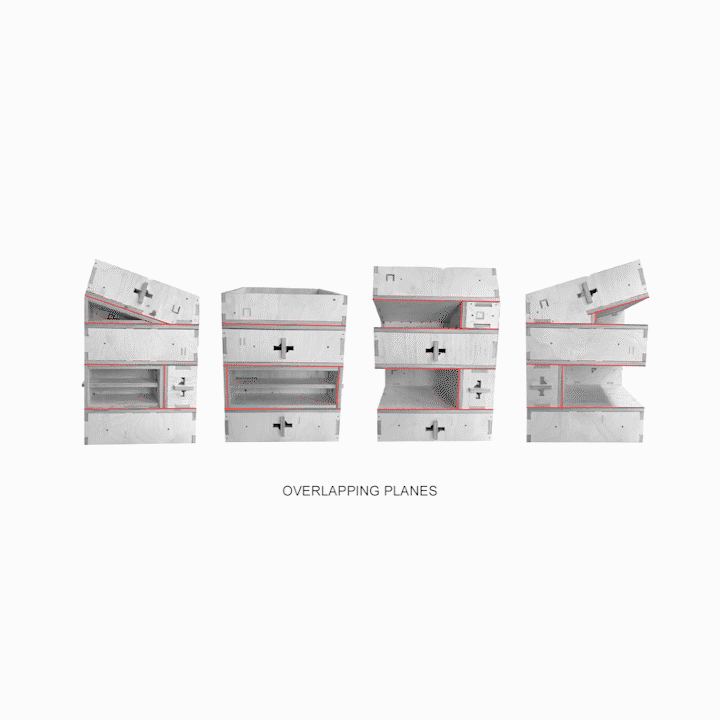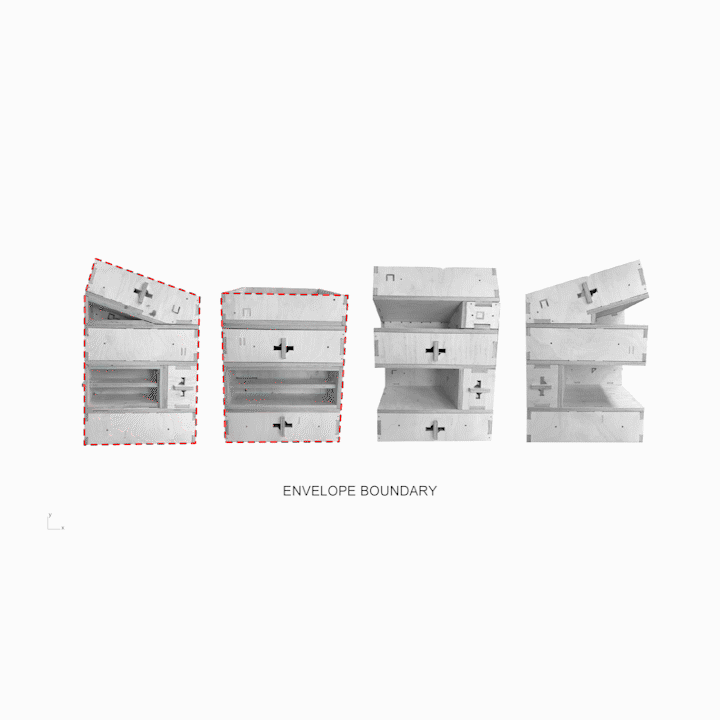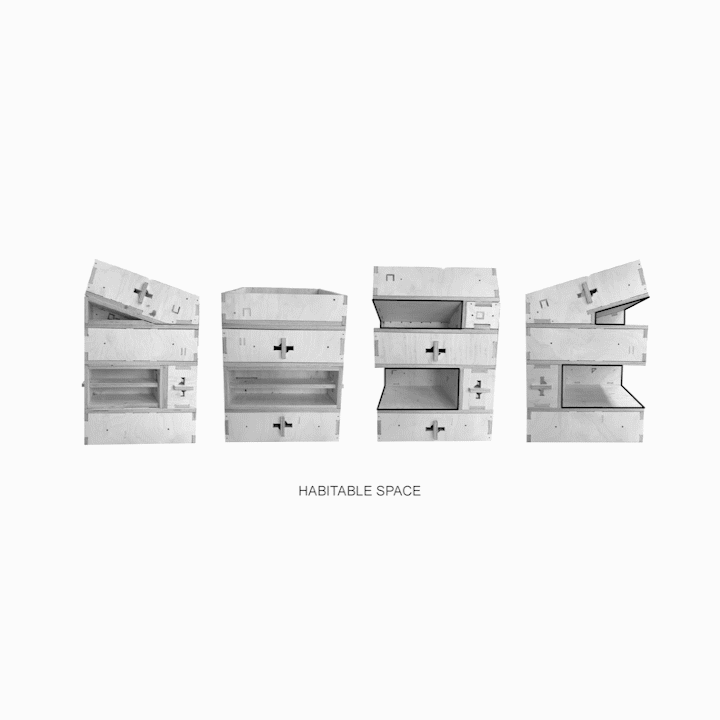
Results of Full Scale Fabrication A] Overlapping Planes B] Insulation Cavity C] Envelope D] Extension for Modules E] Habitable Space F] Locking Blocking
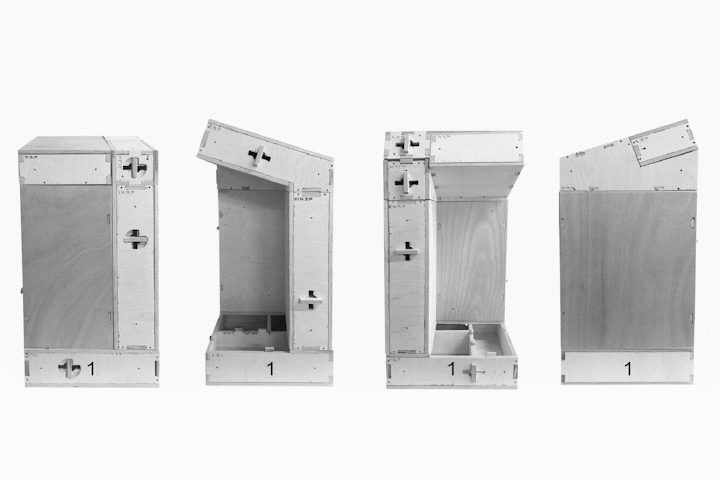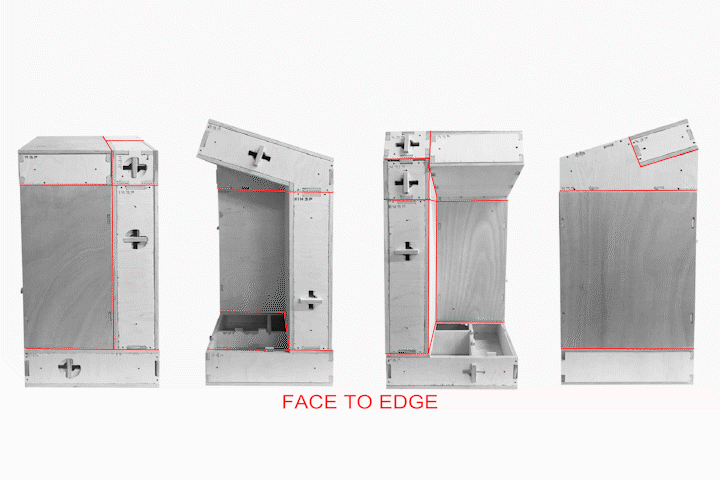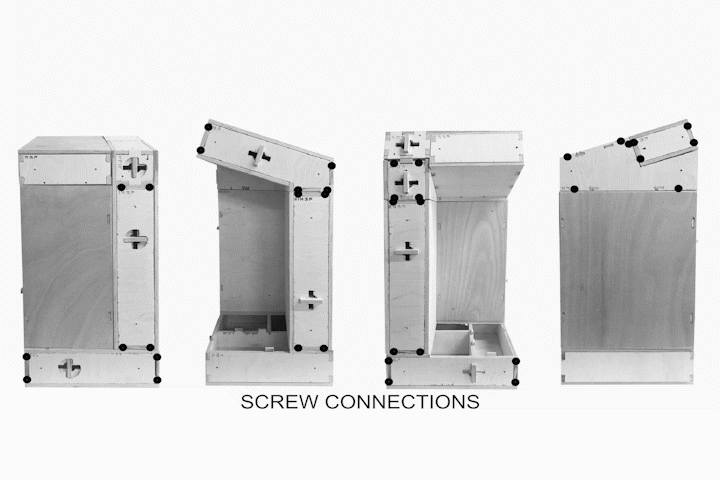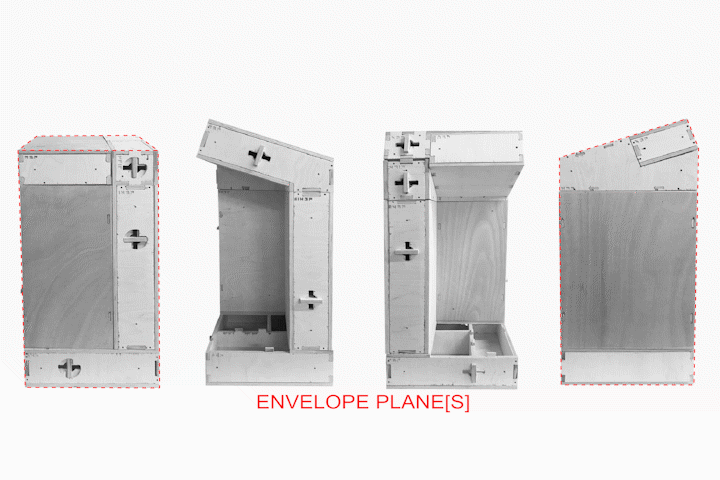
Tectonic Results from Final Fabrication Model

Sequence of Assembly