Introduction
Today more than 70 percent of the earth population are living in the cities which brings the spotlight to this built environment. The increase of cities population expand our cities and shift the paradigm of the urban studies. The study in urban contain the variety of fields like Environmental, Economics, Geography, Public Health, and Sociology. Hence, there is diverse expertise, work on this new phase of urbanization. Furthermore, cities operate by divergent organizations thus it has a complex interconnection among each forum.
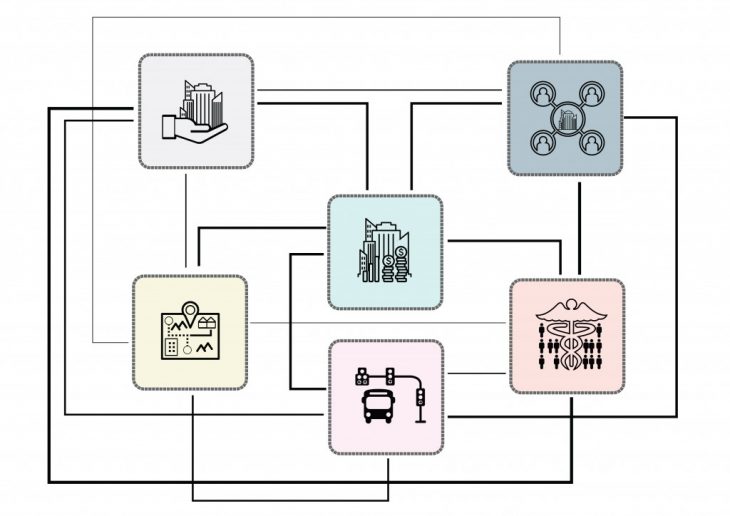
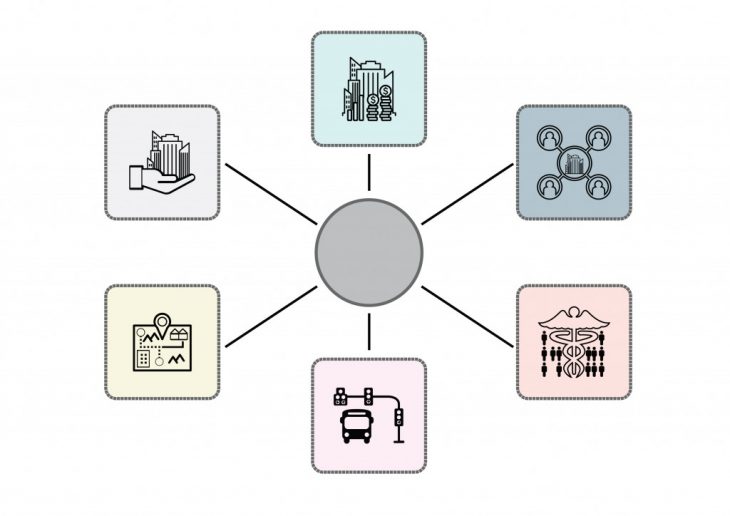
Problem
As mentioned earlier, Cities are based on complex multilayer organizations which are operated by different expertise. However, there is no united platform to manage this manifold relationship in an optimal direction. Thus there is always a lot of material and spiritual waste. Could technology help to solve this issue?
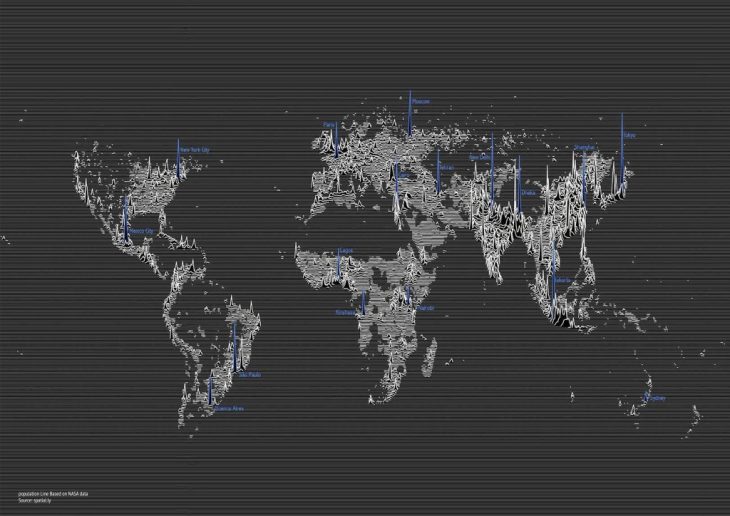
Technology brought many digital layers to the cities. For instance, Mobile network, GPS, CCTV, sensors, and so forth, and it will bring more like IoT, Smarter Material system, Augmentation, Self-Driving car, and so on. These technologies change our perception of the cities.
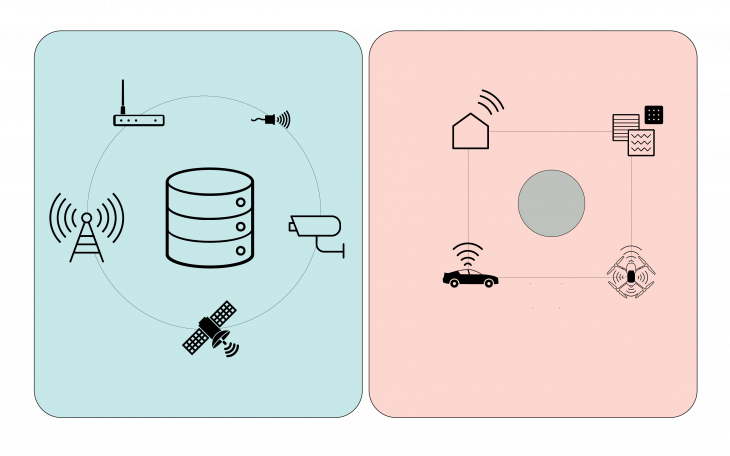

There is a common character among all of this technology from the past until future which is the data. A massive amount of data has been produced and the amount of it increases exponentially during the time. The five main property of this data is the velocity, amount, variety, veracity, and availability. Moreover, the differences in each aspect make that dataset unique and the approach for analyzing it should be particular.
Hypothesis
The hypothesis is that the use of new computer-based technology in the overlap of social, material, urban data can provide a tool to make the collaborative decision-making processes among stakeholders in order to have more informed, sustainable and user-friendly planning decisions for public space.
The state of the art
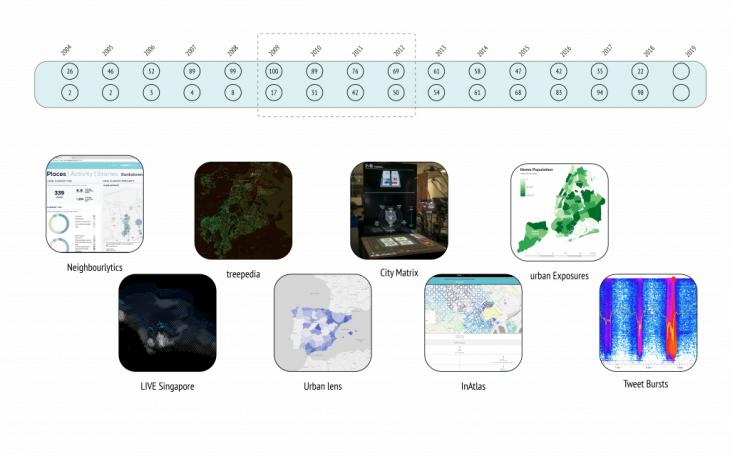
There are several projects, trying to understand the city through the datasets. Through the years, by evolving of technologies and appearance of social media the type of this datasets changed. according to google trend, there is a transition toward the social media data. this presents the interest of the researcher to study the cities phenomena with this perspective.
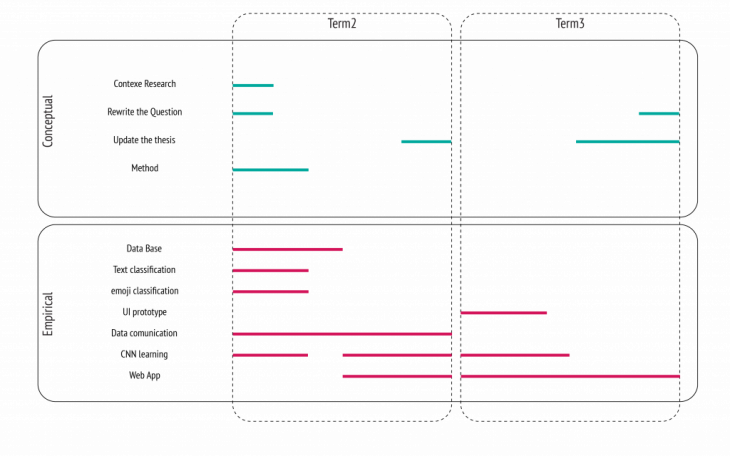
Methodology
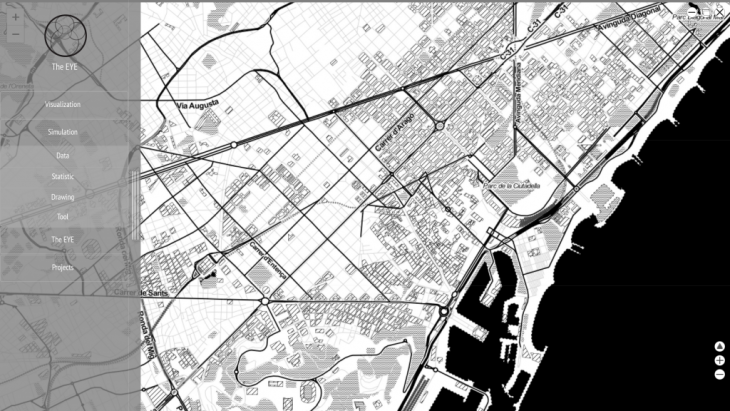
The methodology of the dissertation uses three case studies of the public spaces when it is inhabited differently during time by a variety of citizens flows. The thesis will focus on the effect of air quality and microclimate in public spaces on the dynamic emotion landscape of the citizens based on their social media status (tweets) in that public space.Through the case studies, the dissertation will develop a big data analytics system methodology to be applied in several case studies.
Objective
The aim of this thesis is to develop a web platform as a tool for the urban planner and city governor. The benefit of using web platform is availabilities in any devices without the need for computational power. This tool will consist of computer-based techniques such as analysis, simulation, and visualization of complex urban systems.
Next Phase