Amazing City is a project that takes on the role of the e-commerce giant Amazon in Barcelona. With a proposal that aims to improve the harmonization between digital and physical retailers. This project stems from the current concern on the part of administrations for the identity of the city, where the physical is losing for the growth of the digital world.
Introduction
Some economists have predicted that every 1% growth of eCommerce could mean the closure of some 10,000 businesses. The trend has been growing from 9% to 14%, with an expected growth of 20%, meaning the closure of a further 120,000 out of 700,000 businesses in Spain. (Jose Luis Noeno 2020)
The future of retail is going to be marked by the relationship between physical vs digital retail. The former has the advantage of an “asymmetry of information between the buyer and the seller” which means customers can make a better decision by observing, asking, and holding the product and their substitutes. The latter has the advantage of the ‘death of distance’ or the ability to reach worldwide markets and customers. Both need to invest in their customer ‘experience’; that can be more product variety, shop design, customer personalization, faster deliveries, etc., but today the physical store is the one that continues to have the most difficulties.
Some of the recent surveys add to this:
According to data, 85% of consumers prefer to shop in physical stores
36% of consumers said they don’t like waiting for items to ship
80% like buying items online and picking it up in-store
One of the solutions today is called “Retail Harmonization” when we leverage the advantages of both physical and digital retail and add an optimized customer experience element to it.
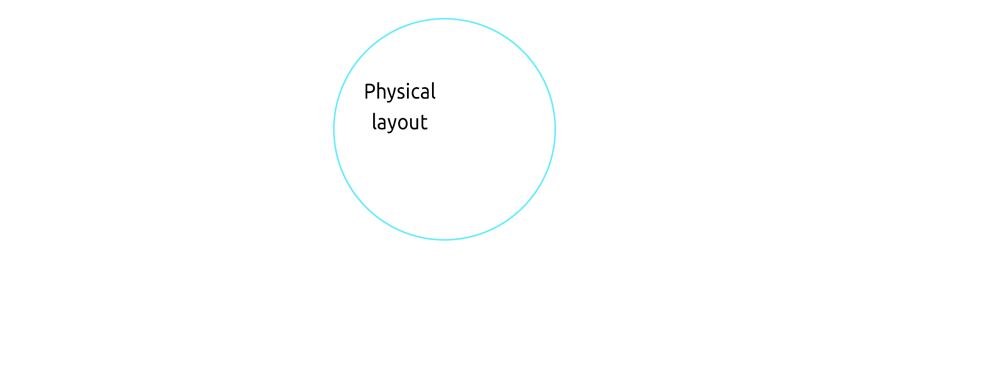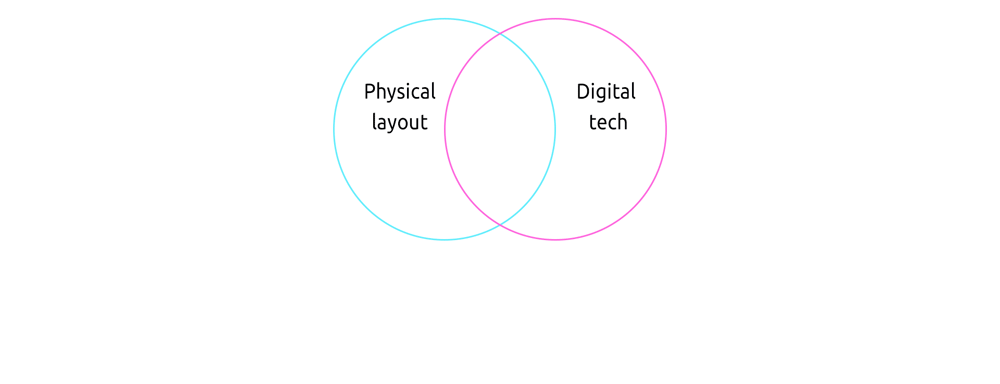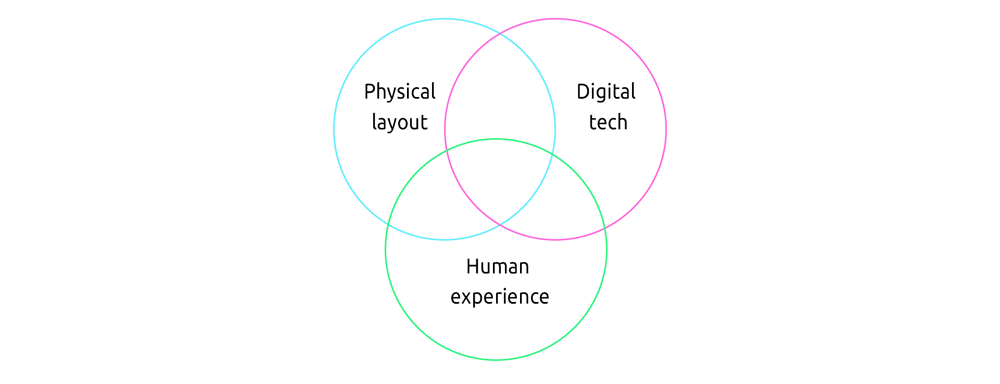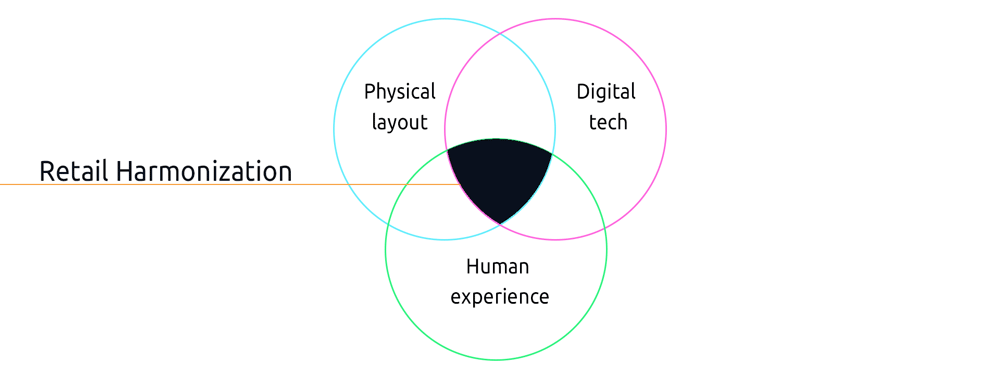
But in order to become really possible, even the management infrastructure and costs will have to change, to make the offline market, which has always had a great identity power for cities, more efficient and accessible.
Amazon company
Over the years Amazon, like many companies, has shifted from a product-oriented business model to a service-oriented business model.
In 2020 only the revenue split recorded showed how only 37% came from eCommerce and 63% from services sold through Amazon AWS.
Out of that 37% less than half comes from amazon products and 59% from third-party sellers and the amazon logistics services they use.
This shows how much the infrastructure created over the past few years is now also used by third parties to feed private businesses that would have much higher costs without our services.
Barcelona Policies
Analyzing the Barcelona Policies on retail trade, the administration experienced different strategies to achieve multiple goals.
The main and salient are listed below:
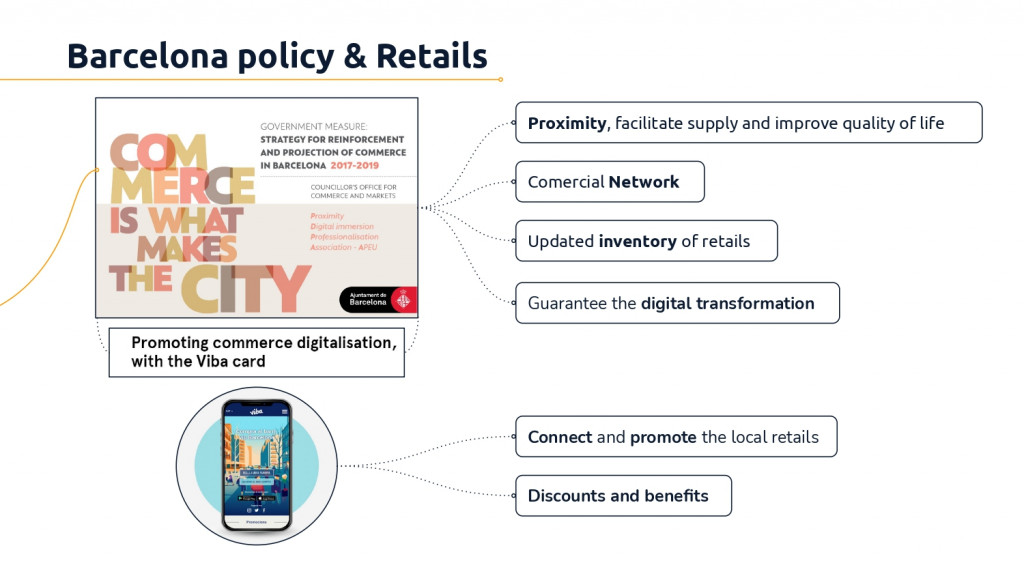
In the context of the Barcelona City Council’s “Eixample Superilla” initiative where one of the objectives is to extend the network of green hubs and squares that have already been created in the Sant Antoni neighborhood.
We have thus developed a series of analyses related to this area, with the aim of understanding its performance and challenges.
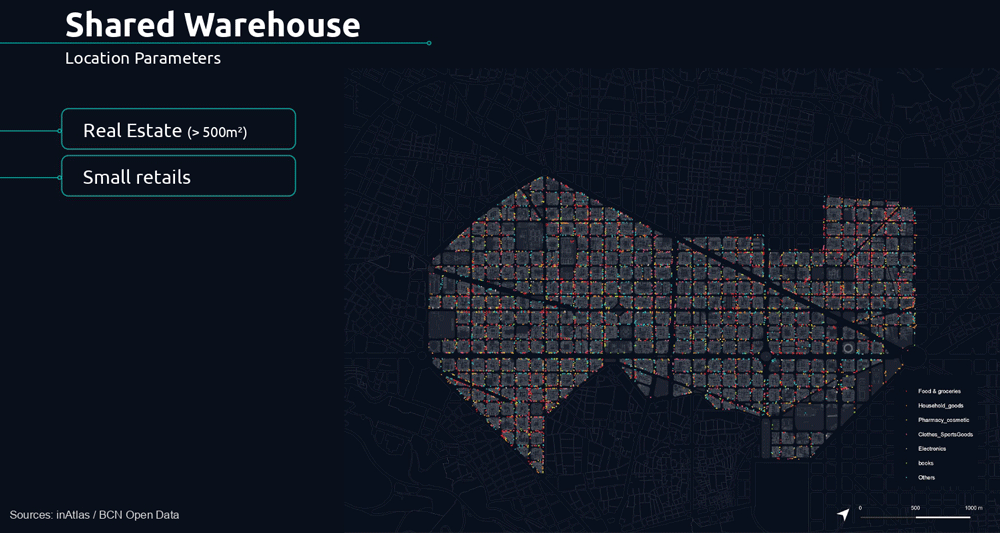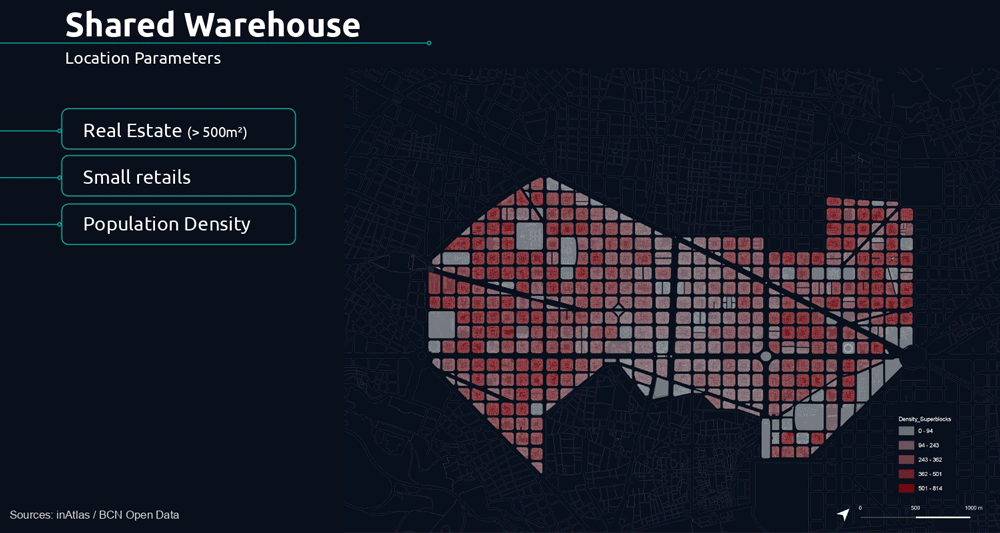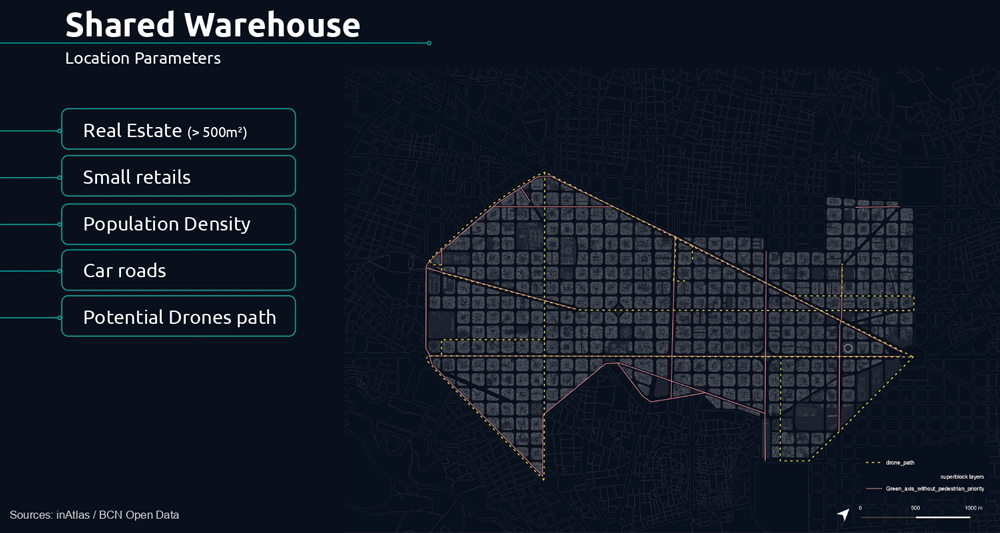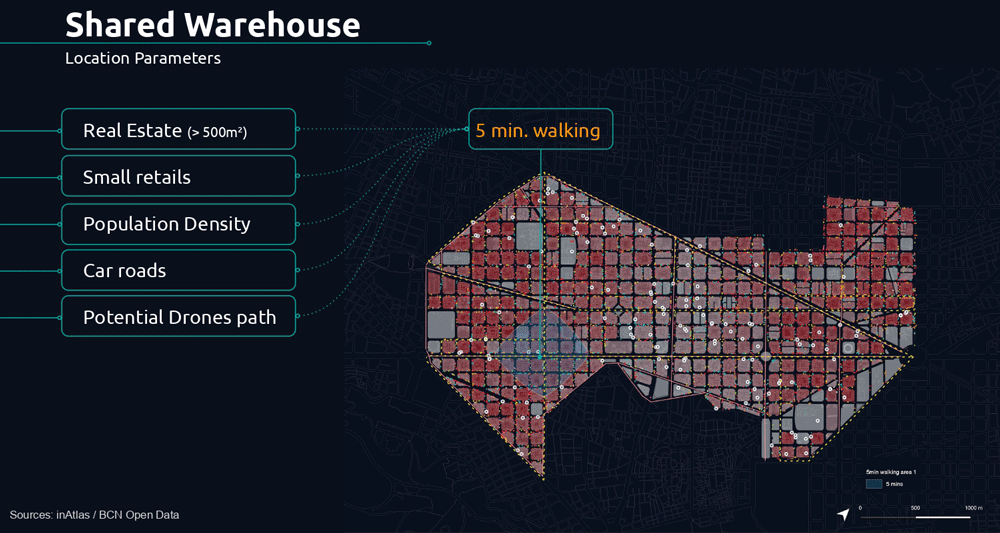
Thus, we have analyzed the distribution of stores according to the macro-categories of products that represent the best sales rates in our eCommerce by neighborhood.
- Food and groceries
- Household goods
- Medicines and cosmetics
- Clothes and sports goods
- Electronics equipment
- Books and magazines
- Others

At the same time, among the challenges to be considered there is the distribution of goods within the target area and at small retailers.
In recent years, the Barcelona City Council has implemented various mobility plans and policies to optimize the distribution and reduce the pollution and congestion caused by it. Today, in fact, the distribution of goods is responsible for 40% of NO2 emissions and 20% of total congestion.
Among the solutions proposed and currently under implementation there is the creation of micro platforms for the decentralization and redistribution of goods through the use of more sustainable modes of transport.
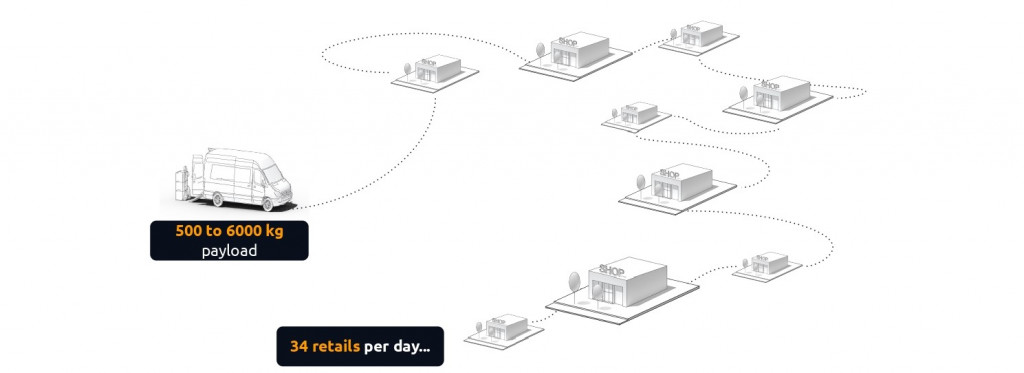
But by analysing the data, and in particular the movement of the couriers’ mobile devices, it has emerged that one of the main challenges in distribution is the fact that on average every day a truck stops at least at 34 different stores to distribute goods.

Actual Micro Platform
Two of the micro platforms designed with the intention to decentralize the distribution of goods with alternative modes of transportation like tricycles and bikes, are the Mercat del Ninot and Estació de Franca.
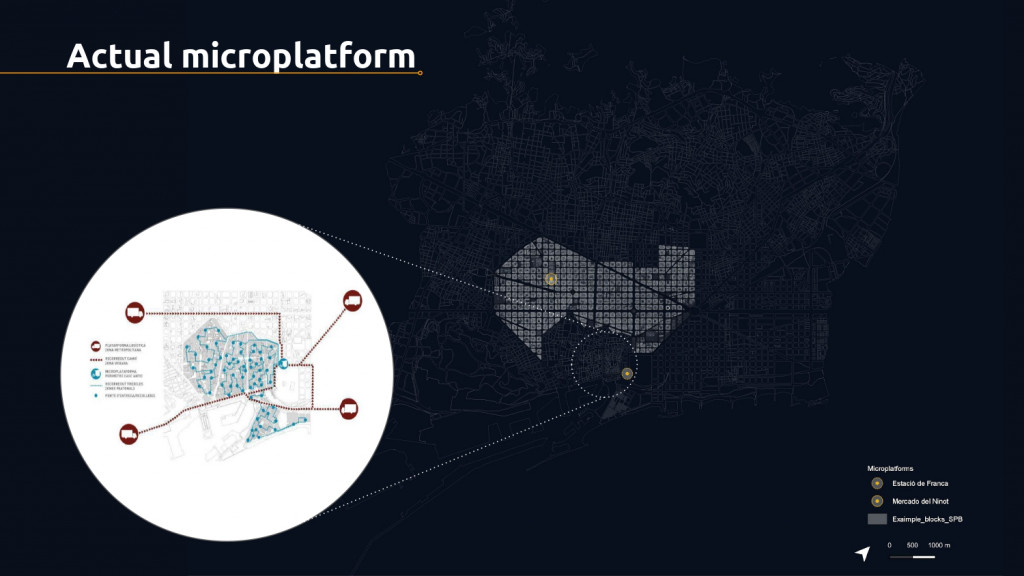
To update this system, Barcelona has issued a competition to generate a new solution to optimize the distribution of the last mile, which still represents the highest cost in freight transport.
The municipality worked with private companies for the new project and the winner was 300,000 km/s. In summary, the proposal is based on the creation of 16 micro-platforms around the whole of Barcelona to cover a distribution area of 30 minutes walk.
The location of the micro-platform was based primarily on demographics and eCommerce demand and uses the existing public infrastructure, such as the underground parking and the municipal market. for the creation of these micro-platforms. The idea is to enable and facilitate the delivery of goods from eCommerce using bikes and sustainable vehicles.
What is the potential of using these micro platforms to distribute goods for small merchants?
We concluded that for a 30-minute walking distance, the Ninot platform could supply 12,924 retailers and 114,753 citizens.

Retail Challenges Today
Our challenge remains the small retailers and who better than them knows the challenges and issues they incur every day in their business.
Talking to many of them, to try to elaborate, the common answer and the reason they remain less competitive with eCommerce is that their costs are getting higher and higher.
This is even more evident when we analyze their costs.
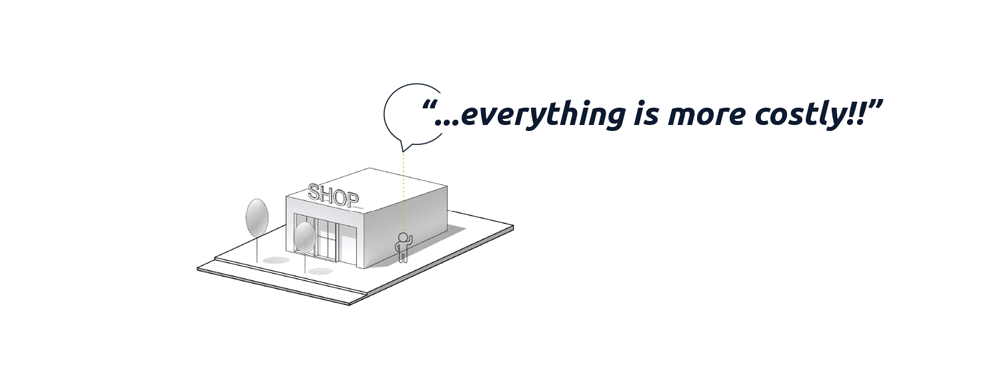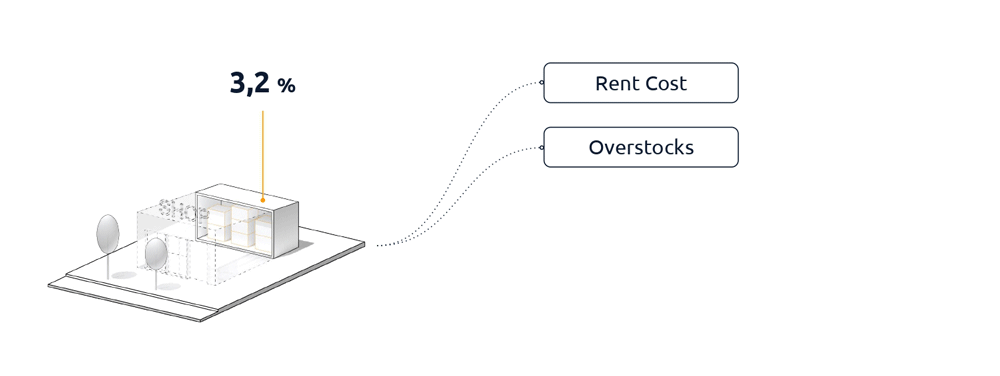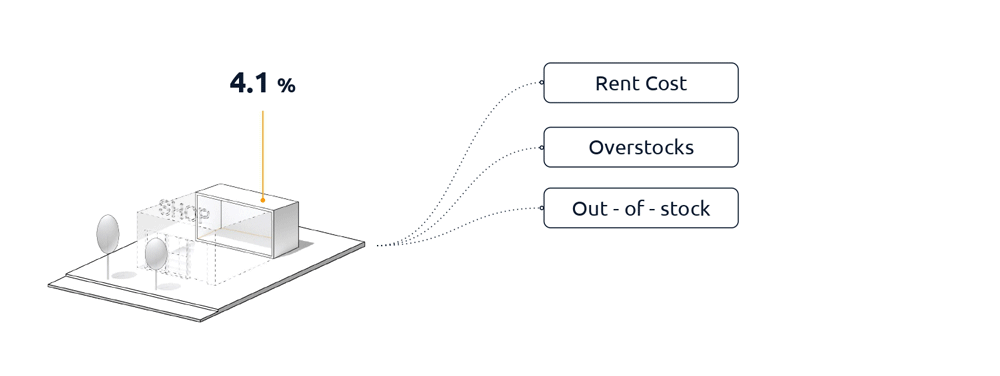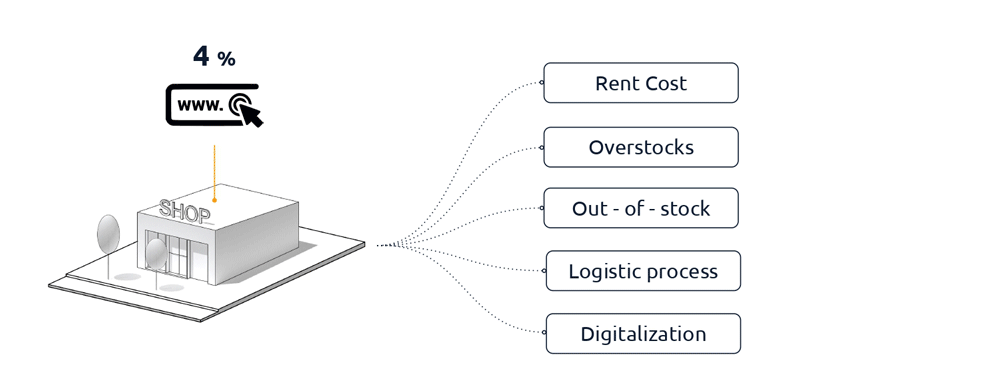
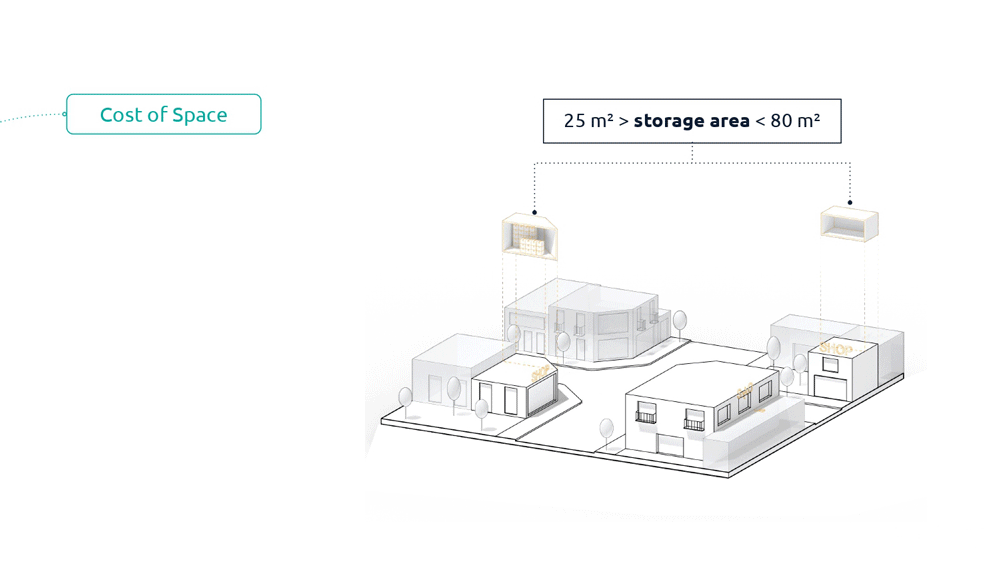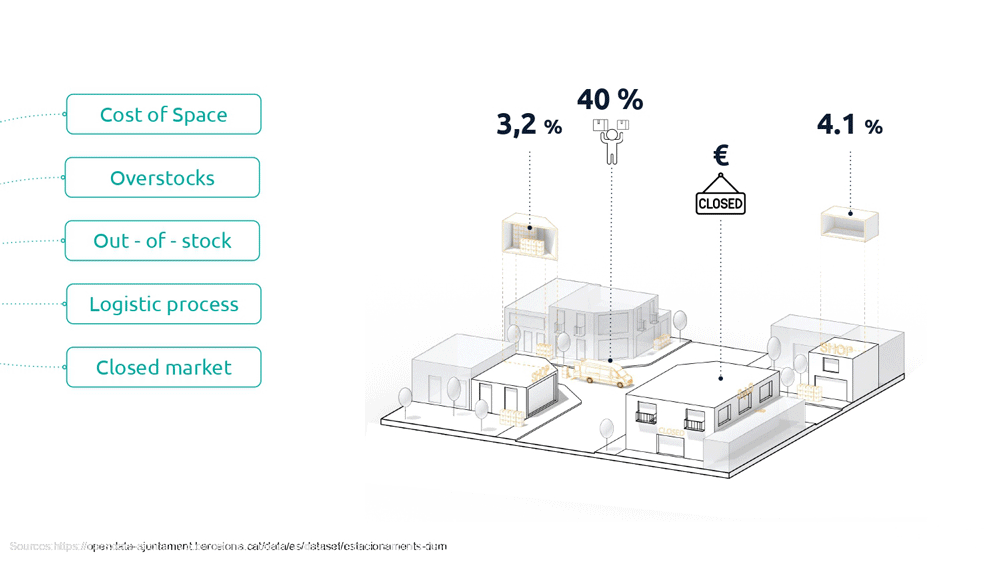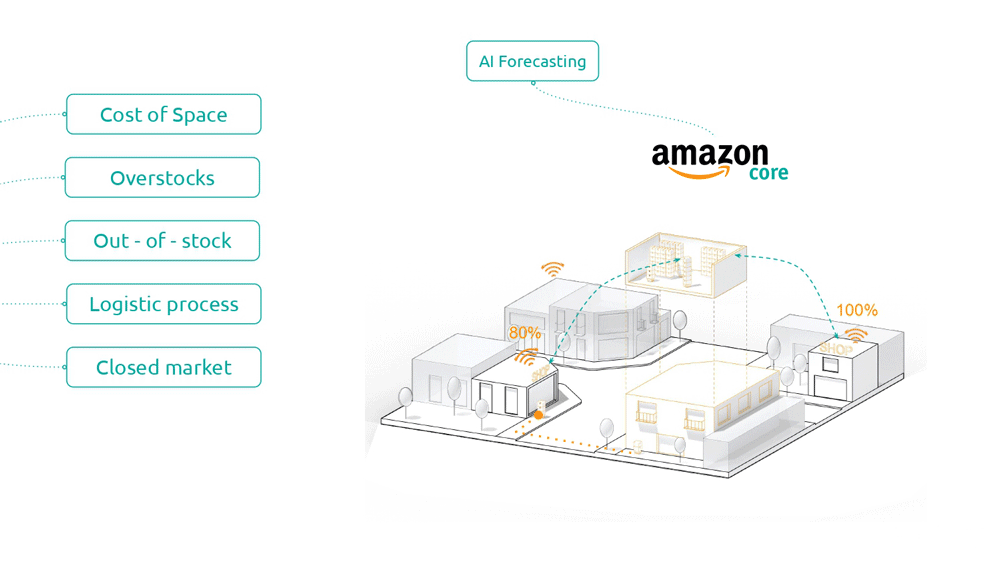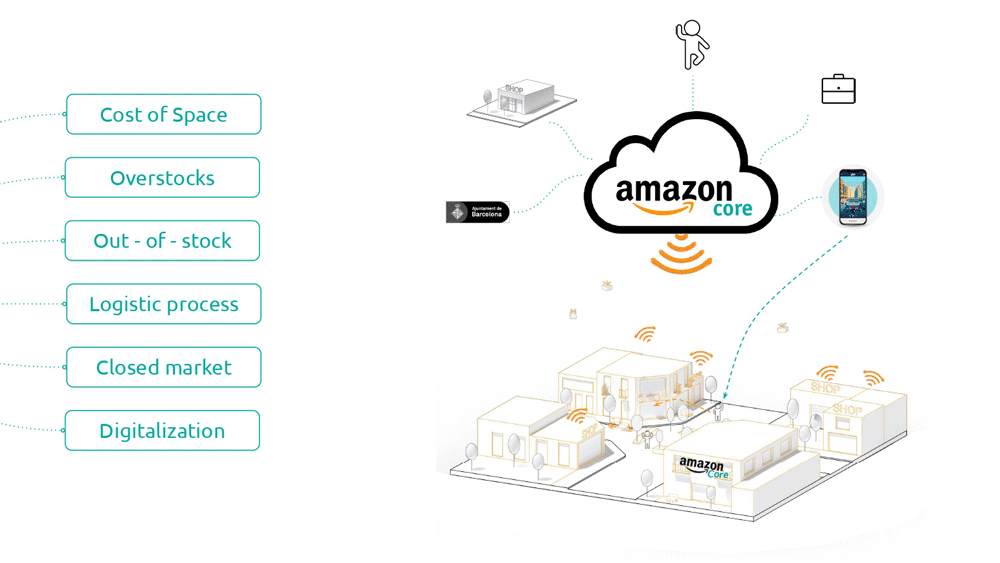
On average, the cost of rent is 22% of their revenue, the overstock is responsible for 3.2% of lost revenue and out-of-stocks 4.1%, the manual tasks in logistics, due to limited opportunities to use technology, is 40% and the cost of digitization with the 4% is still too high to change their models.
Amazon Core
It is from this all that we designed a new exclusive service for retails, based on our experience and their needs.

There is a positive relationship between cost and usable space; space is often taken up by unsold merchandise, which accounts for at least 3.2% of total costs.
This space in fact is probably required by a nearby store or there is probably a store that needs that merchandise.
This element added to the costs of logistics and digitalization bring the costs to 47,3% making the offline market almost inaccessible and inconvenient.
What could be the result of applying our technologies and efficiencies to decentralize costs and activate a circular system capable of making the small business sector accessible and affordable?
Amazon core is a service for creating shared warehouses within a 5-minute radius of the store as an enabler of multiple benefits for multiple stakeholders.
Among these, there is the decrease and optimization of costs related to space and products on sale. The activation of a new system of logistics for distribution of goods, to move from the 34 points of rest mentioned above to single points, able to absorb the demand for products, ensure the speed of delivery to the small retailer and its customers and digitize the services, using the AI forecasting service.
Using the shared warehouse network as an opportunity to activate these points of distribution according to the daily demands of retailers, and flexible to the future introduction of new methods of transport like drones and other autonomous vehicles.
A service that can make the opening of new retail stores within the city more accessible and reverse a model that is today too outdated and expensive to compete with eCommerce giants.
Stakeholders
The new system allows the integration of different stakeholders, to be part of the system seeking a circular economy where the private and public companies can be part of the solution for Barcelona city. The system is from the citizens to the city, activating the digital system sought by the city and mobilizing private companies engaged in logistics, real estate and telecommunications that will find fertile soil for the implementation of new services.
 Business Model
Business Model
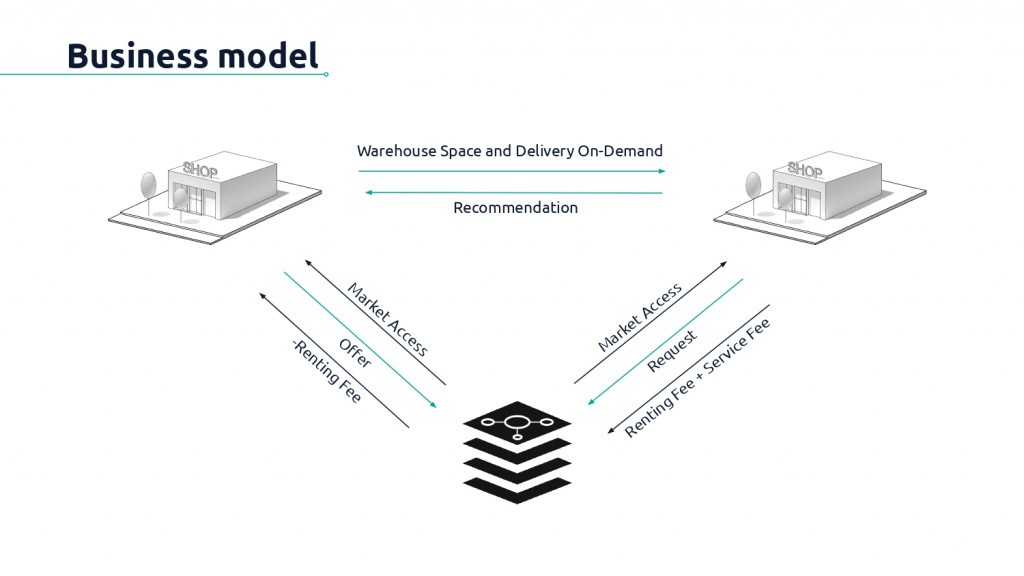
The business model explains how the retailers and citizens can offer their underused space, underused freight vehicles, and underused time to the platform in exchange for a fee.
The platform serves as the market connection and a payment facilitator between the actors.
It will have the optional services of warehouse and order transportation management systems (based on subscription service) This means small retailers can have real-time data of their goods and would be able to forecast demand using technologies such as AI and machine learning, based on the following 4 points to have a centralized database of information, crucial for logistic decision processes.
- This would hugely reduce operation and space costs for small retailers.
- It acts as a new source of income for small retailers and citizens.
- Would generate incentives to increase available space, which in turn can be used to enhance store design and new overall experiences to customers.
- In future economic shocks and trends –such as a pandemic—this system would help the retailers to adapt to new realities. In other words, embrace the so-called ‘creative destruction instead of protectionism.
Drone Swarm
We propose the use of alternative delivery technology of drones because the drone freight estimate that the delivery is 3-7 times more energy-intensive than terrestrial transport, they are a much faster and ecological method of delivery for smaller packages. In each shared warehouse we propose a space for drones landing and parking, for the efficiency of energy we propose the use of using machine learning techniques to calculate the shortest distance from pick up, delivery and return, drones could move and disperse according to real-time demand in the city, similar to a ‘swarm’ of flies to avoid the centralization of drones in one point.
This platform is an opportunity to become a centralized drone flight system. Such flight systems would control crucial issues in the city drone management, such as safety, drone traffic, sensory data, and overall greener and more efficient logistics.
The system allows the recollection of data to share this data with the municipality for the implementation of new projects or policies in the city.
Implementation
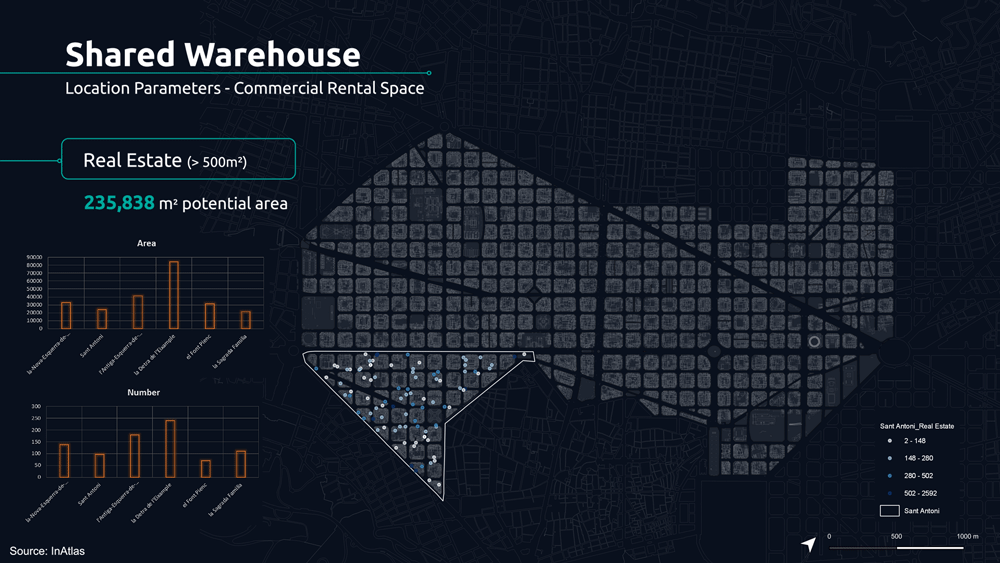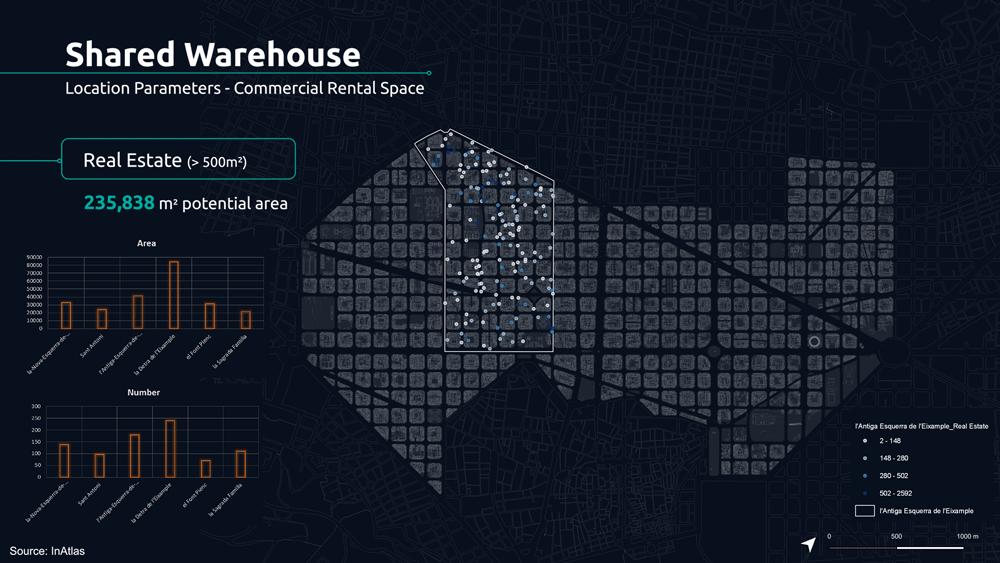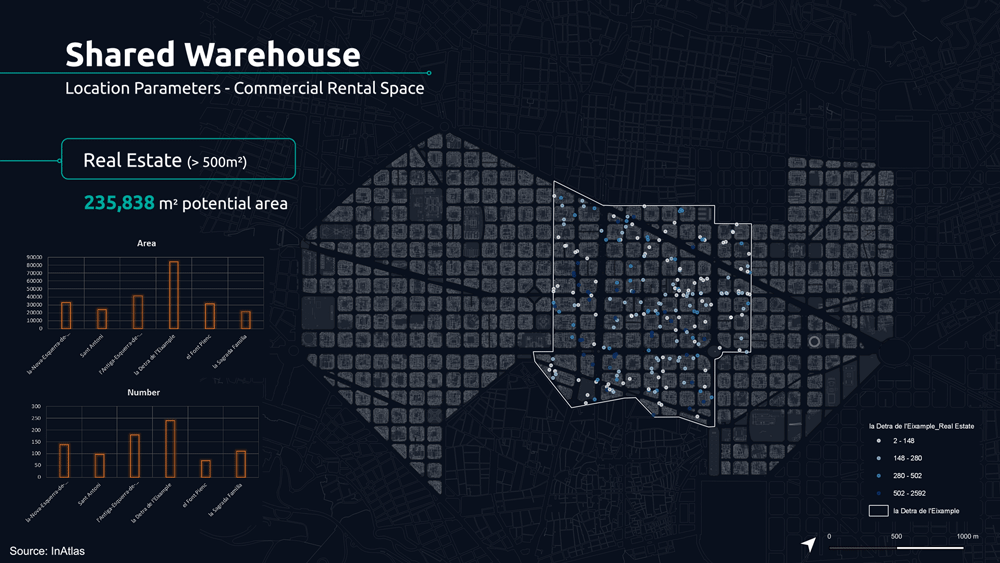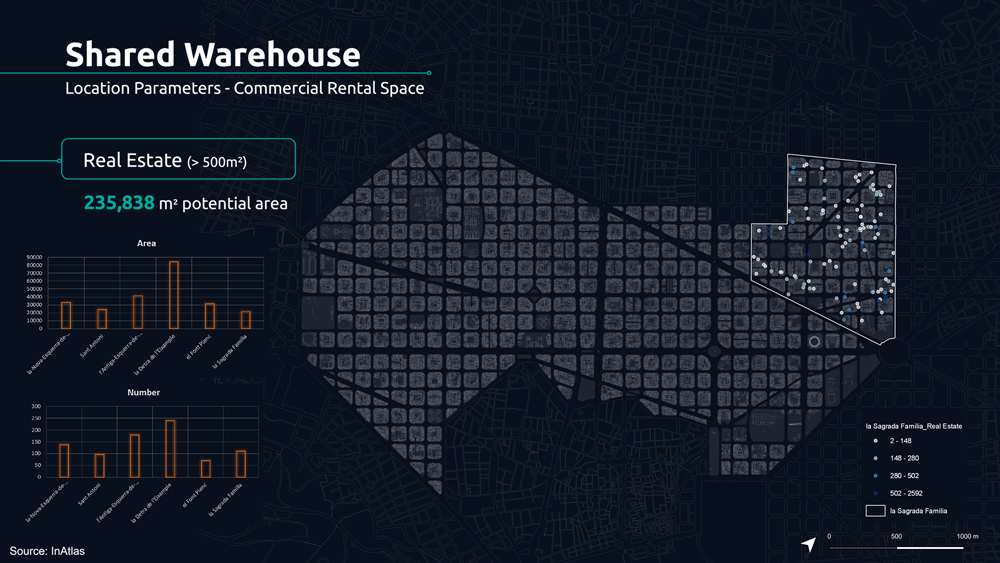
The following parameters determine the potential location of the shared warehouse.
The first is the analysis of commercial stores for rent, nowadays increasing due to the pandemic, giving us the reality of these spaces that can represent an opportunity.
For this reason, we analyzed the real estate market for each neighborhood, filtering by the size of 500 m2 to understand what were the potential spaces from which we could start today.
From this, we applied additional analytical filters such as small retailers distribution, housing density, and dedicated drone infrastructure to understand potential demands.
Based on these parameters we analyzed the 5 minute walk for proximity between retailers, potential shared warehouse and customers.
For implementation, we present below two examples of applications in the case of high and low density of small retailers.
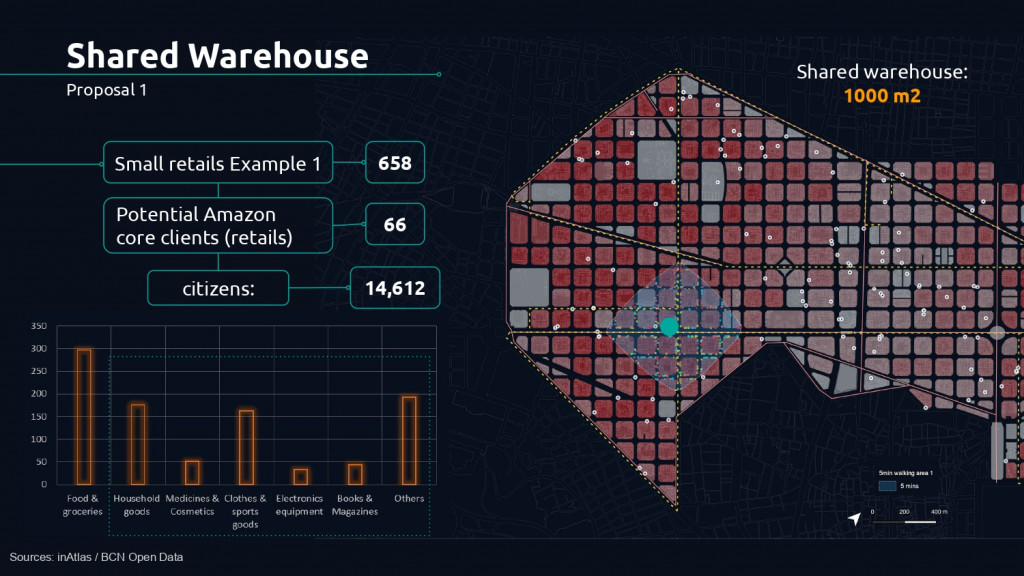
In the case of an area with high density, a warehouse of 1000 m2 was identified, now in the market, with which, using 94% of its useful area, we could absorb the demand from about 66 small retailers and have an impact on 14,612 citizens.
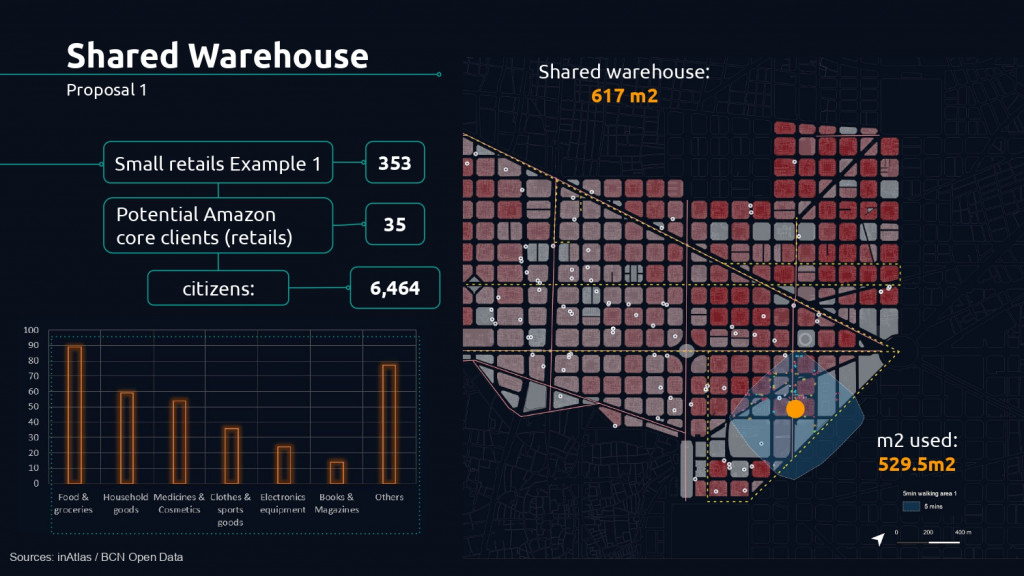
In the case of an area with low density of retailers, we identified a warehouse of 617 m2 , now in the market, with which we could absorb the demand from about 35 small retailers and have an impact on 6,464 citizens.
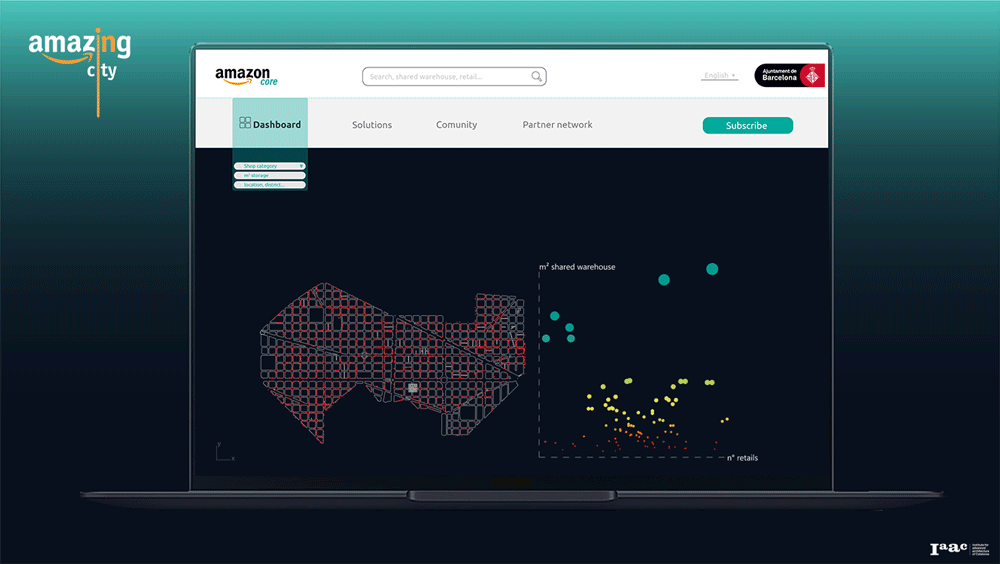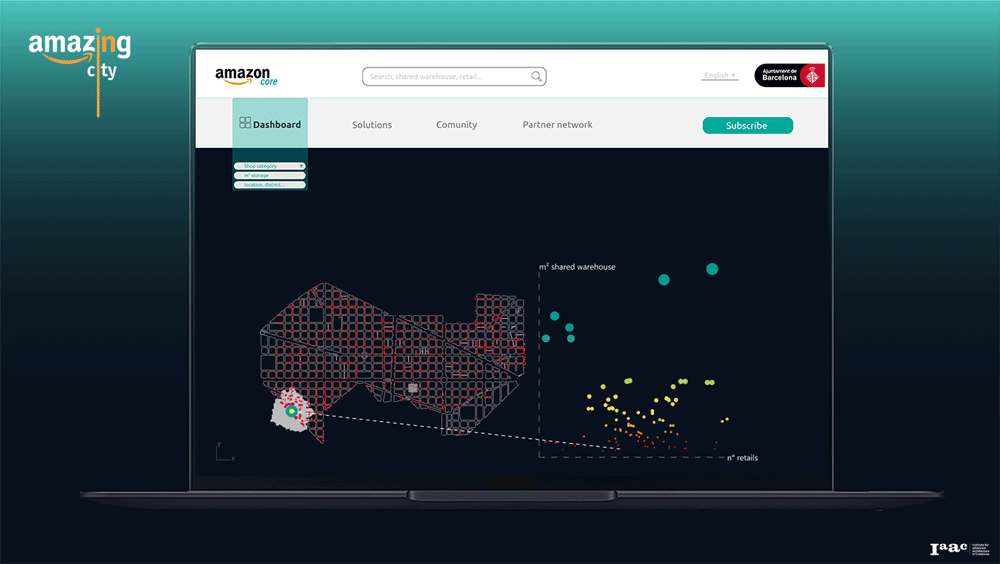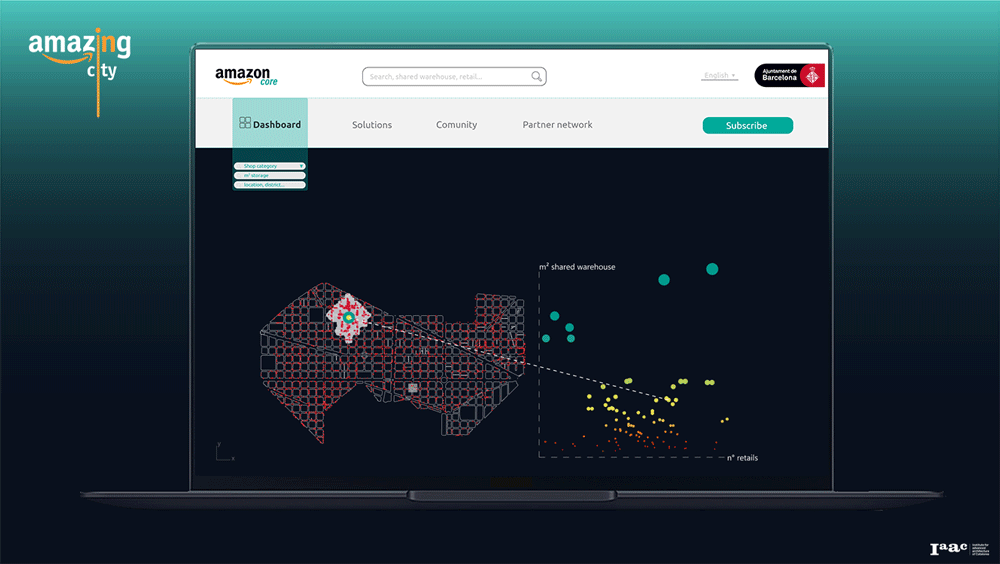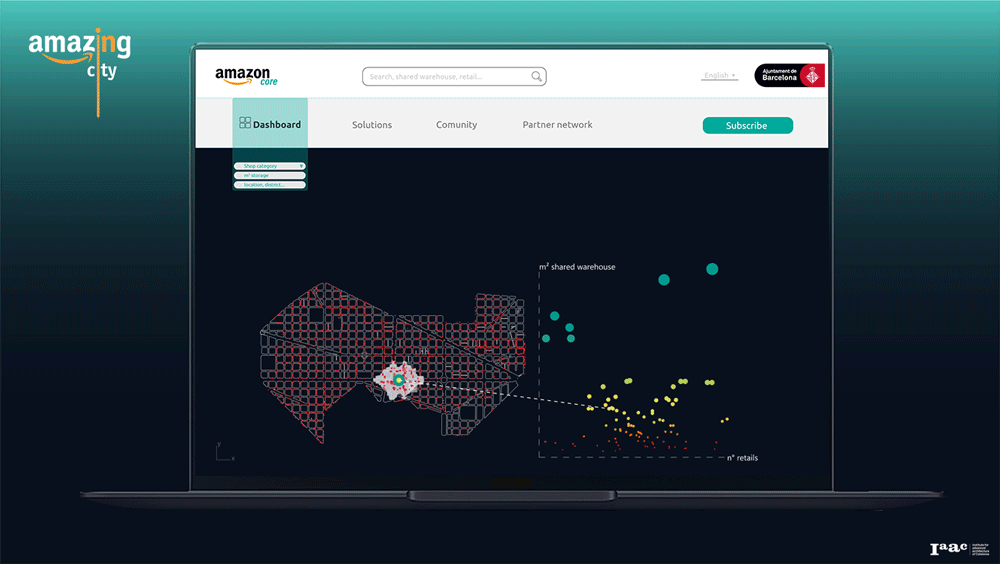
Amazon Core Platform
Using our service, the users, as a retailers or the owner of an empty shop, can find the first potential location based on the size of the shared warehouse and the number of stores within the 5-minute walking distance. Become part of the community and have access to the benefits provided by the infrastructure and its stakeholders.
Amazon core thus represents an opportunity to generate a new value network within the city and activate a new efficient infrastructure to improve and strengthen Barcelona’s identity.
Amazing City: the experience value for retail service is a project of IAAC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at Master in City & Technology in 2020/21 by students: Simone Grasso, Sasan Bahrami, Kevin Aragón, Juan Pablo Pintado Miranda and faculty: Luis Falcon & Iacopo Neri