878 J.kg?1 C?1
3d printing architecture for a better heat performance
In the world, more than 70% of the residential sector consumes energy for heating in an unsustainable manner. The advanced 3D printing technology of integrating cavities inside the wall helps to channel heat through walls as well a radiate heat while it passes through.

The project attempts Incorporating the heating mechanism of building using the active source in a 3D printing architecture located in a colder region. A question, can a 3D printed building component could be a heating element for the building is to be navigated throughout the design.
Project location
Kazakhstan is a transcontinental country mainly located in Central Asia with a smaller portion west of the Ural River in Eastern Europe. Semey is a port on the Irtysh (Ertis) River where the latter emerges into the West Siberian Plain. The extreme cold conditions of eight months forced a higher heating demand reaching -30°C in winter.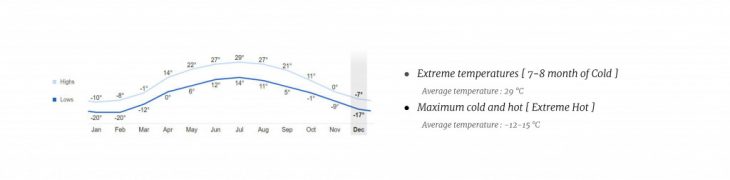
Due to the fact that the extreme cold temperature exists, massive heat loss occurs throughout the building and an additional need for containing the heat created inside the building, different strategies are applied.
Climatic strategies  A. Decreasing surface area by maintaining the volume of occupancy | B. Earth as a shelter |C. Integration of ventilation shafts|D. Orientation for maximum sunlight hours ( Solar energy ).
A. Decreasing surface area by maintaining the volume of occupancy | B. Earth as a shelter |C. Integration of ventilation shafts|D. Orientation for maximum sunlight hours ( Solar energy ).
Resources and features
Availability of timber in the vernacular way of construction using the clay, The nomadic way of lifestyle in Semey, Kazakhstan as evolved through the urbanisation for the need of static housing leads to the components of the materiality of the project. Moreover, animal skins are widely used in combating extreme cold insulations.

Site plan
Features Include a 6m difference in elevation with riverfront and a 4m access road to the site of 20m X 30m .
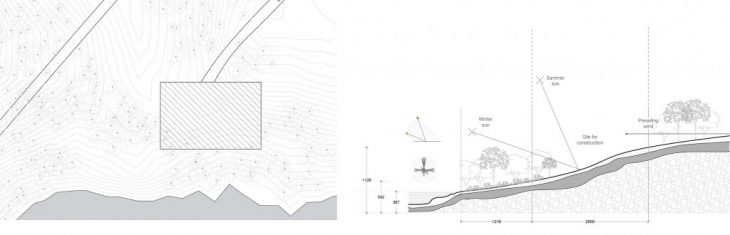
Soil profile
Topsoil is a mixture of sand, silt, clay and broken humus. Beneath the humus exists the material, which is used for printing the project. The subsoil is mostly made of weathered rocks and clay minerals. Bedrock is a hard rock that is useful for sheltering strategy and foundation bed.
Heating demand and spatial arrangement
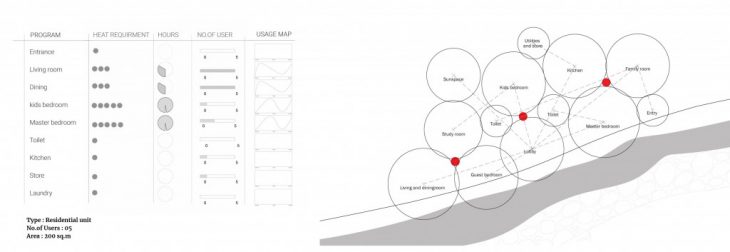
Communal heating spots are mapped with relation to the heating demands of individual space. Vertical arrangements based on the need for heating implies the definition of sheltered spaces by mapping diurnal heating demands.
Wall typologies
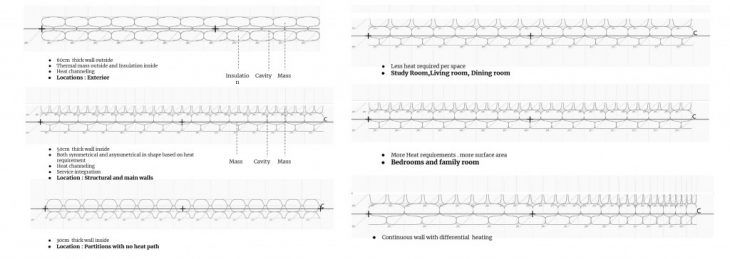
Based on the surface area and position, the wall responds to different heating requirements and functions like heat distribution, structure and insulation.
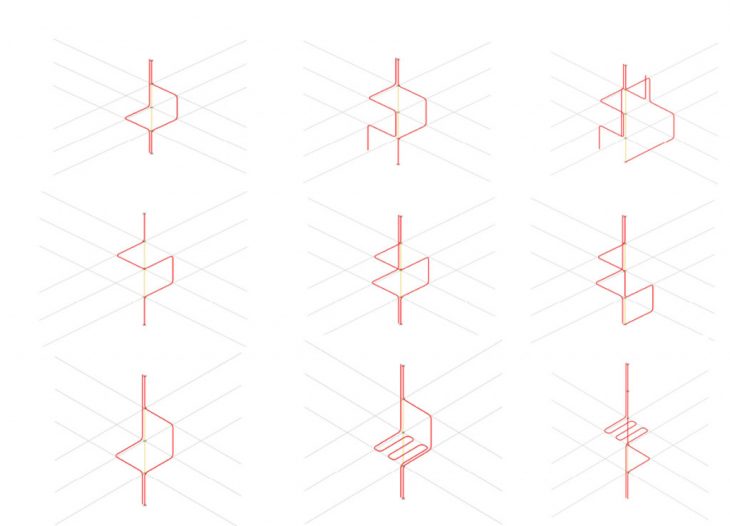
Heat path connecting spatial components between floors and walls are proposed and to be integrated with the structure.
Architectural Tectonics.
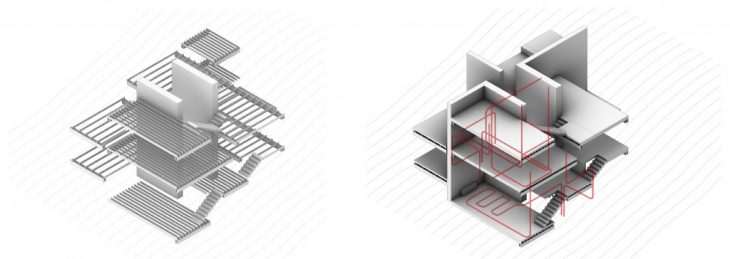
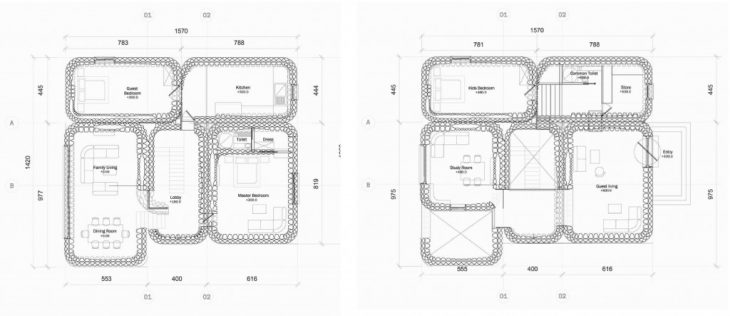
Having summarized all the strategies, structure, heat with the spatial arrangement and heat source, hereunder plan and a section showing the tectonics in 3d Printing Architecture with the methodology of an architectural drawing with the above parameters.
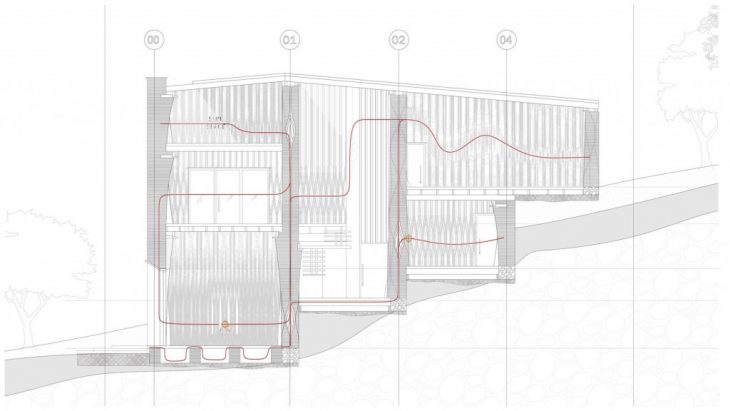
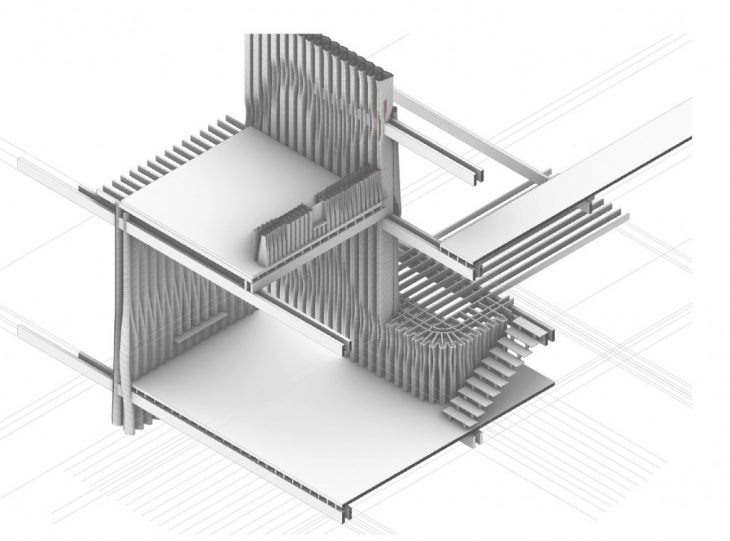
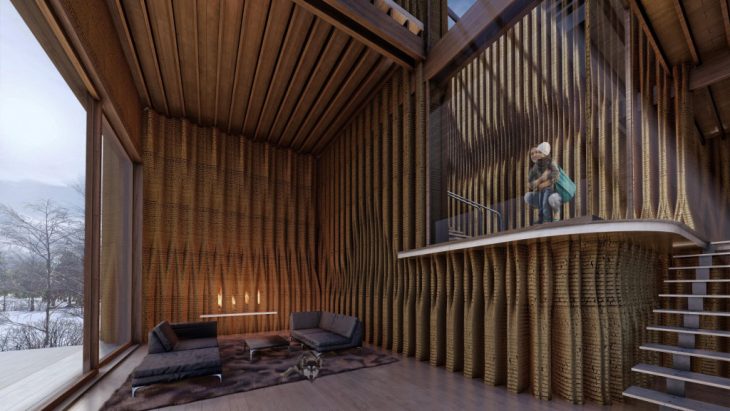
Generating building component-based on heat path and shelter from the earth is viewed on the section above in which the walls change the typology based on location, structure and heat demand. The intricacy of Primary Load bearing clay wall and secondary timber beams for supporting the suspended CLT plates based on the heat demand and spatial interactions is clearly expressed in the axonometric drawing below.
Redesigning a fireplace by integrating with 3D printed clay wall is shown below with the tectonics of structure, porosity and bell for a better performance of indoor comfort.

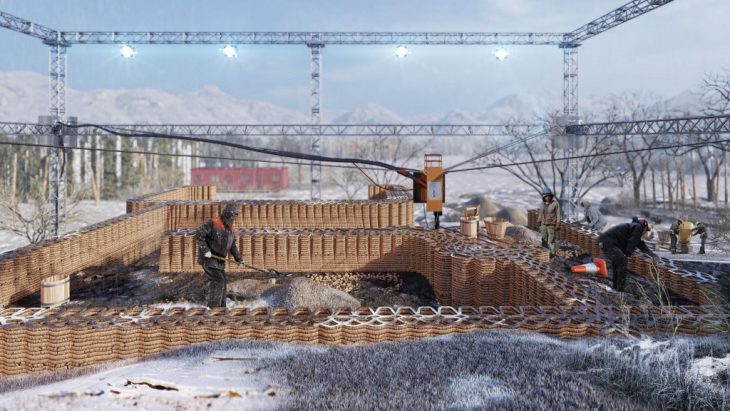
Robotic construction
The three-story building proposed could be printed in one month time which is 10days per floor with manpower of 3-5 people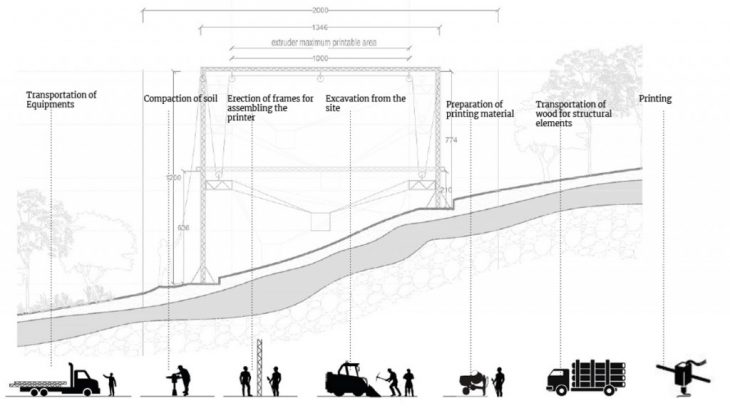

878 J.kg?1 C?1 is a project of IaaC, Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia developed at Open Thesis Fabrication in 2020/2021 by Students: Roshin Anthooravalappil |Teklehaymanot Woldesenbet|Timur Mukhametkaliyev Faculty: Edouard Cabay | Alexander Dubor | Kunaljit Chadha | Ashkan Foroughi Dehnavi
